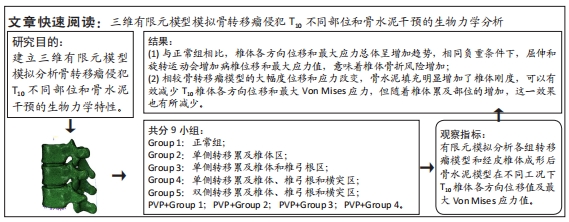
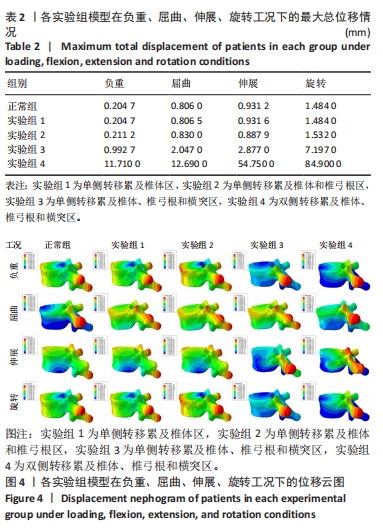
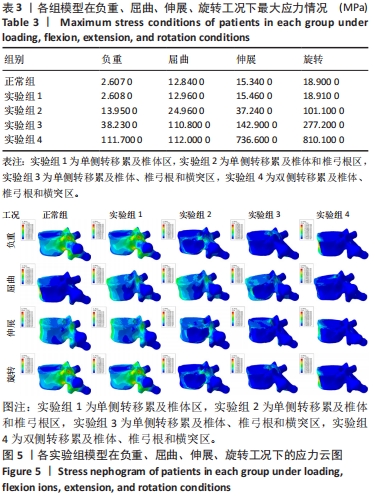
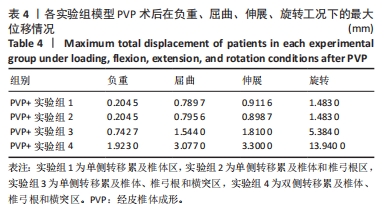
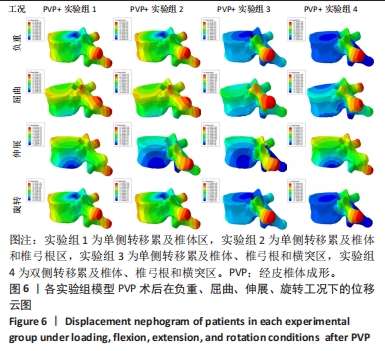
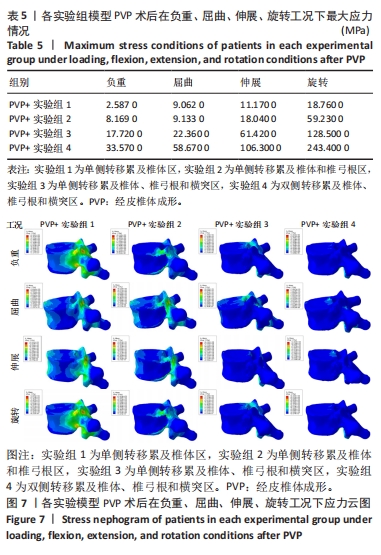
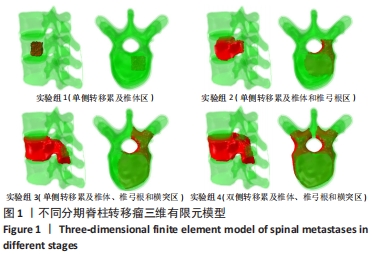
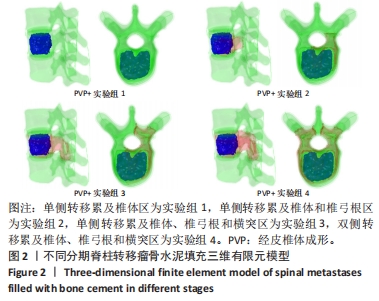
[1] XIONG Z, DENG G, HUANG X, et al. Bone metastasis pattern in initial metastatic breast cancer: a population-based study. Cancer Manag Res. 2018;10:287-295.
[2] WANG P, ZANG S, LI G, et al. The role of surgery on the primary tumor site in bladder cancer with distant metastasis: significance of histology type and metastatic pattern. Cancer Med. 2020;9(24):9293-9302.
