2.1 成纤维生长因子家族 成纤维生长因子又被称为肝素亲和生长因子,是一类可以通过与细胞膜上特异性的受体相结合从而发挥多种生物学作用的多肽分子[21]。目前已经发现的成纤维生长因子有23种,它们之间有25%-50%的同源氨基酸序列,即含有约120个相同的氨基酸,其同源氨基酸序列折叠成球形β-三叶形,高度同源的氨基酸序列决定了不同分子结构之间具有相似的生物学效应[22]。而它们的核心结构域是保守的高度不同的氨基末端和羧基末端序列,其又赋予成纤维生长因子家族各成员之间具有独特的功能特性。成纤维生长因子的分泌方式主要有旁分泌和自分泌,旁分泌成纤维生长因子具有由12个β链组成的规则的β-三叶域,而自分泌成纤维生长因子由于缺少β11链而不具有典型的β-三叶形。成纤维生长因子活性受多种机制调节,包括与硫酸乙酰肝素结合、N-末端选择性剪接、同源二聚化以及成纤维生长因子配体的位点特异性蛋白水解切割。而成纤维生长因子与硫酸乙酰肝素的相互作用是决定配体生物活性的最重要因素,其不仅决定成纤维生长因子发挥作用的方式,即成纤维生长因子是否以旁分泌还是以自分泌的方式起作用,而且还决定了同一亚家族内旁分泌配体的不同生物学活性[23]。
成纤维细胞生长因子受体是一类穿膜的酪氨酸激酶受体,在大多数组织细胞中均有表达,能够介导成纤维生长因子信号传递入细胞质中。目前已经发现的成纤维生长因子受体共有4种,其主要由3部分构成:细胞外3个免疫球蛋白样重复序列组成的配体结域、疏水氨基酸组成的跨膜结构域、细胞内的酪氨酸蛋白激酶活性结构域[23]。当成纤维生长因子与其受体结合后,细胞内的酪氨酸蛋白激酶活性结构域首先发生自身的磷酸化,然后使靶蛋白发生反式磷酸化,通过级联反应将信号传递到细胞核,从而在损伤修复、血管和神经再生、胚胎发育和骨骼形成发挥重要作用[24-25]。
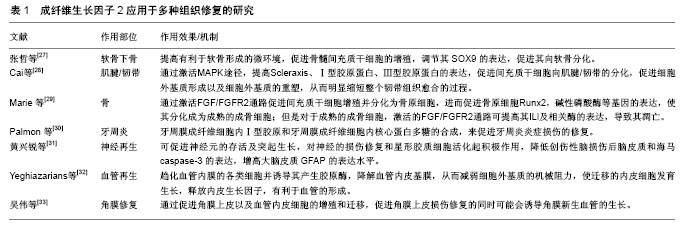
成纤维生长因子2是最先被发现、也是迄今为止研究最充分的成员之一。人类成纤维生长因子2基因为单拷贝基因,定位于4号染色体的短臂上,全长大于40 kb。在基因的5’端和3’端都有对基因转录起调控作用的非编码序列[26]。成纤维生长因子2在体内分布极为广泛,除了血液外,几乎分布于所有的器官、组织或细胞中。由于其在体内广泛的分布和较强的促细胞增生能力,成纤维生长因子2在腱-骨愈合、软骨修复、骨修复、神经再生等多个方面发挥着重要的作用,见表1。
2.2 成纤维生长因子2对腱-骨愈合的影响 据统计美国每年大约20万例前交叉韧带损伤需行手术治疗[34]。治疗主要通过韧带重建,常用的移植物包括自体韧带、异体韧带和人工韧带,而有0.7%-10%的患者因手术失败需二次手术[34]。重建后的韧带需要腱-骨愈合才能完成韧带功能的重建,但肌腱移植物在多种因素影响下会出现移植物与骨隧道愈合强度差或不愈合,即腱-骨不愈合,是手术失败的主要原因之一。所以,如何提高腱-骨愈合速度和效果,加快骨整合是当前的研究热点。许多研究者通过提高移植物的活性、加快移植物再血管化、重建移植物的生物力学特性,最终形成正常的腱-骨位 点[35]。目前,基于组织工程学的基因治疗发展迅速,例如:通过转染技术将特定基因转入感受态细胞,在合适的条件下培养,从而促进细胞的增殖分化。成纤维生长因子2是一种在韧带损伤愈合过程中重要的生长因子,作为韧带/肌腱损伤后高表达的特定因子,在韧带重建后1周达到峰值,持续表达3周,并在第8周再次升高[36-37]。在韧带组织愈合的早期,韧带细胞及腱鞘细胞开始分泌内源性成纤维生长因子2并发挥作用,其可促进细胞增殖、刺激细胞迁移、血管再生及提高Ⅲ型胶原的表达等作用,但是其作用时间和效果有限,导致韧带的愈合缓慢。因此,Thomopoulos等[38]通过在韧带损伤后的前 10 d(即损伤修复早期)加入外源性成纤维生长因子2,其能够与内源性的成纤维生长因子2产生协同效应,促进细胞增殖、细胞外基质形成以及细胞外基质的重塑,从而明显促进整个韧带组织愈合的进程。
