中国组织工程研究 ›› 2018, Vol. 22 ›› Issue (2): 294-302.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.0021
• 生物材料综述 biomaterial review • 上一篇 下一篇
透明质酸支架材料:应用研究与产品转化前景
- 华熙福瑞达生物医药有限公司,山东省济南市 250101
-
收稿日期:2017-12-11出版日期:2018-01-18发布日期:2018-01-18 -
通讯作者:郭学平,研究员,华熙福瑞达生物医药有限公司,山东省济南市 250101 -
作者简介:张晓鸥,女,1979年生,辽宁省大连市人,汉族,2010年大连理工大学毕业,博士,主要从事透明质酸相关细胞生物学,干细胞与组织工程方面的研究。
Hyaluronic acid scaffolds: application research and product prospects
- Bloomage Freda Biopharm Co., Ltd., Jinan 250101, Shandong Province, China
-
Received:2017-12-11Online:2018-01-18Published:2018-01-18 -
Contact:Guo Xue-ping, Researcher, Bloomage Freda Biopharm Co., Ltd., Jinan 250101, Shandong Province, China -
About author:Zhang Xiao-ou, Doctor, Bloomage Freda Biopharm Co., Ltd., Jinan 250101, Shandong Province, China
摘要:
文章快速阅读:
.jpg)
中图分类号:
引用本文
张晓鸥,吕 旸,毛 华,范馨仪,黄思玲,郭学平. 透明质酸支架材料:应用研究与产品转化前景[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2018, 22(2): 294-302.
Zhang Xiao-ou, Lv Yang, Mao Hua, Fan Xin-yi, Huang Si-ling, Guo Xue-ping.
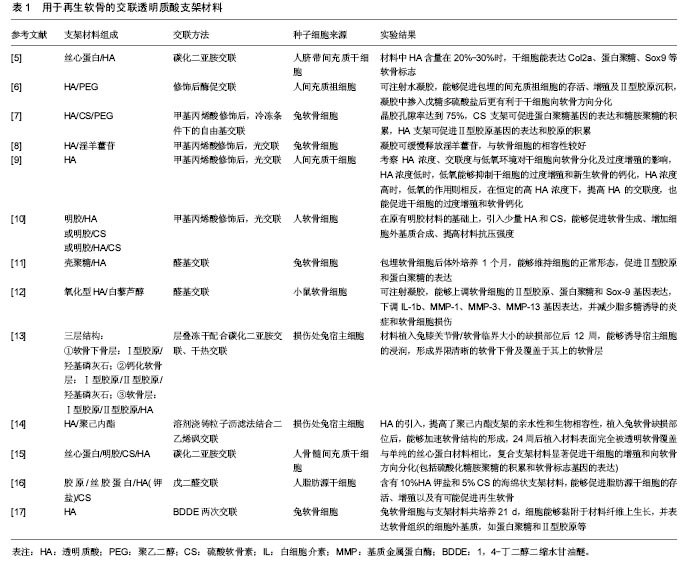
| [1]Hemshekhar M, Thushara RM, Chandranayaka S, et al. Emerging roles of hyaluronic acid bioscaffolds in tissue engineering and regenerative medicine. Int J Biol Macromol. 2016;86:917-928.[2]Lam J, Truong NF, Segura T. Design of cell-matrix interactions in hyaluronic acid hydrogel scaffolds. Acta Biomater. 2014;10(4): 1571-1580.[3]Collins MN, Birkinshaw C. Hyaluronic acid based scaffolds for tissue engineering--a review. Carbohydr Polym. 2013;92(2): 1262-1279.[4]Cavallo C, Desando G, Columbaro M, et al. Chondrogenic differentiation of bone marrow concentrate grown onto a hylauronan scaffold: rationale for its use in the treatment of cartilage lesions. J Biomed Mater Res A. 2013;101(6): 1559-1570.[5]Jaipaew J, Wangkulangkul P, Meesane J, et al. Mimicked cartilage scaffolds of silk fibroin/hyaluronic acid with stem cells for osteoarthritis surgery: Morphological, mechanical, and physical clues. Mater Sci Eng C Mater Biol Appl. 2016;64:173-182.[6]Frith JE, Cameron AR, Menzies DJ, et al. An injectable hydrogel incorporating mesenchymal precursor cells and pentosan polysulphate for intervertebral disc regeneration. Biomaterials. 2013;34(37):9430-9440.[7]Han ME, Kim SH, Kim HD, et al. Extracellular matrix-based cryogels for cartilage tissue engineering. Int J Biol Macromol. 2016;93(Pt B):1410-1419. [8]He L, Yang J, Lu J, et al. Preparation and characterization of a novel hyaluronic acid–icariin conjugate hydrogel. Mater Lett. 2014;136: 41-44.[9]Zhu M, Feng Q, Bian L. Differential effect of hypoxia on human mesenchymal stem cell chondrogenesis and hypertrophy in hyaluronic acid hydrogels. Acta Biomater. 2014;10(3):1333-1340.[10]Levett PA, Melchels FP, Schrobback K, et al. A biomimetic extracellular matrix for cartilage tissue engineering centered on photocurable gelatin, hyaluronic acid and chondroitin sulfate. Acta Biomater. 2014;10(1):214-223.