中国组织工程研究 ›› 2018, Vol. 22 ›› Issue (2): 288-293.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.0020
• 材料生物相容性 material biocompatibility • 上一篇 下一篇
心内超声探头实时定位技术的仿真实验
李向飞,段军涛,苏智剑
- 郑州大学机械工程学院,河南省郑州市 450001
Real-time positioning of the ablation catheter ultrasonic probe in the heart: a simulation experiment
Li Xiang-fei, Duan Jun-tao, Su Zhi-jian
- School of Mechanical Engineering, Zhengzhou University, Zhengzhou 450001, Henan Province, China
摘要:
文章快速阅读:
.jpg)
文题释义:
消融手术中导管定位方法:主要有三维磁场定位法和三维电场定位法2种。磁场导管定位方法使用固定在手术床下的3个线圈来分别产生磁场,然后用埋藏在消融导管头部附近的探测线圈来感知3个定位磁场的强度,以此得到导管在磁场中的位置,使用此方法进行定位时,要求患者不能相对病床发生移动,否则会出现较大的定位误差;电场定位方法采用粘贴在患者皮肤表面的3对电极片产生的3个正交电场来定位,手术中埋藏在导管头部的电极用来分别探测3个电场的电场强度,以此来确定导管头部在心脏中的位置。
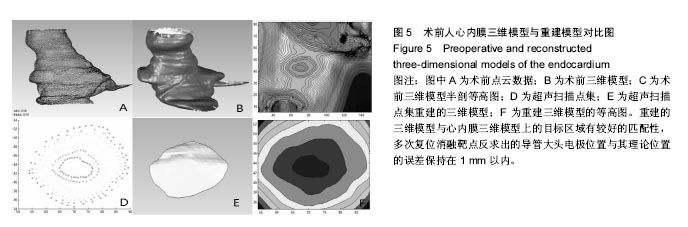
心内超声探头实时定位技术:以“地形”匹配技术来确定导管探头位置,具体方式如下:术前根据扫描设备(例如CT、MRI等)获得扫描数据建立心内膜表面模型,术中用超声探头获得的扫描数据重建心内膜局部表面模型,然后通过该局部表面模型与术前扫描设备获得的全局表面模型进行特征匹配,最终反求得超声探头位置。
背景:目前心脏消融手术中主要使用三维磁场定位和三维电场定位两种导管定位方法,但所需设备均较昂贵。
目的:将超声探头与消融导管组合起来提出一种新的消融导管定位方法。
方法:通过人体全身解剖数据集获取人体心脏的三维数据,建立心内膜表面的三维矢量模型;设计计算定位用超生探头的基本参数及扫描策略,编制相应的仿真计算软件;以所建的三维心内膜矢量模型为照射目标,通过仿真计算获得超声探头的探测数据;对仿真得到的探测数据进行数据处理,获得由探测数据重建的目标表面特征;将重建的目标表面特征与所建矢量模型的表面特征进行匹配,最终反求确定探头的位置。
结果与结论:基于解剖数据集建立了精确的心内膜三维模型,并通过对其的模拟超声照射获得了超声曲面探测数据,重建的曲面模型精度高,与所建的心内膜三维模型上的目标区域有较好的匹配性,反求出的探头位置与其理论位置误差满足定位精度要求。利用超声成像技术实现对消融导管探头的术中定位方法,能够实现导管探头在心脏中的精确定位,为手术实施提供精确可靠的导航作用。
ORCID: 0000-0003-4636-2827(李向飞)
中图分类号:
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)


.jpg)