Zhang等[39]研究显示:通过纤维蛋白凝胶载体缓释成纤维生长因子2可以在体外及体内促进骨髓间充质干细胞向韧带的分化,以及兔髌骨髌腱的腱-骨愈合。Hankemeier等[40]通过研究不同浓度的成纤维生长因子2对骨髓间充质干细胞增殖分化的影响发现:低剂量的成纤维生长因子2(3 g/L)既能够促进骨髓间充质干细胞增殖又能够增加Ⅰ型胶原,Ⅲ型胶原,纤维连蛋白,α-SMA和波形蛋白mRNA水平的表达。因此,为组织工程韧带提供了可推荐的诱导骨髓间充质干细胞增殖分化的成纤维生长因子2的量。Maclean等[41]通过将猪的前交叉韧带脱细胞处理来降低异种前交叉韧带移植的免疫排斥反应发现:成纤维生长因子2有利于前交叉韧带纤维母细胞的增殖,且质量浓度为6 g/L时增殖效果最佳,但再增加或降低成纤维生长因子2的质量浓度并不会增加其生物学效能。Madry等[42]以人的前交叉韧带为种子细胞,通过直接重组腺病毒将成纤维生长因子2导入来修复韧带损伤,发现:成纤维生长因子2能够促进人前交叉韧带纤维母细胞的增殖,并且能够增强Ⅰ型胶原和Ⅲ型胶原的沉积以及增高其比例。
肌腱是位于肌肉和骨骼之间的致密结缔组织,其主要成分是Ⅰ型胶原,参与肌肉和骨骼之间的力量传递并带动关节活动[43]。由于经常承受高强度的机械负荷,所以常导致肌腱功能受损[44]。临床上治疗肌腱损伤主要是通过手术的方式,但是由于其特殊的解剖结构:缺乏血管和神经,不具备完全再生能力,所以临床结果并不总是令人满意的[45]。修复后的肌腱在结构和力学性能等方面都不如正常肌腱,容易发生肌腱粘连和再断裂[46]。肌腱修复的核心问题是产生和沉积胶原蛋白,特别是Ⅰ型胶原蛋白[47]。因此,肌腱损伤修复后如何加快肌腱的再
生及愈合也是临床急需解决的问题。
研究发现,生长因子在肌腱愈合中起重要作用,其中成纤维生长因子2在肌腱组织的分化中起关键作用,其能够刺激细胞的增殖,从而在肌腱损伤后愈合的过程中发挥着重要的作用[48-49]。肌腱祖细胞来自胚胎生骨节层,该层有个区域浓集SCX,FGF和TGFβ通路是肌腱组织细胞分化、SCX浓集的重要诱导因素;FGF信号通路也是该层诱导生成肌腱祖细胞重要通路;同时对于生骨层的生肌节的发育十分重要[50]。
Heisterbach等[51]研究发现:在跟腱损伤后,内源性成纤维生长因子2的表达迅速上升,在1周时达到最大值,然后开始下降直到恢复正常。其原因可能是损伤后炎症反应刺激成纤维生长因子2的升高,1周后炎症反应消退,所以成纤维生长因子2也逐渐开始下降。并且还发现,自身的血清与成纤维生长因子2、骨形态发生蛋白12 等表达的升高有密切联系。所以,也可以通过外源性的成纤维生长因子2来刺激内源性成纤维生长因子2更长时间的表达,从而促进肌腱愈合。Ide等[52]将成纤维生长因子2局部注射到大鼠冈上肌肌腱损伤的模型中发现:局部应用成纤维生长因子2可加速大鼠冈上肌肌腱损伤后早期的腱-骨重建和愈合。其主要机制是:①成纤维生长因子2可刺激间充质细胞的增殖,这些细胞随后分化成前体细胞并维持这种分化;②成纤维生长因子2在体内诱导转化生长因子β和骨形态发生蛋白基因的表达,它们对骨长入腱-骨界面有着积极的作用。Cai等[28]研究发现:成纤维生长因子2能够通过激活MAPK途径促进人基质干细胞向肌腱的分化,调节肌腱细胞分子生物标志物的表达,如:Ⅰ型胶原蛋白、Ⅲ型胶原蛋白和scleraxis,从而促进肌腱损伤后的再生和修复。Yun等[53]研究也发现: 成纤维生长因子2可通过刺激C2C12成肌细胞的生长黏附、增殖,从而有助于肌腱损伤后的修复。