[11]Remya NS, Nair PD. Engineering cartilage tissue interfaces using a natural glycosaminoglycan hydrogel matrix--an in vitro study. Mater Sci Eng C Mater Biol Appl. 2013;33(2):575-582.[12]Sheu SY, Chen WS, Sun JS, et al. Biological characterization of oxidized hyaluronic acid/resveratrol hydrogel for cartilage tissue engineering. J Biomed Mater Res A. 2013;101(12):3457-3466.[13]Levingstone TJ, Thompson E, Matsiko A, et al. Multi-layered collagen-based scaffolds for osteochondral defect repair in rabbits. Acta Biomater. 2016;32:149-160.[14]Lebourg M, Martínez-Díaz S, García-Giralt N, et al. Cell-free cartilage engineering approach using hyaluronic acid-polycaprolactone scaffolds: a study in vivo. J Biomater Appl. 2014;28(9):1304-1315.[15]Sawatjui N, Damrongrungruang T, Leeanansaksiri W, et al. Silk fibroin/gelatin-chondroitin sulfate-hyaluronic acid effectively enhances in vitro chondrogenesis of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells. Mater Sci Eng C Mater Biol Appl. 2015;52:90-96.[16]Dinescu S, G?l??eanu B, Albu M, et al. Biocompatibility assessment of novel collagen-sericin scaffolds improved with hyaluronic Acid and chondroitin sulfate for cartilage regeneration. Biomed Res Int. 2013;2013:598056.[17]刘少英,陈建英,陈倩倩,等. 以交联透明质酸钠为支架体外构建组织工程软骨[J].中国组织工程研究,2014,18(8):1191-1197.[18]Tavakoli E, Mehdikhani-Nahrkhalaji M, Hashemi-Beni B, et al. Preparation, Characterization and Mechanical Assessment of Poly (Lactide-Co-Glycolide)/ Hyaluronic Acid/ Fibrin/ Bioactive Glass Nano-composite Scaffolds for Cartilage Tissue Engineering Applications. Procedia Materials Science. 2015; 11:124-130.[19]Skaalure SC, Dimson SO, Pennington AM, et al. Semi-interpenetrating networks of hyaluronic acid in degradable PEG hydrogels for cartilage tissue engineering. Acta Biomater. 2014;10(8):3409-3420.[20]Park H, Choi B, Hu J, et al. Injectable chitosan hyaluronic acid hydrogels for cartilage tissue engineering. Acta Biomater. 2013; 9(1):4779-4786.[21]李音,颜廷亭,朱伟波,等. 魔芋葡甘聚糖/透明质酸钠纤维膜生物性能的研究[J]. 材料导报B:研究篇, 2013,27(7):90-92,112.[22]Li Z, Kaplan KM, Wertzel A, et al. Biomimetic fibrin-hyaluronan hydrogels for nucleus pulposus regeneration. Regen Med. 2014; 9(3):309-326.[23]Mercuri J, Addington C, Pascal R 3rd, et al. Development and initial characterization of a chemically stabilized elastin-glycosaminoglycan-collagen composite shape-memory hydrogel for nucleus pulposus regeneration. J Biomed Mater Res A. 2014;102(12):4380-4393.[24]Kim DH, Martin JT, Elliott DM, et al. Phenotypic stability, matrix elaboration and functional maturation of nucleus pulposus cells encapsulated in photocrosslinkable hyaluronic acid hydrogels. Acta Biomater. 2015;12:21-29.[25]Jeong CG, Francisco AT, Niu Z, et al. Screening of hyaluronic acid-poly(ethylene glycol) composite hydrogels to support intervertebral disc cell biosynthesis using artificial neural network analysis. Acta Biomater. 2014;10(8):3421-3430.[26]Cui N, Qian J, Xu W, et al. Preparation, characterization, and biocompatibility evaluation of poly(N?-acryloyl-L-lysine)/hyaluronic acid interpenetrating network hydrogels. Carbohydr Polym. 2016; 136:1017-1026.[27]Cui N, Qian J, Liu T, et al. Hyaluronic acid hydrogel scaffolds with a triple degradation behavior for bone tissue engineering. Carbohydr Polym. 2015;126:192-198.[28]Zhu M, Lin S, Sun Y, et al. Hydrogels functionalized with N-cadherin mimetic peptide enhance osteogenesis of hMSCs by emulating the osteogenic niche. Biomaterials. 2016;77:44-52.[29]Bellini D, Cencetti C, Meraner J, et al. An in situ gelling system for bone regeneration of osteochondral defects. European Polymer Journal. 2015;72:642-650.[30]Kisiel M, Martino MM, Ventura M, et al. Improving the osteogenic potential of BMP-2 with hyaluronic acid hydrogel modified with integrin-specific fibronectin fragment. Biomaterials. 2013;34(3): 704-712.[31]Wu AT, Aoki T, Sakoda M, et al. Enhancing osteogenic differentiation of MC3T3-E1 cells by immobilizing inorganic polyphosphate onto hyaluronic acid hydrogel. Biomacromolecules. 2015;16(1):166-173.[32]林永新,丁志勇,周孝斌,等. 透明质酸/壳聚糖复合支架的制备及其力学性能评价[J].中国临床解剖学杂志, 2014,32(1):52-56.[33]Subramaniam S, Fang YH, Sivasubramanian S, et al. Hydroxyapatite-calcium sulfate-hyaluronic acid composite encapsulated with collagenase as bone substitute for alveolar bone regeneration. Biomaterials. 2016;74:99-108.[34]Lequeux C, Rodriguez J, Boucher F, et al. In vitro and in vivo biocompatibility, bioavailability and tolerance of an injectable vehicle for adipose-derived stem/stromal cells for plastic surgery indications. J Plast Reconstr Aesthet Surg. 2015;68(11):1491-1497.[35]Açil Y, Zhang X, Nitsche T, et al. Effects of different scaffolds on rat adipose tissue derived stroma cells. J Craniomaxillofac Surg. 2014;42(6):825-834.[36]Chang KH, Liao HT, Chen JP. Preparation and characterization of gelatin/hyaluronic acid cryogels for adipose tissue engineering: in vitro and in vivo studies. Acta Biomater. 2013;9(11):9012-9026.[37]Jia Y, Fan M, Chen H, et al. Magnetic hyaluronic acid nanospheres via aqueous Diels-Alder chemistry to deliver dexamethasone for adipose tissue engineering. J Colloid Interface Sci. 2015;458:293-299.[38]Dahlmann J, Krause A, Möller L, et al. Fully defined in situ cross-linkable alginate and hyaluronic acid hydrogels for myocardial tissue engineering. Biomaterials. 2013;34(4):940-951.[39]Fiumana E, Pasquinelli G, Foroni L, et al. Localization of mesenchymal stem cells grafted with a hyaluronan-based scaffold in the infarcted heart. J Surg Res. 2013;179(1):e21-29.[40]Young JL, Tuler J, Braden R, et al. In vivo response to dynamic hyaluronic acid hydrogels. Acta Biomater. 2013;9(7):7151-7157.[41]Muscari C, Bonafè F, Martin-Suarez S, et al. Restored perfusion and reduced inflammation in the infarcted heart after grafting stem cells with a hyaluronan-based scaffold. J Cell Mol Med. 2013; 17(4):518-530.