成纤维生长因子2在骨发育和骨修复过程中也发挥着重要的作用。Yin等[54]以骨膜来源的干细胞为种子细胞,并将种子细胞黏附在能够不断释放成纤维生长因子2和骨形态发生蛋白2的壳聚糖/胶原支架上,来观察对SD大鼠颅骨缺损修复的效果。实验结果显示:实验组的修复效果明显优于对照组,提示成纤维生长因子2和骨形态发生蛋白2为种子细胞的增殖和分化提供了更好的环境,提高了组织工程化骨膜的骨修复效率。Ikpegbu等[55]研究E11上游的成纤维生长因子2是如何对E11起调控作用的实验发现:成纤维生长因子2能够增加骨细胞的表型,促进骨细胞的分化,促进成骨细胞向骨细胞的转化从而加速骨损伤修复的进程,其主要是通过上调下游E11蛋白的表达来实现的。成纤维生长因子2-E11信号通路可能还与骨骼发育和其他疾病有关系,其机制需要更进一步的研究。Lee等[56]研究不同浓度的成纤维生长因子2对新西兰大白兔骨缺损修复情况的实验发现:在不同的时间点,不同浓度的成纤维生长因子2均有促进新生骨生长的作用,提示成纤维生长因子2对新西兰大白兔骨缺损的修复有促进作用。
2.3 成纤维生长因子2对软骨修复的影响 由于软骨的自身修复能力非常受限,目前采用的治疗方式效果欠佳,因此软骨组织工程学修复软骨缺损是目前研究的热点。研究发现,成纤维生长因子2在软骨再生过程中起重要作用,基于此,应用成纤维生长因子2来促进软骨再生和修复的研究越来越多,也取得了不错的效果。
成纤维生长因子2是关节软骨中固有的一种内源性生长因子,最早被发现于软骨细胞及成骨细胞的细胞外基质,其可与硫酸类肝素蛋白聚糖结合并储存于关节软骨的细胞外基质中[57-58]。损伤发生时,其从细胞外基质中释放出来,激活ERK信号通路,参与相应的生物学调控,成纤维生长因子2从细胞外基质中释放,参与修复过程[59]。成纤维生长因子2对软骨的作用具有两面性,既可以促进软骨的再生和修复,也可促进软骨退化,其主要与结合的受体有关。成人关节软骨细胞表达的成纤维生长因子受体有4种,但是主要是受体1和3[64]。
成纤维生长因子2与其受体1的结合导致受体磷酸化,其又激活2种关键信号介质Ras和蛋白激酶Cδ,这些分子然后将其信号输入整合到Raf-MEK1/2-ERK1/2级联中以调节靶基因表达[60]。活化的ERK1/2利用至少2种关键转录因子:Elk-1和RUNX2来上调一系列基因,包括MMP-13,ADAMTS-4,ADAMTS-5,COL10A1和VEGF,最终促进软骨退化。同时,p38和JNK通路也被PKCδ激活,其效应与ERK1 /2促进ECM变性和抑制合成代谢活性一致[58]。
与此相反,当成纤维生长因子2与其受体3结合可促进关节软骨的修复。因此,可通过研究受体1拮抗剂和受体3激动剂的方法来预防软骨退化、促进软骨修复。成纤维生长因子2对软骨的作用还表现出时间差异性和物种差异性。有研究表明,成纤维生长因子2可促进幼龄兔浅层软骨损伤的修复,但对成年兔并无促进修复的效果,因此提示成纤维生长因子2对软骨修复的时间差异性,但是具体机制还不明确[61]。除此之外,成纤维生长因子2对软骨的作用还表现出物种差异性,其可能主要与相应的受体差异有关。人关节软骨主要含有成纤维生长因子受体1和3,而老鼠的关节软骨主要含成纤维生长因子受体2和4,但是造成这种差异的原因还需要进一步研究证实。