[42]Yoon SJ, Hong S, Fang YH, et al. Differential regeneration of myocardial infarction depending on the progression of disease and the composition of biomimetic hydrogel. J Biosci Bioeng. 2014;118(4):461-468.[43]Gaetani R, Feyen DA, Verhage V, et al. Epicardial application of cardiac progenitor cells in a 3D-printed gelatin/hyaluronic acid patch preserves cardiac function after myocardial infarction. Biomaterials. 2015;61:339-348.[44]Duan B, Kapetanovic E, Hockaday LA, et al. Three-dimensional printed trileaflet valve conduits using biological hydrogels and human valve interstitial cells. Acta Biomater. 2014;10(5):1836-1846.[45]Eslami M, Vrana NE, Zorlutuna P, et al. Fiber-reinforced hydrogel scaffolds for heart valve tissue engineering. J Biomater Appl. 2014;29(3):399-410.[46]Zhu C, Fan D, Wang Y. Human-like collagen/hyaluronic acid 3D scaffolds for vascular tissue engineering. Mater Sci Eng C Mater Biol Appl. 2014;34:393-401.[47]Wang LS, Lee F, Lim J, et al. Enzymatic conjugation of a bioactive peptide into an injectable hyaluronic acid-tyramine hydrogel system to promote the formation of functional vasculature. Acta Biomater. 2014;10(6):2539-2550.[48]Addington CP, Heffernan JM, Millar-Haskell CS, et al. Enhancing neural stem cell response to SDF-1α gradients through hyaluronic acid-laminin hydrogels. Biomaterials. 2015;72:11-19.[49]Schizas N, Rojas R, Kootala S, et al. Hyaluronic acid-based hydrogel enhances neuronal survival in spinal cord slice cultures from postnatal mice. J Biomater Appl. 2014;28(6):825-836.[50]Mothe AJ, Tam RY, Zahir T, et al. Repair of the injured spinal cord by transplantation of neural stem cells in a hyaluronan-based hydrogel. Biomaterials. 2013;34(15):3775-3783.[51]吴婷,李朝晖,崔占峰,等. 应用多种水凝胶支架材料构建三维神经干细胞培养模型[J]. 中国细胞生物学学报,2015,37(1):66-73.[52]Entekhabi E, Haghbin Nazarpak M, Moztarzadeh F, et al. Design and manufacture of neural tissue engineering scaffolds using hyaluronic acid and polycaprolactone nanofibers with controlled porosity. Mater Sci Eng C Mater Biol Appl. 2016;69:380-387.[53]Arulmoli J, Wright HJ, Phan DTT, et al. Combination scaffolds of salmon fibrin, hyaluronic acid, and laminin for human neural stem cell and vascular tissue engineering. Acta Biomater. 2016;43:122-138. [54]Wang S, Guan S, Wang J, et al. Fabrication and characterization of conductive poly (3,4-ethylenedioxythiophene) doped with hyaluronic acid/poly (l-lactic acid) composite film for biomedical application. J Biosci Bioeng. 2017;123(1):116-125.[55]Kuo YC, Chen YC. Regeneration of neurite-like cells from induced pluripotent stem cells in self-assembled hyaluronic acid-gelatin microhydrogel. J Taiwan Inst Chem E. 2016;67:74-87.[56]Monteiro IP, Shukla A, Marques AP, et al. Spray-assisted layer-by-layer assembly on hyaluronic acid scaffolds for skin tissue engineering. J Biomed Mater Res A. 2015;103(1):330340.[57]Yan S, Zhang Q, Wang J, et al. Silk fibroin/chondroitin sulfate/hyaluronic acid ternary scaffolds for dermal tissue reconstruction. Acta Biomater. 2013;9(6):6771-6782.[58]Monteiro IP, Gabriel D, Timko BP, et al. A two-component pre-seeded dermal-epidermal scaffold. Acta Biomater. 2014; 10(12):4928-4938.[59]Xiang J, Sun J, Hong J, et al. T-style keratoprosthesis based on surface-modified poly (2-hydroxyethyl methacrylate) hydrogel for cornea repairs. Mater Sci Eng C Mater Biol Appl. 2015;50: 274-285.[60]Liu Y, Ren L, Wang Y. Crosslinked collagen-gelatin-hyaluronic acid biomimetic film for cornea tissue engineering applications. Mater Sci Eng C Mater Biol Appl. 2013;33(1):196-201.[61]Liu Y, Wang R, Zarembinski TI, et al. The application of hyaluronic acid hydrogels to retinal progenitor cell transplantation. Tissue Eng Part A. 2013;19(1-2):135-142.[62]Shang Y, Tamai M, Ishii R, et al. Hybrid sponge comprised of galactosylated chitosan and hyaluronic acid mediates the co-culture of hepatocytes and endothelial cells. J Biosci Bioeng. 2014;117(1):99-106. |
| [1] | 蒲 锐, 陈子扬, 袁凌燕. 不同细胞来源外泌体保护心脏的特点与效应[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2021, 25(在线): 1-. |
| [2] | 张同同, 王中华, 文 杰, 宋玉鑫, 刘 林. 3D打印模型在颈椎肿瘤手术切除与重建中的应用[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2021, 25(9): 1335-1339. |
| [3] | 张 超, 吕 欣. 髋臼骨折固定后的异位骨化:危险因素、预防及其治疗进展[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2021, 25(9): 1434-1439. |
| [4] | 周继辉, 李新志, 周 游, 黄 卫, 陈文瑶. 髌骨骨折修复内植物选择的多重问题[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2021, 25(9): 1440-1445. |
| [5] | 王德斌, 毕郑刚. 尺骨鹰嘴骨折-脱位解剖力学、损伤特点、固定修复及3D技术应用的相关问题[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2021, 25(9): 1446-1451. |
| [6] | 姬志祥, 蓝常贡. 尿酸盐转运蛋白在痛风中的多态性和治疗相关性[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2021, 25(8): 1290-1298. |
| [7] | 袁 美, 张新新, 郭祎莎, 毕 霞. 循环microRNA在血管性认知障碍诊断中的应用[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2021, 25(8): 1299-1304. |
| [8] | 汪显耀, 关亚琳, 刘忠山. 提高间充质干细胞治疗难愈性创面的策略[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2021, 25(7): 1081-1087. |
| [9] | 万 然, 史 旭, 刘京松, 王岩松. 间充质干细胞分泌组治疗脊髓损伤的研究进展[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2021, 25(7): 1088-1095. |
| [10] | 廖成成, 安家兴, 谭张雪, 王 倩, 刘建国. 口腔鳞状细胞癌干细胞的治疗靶点及应用前景[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2021, 25(7): 1096-1103. |
| [11] | 赵 敏, 冯柳祥, 陈 垚, 顾 霞, 王平义, 李一梅, 李文华. 低氧环境下外泌体可作为疾病的标志物[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2021, 25(7): 1104-1108. |
| [12] | 谢文佳, 夏天娇, 周卿云, 刘羽佳, 顾小萍. 小胶质细胞介导神经元损伤在神经退行性疾病中的作用[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2021, 25(7): 1109-1115. |
| [13] | 李珊珊, 郭笑霄, 尤 冉, 杨秀芬, 赵 露, 陈 曦, 王艳玲. 感光细胞替代治疗视网膜变性疾病[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2021, 25(7): 1116-1121. |
| [14] | 焦 慧, 张一宁, 宋雨晴, 林 宇, 王秀丽. 乳腺癌类器官研究进展及临床应用前景[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2021, 25(7): 1122-1128. |
| [15] | 王诗琦, 张金生. 中医药调控缺血缺氧微环境对骨髓间充质干细胞增殖、分化及衰老的影响[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2021, 25(7): 1129-1134. |
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||