近年来,关于成纤维生长因子2对软骨修复的研究越来越多,其己证实可促进全层软骨损伤的修复,但其在损伤修复中的机制尚不明确[62]。除了通过激活FGF/FGFR2通路外,还可激活P13K-Akt、ERK l/2通路促进骨髓间充质干细胞的增殖,调节其SOX9的表达, 促进其向软骨分化[63]。研究发现如果成纤维生长因子2直接作用于软骨层或软骨细胞,可加速软骨细胞外基质的降解、抑制修复相关内源性生长因子的表达,并可引起软骨细胞纤维化。虽然可以上调内源性生长因子硒F82、成纤维生长因子2和骨形态发生蛋白4的表达水平,但不能上调软骨形成关键转录因子SOX9的表达,不利于关节软骨的修复,说明其作用于软骨层细胞时不能有效促进软骨的形成[64]。但研究也惊奇的发现成纤维生长因子2可有效调节软骨下骨,从而促进软骨形成,其主要是通过上调软骨下骨中骨形态发生蛋白2和4等内源性生长因子的表达,进而上调软骨形成早期的关键转录因子SOX9的表达,从而调节软骨下骨促进关节软骨形成。有研究通过用成纤维生长因子2诱导骨髓间充质干细胞增殖分化成软骨细胞的方法证实了成纤维生长因子2能够调节SOX9的表达,从而促进软骨的形成。
.jpg) 文题释义:
成纤维生长因子2:是成纤维生长因子家族中的一员,能够促进细胞的有丝分裂,加速细胞的增殖,促进新血管的形成,现己广泛应用于各种组织修复的研究。
成纤维生长因子受体:是一类穿膜的酪氨酸激酶受体,在大多数组织细胞中均有表达,能够介导成纤维生长因子信号传递入细胞质中使其发挥各种生物学效应。
文题释义:
成纤维生长因子2:是成纤维生长因子家族中的一员,能够促进细胞的有丝分裂,加速细胞的增殖,促进新血管的形成,现己广泛应用于各种组织修复的研究。
成纤维生长因子受体:是一类穿膜的酪氨酸激酶受体,在大多数组织细胞中均有表达,能够介导成纤维生长因子信号传递入细胞质中使其发挥各种生物学效应。.jpg) 文题释义:
成纤维生长因子2:是成纤维生长因子家族中的一员,能够促进细胞的有丝分裂,加速细胞的增殖,促进新血管的形成,现己广泛应用于各种组织修复的研究。
成纤维生长因子受体:是一类穿膜的酪氨酸激酶受体,在大多数组织细胞中均有表达,能够介导成纤维生长因子信号传递入细胞质中使其发挥各种生物学效应。
文题释义:
成纤维生长因子2:是成纤维生长因子家族中的一员,能够促进细胞的有丝分裂,加速细胞的增殖,促进新血管的形成,现己广泛应用于各种组织修复的研究。
成纤维生长因子受体:是一类穿膜的酪氨酸激酶受体,在大多数组织细胞中均有表达,能够介导成纤维生长因子信号传递入细胞质中使其发挥各种生物学效应。
.jpg)
.jpg) 文题释义:
成纤维生长因子2:是成纤维生长因子家族中的一员,能够促进细胞的有丝分裂,加速细胞的增殖,促进新血管的形成,现己广泛应用于各种组织修复的研究。
成纤维生长因子受体:是一类穿膜的酪氨酸激酶受体,在大多数组织细胞中均有表达,能够介导成纤维生长因子信号传递入细胞质中使其发挥各种生物学效应。
文题释义:
成纤维生长因子2:是成纤维生长因子家族中的一员,能够促进细胞的有丝分裂,加速细胞的增殖,促进新血管的形成,现己广泛应用于各种组织修复的研究。
成纤维生长因子受体:是一类穿膜的酪氨酸激酶受体,在大多数组织细胞中均有表达,能够介导成纤维生长因子信号传递入细胞质中使其发挥各种生物学效应。