[3] HOSHIAI S, MASUMOTO T, HANAOKA S, et al. Clinical usefulness of temporal subtraction CT in detecting vertebral bone metastases. Eur J Radiol. 2019;118:175-180.
[4] LI K, HAN X, CHEN X, et al. Poorer surgical outcomes at 2 years postoperatively in patients with lumbar spinal stenosis with long-term preoperative leg numbness: a single-center retrospective study. J Orthop Surg Res. 2022;17(1):1-8.
[5] 张静,吕东来,周俊平. 椎体转移癌放疗患者的临床特征及预后影响因素分析[J]. 颈腰痛杂志,2019,40(1):1-4.
[6] 余祥艳,罗世政,田素魁,等.经皮椎体成形术联合放疗治疗脊椎骨转移瘤的临床观察[J].世界最新医学信息文摘,2019,19(32):104-105.
[7] 王景东,刘耀升,刘蜀彬. 转移瘤硬膜外脊髓压迫症运动功能障碍与影像学及临床特征相关性分析[J]. 中国骨伤,2011,24(11):943-947.
[8] 耿元元,张燕,梁露文. 经皮椎体成形术治疗脊柱转移瘤合并椎体骨折的临床效果及其影响因素[J]. 实用癌症杂志,2022,37(4):598-600.
[9] 崔云鹏,潘元星,米川,等. 经皮椎体成形术治疗后壁缺失脊柱转移瘤的安全性和有效性[J]. 肿瘤防治研究,2019,46(7):622-626.
[10] BASTOS D, EVERSON RG, SANTOS B, et al. A comparison of spinal laser interstitial thermotherapy with open surgery for metastatic thoracic epidural spinal cord compression. J Neurosurg Spine. 2020; 32(5):1-9.
[11] CUI YP, SHI X , CHUAN MI, et al. Efficacy analysis of percutaneous vertebroplasty and percutaneous kyphoplasty for spinal metastases in 321 patients.Chin J Cancer. 2018;25(8):586-590.
[12] AMORETTI N, DIEGO P, AMÉLIE P, et al. Percutaneous vertebroplasty in tumoral spinal fractures with posterior vertebral wall involvement: Feasibility and safety. Eur J Radiol. 2018;104:38-42.
[13] EBIHARA H, ITO M, ABUMI K, et al. A biomechanical analysis of metastatic vertebral collapse of the thoracic spine: a sheep model study. Spine. 2004;29(9):994-999.
[14] SALVATORE G, BERTON A, GIAMBINI H, et al. Biomechanical effects of metastasis in the osteoporotic lumbar spine:A Finite Element Analysis. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2018;19:38
[15] 董晖,赵立晶,欧阳鹏荣,等. 脊柱转移瘤姑息性切除减压内固定联合骨水泥填充的临床疗效研究[J]. 生物骨科材料与临床研究, 2019,16(6):31-34.
[16] HASANAIN M, ENGLISCH CN, GARNER M, et al. Radiological analyses of the dimensions of the pedicle and dorsal part of the transverse process of subaxial vertebrae in the context of cervical spine surgery. Ann Anat. 2021;238:151790.
[17] ZHAO WT, QIN DP, ZHANG XG, et al. Biomechanical effects of different vertebral heights after augmentation of osteoporotic vertebral compression fracture:a three dimensional finite element analysis. J Orthop Surg Res. 2018;13:32
[18] QIU TX, TEO EC, LEE KK, et al. Validation of T10-T11 Finite Element Model and Determination of Instantaneous Axes of Rotations in Three Anatomical Planes. Spine. 2003;28(24):2694-2699
[19] VIET NV, ZAKI W. Modeling bending behavior of shape memory alloy wire-reinforced composites: Semi-analytical model and finite element analysis - ScienceDirect. Chin J A. 2021;34(8):176-191.
[20] CHOY WJ, MOBBS RJ, WILCOX B, et al. Reconstruction of Thoracic Spine Using a Personalized 3D-Printed Vertebral Body in Adolescent with T9 Primary Bone Tumor. World Neurosurg. 2017;105:1032.e13-1032.e17.
[21] WHYNE CM, HU SS, LOTZ JC. Burst fracture in the metastatically involved spine: development, validation, and parametric analysis of a three-dimensional poroelastic finite-element model. Spine. 2003;28(7): 652-660.
[22] ROHLMANN A, BOUSTANI HN, BERGMANN G, et al. A probabilistic finite element analysis of the stresses in the augmented vertebral body after vertebroplasty. Eur Spine J. 2010;19(9):1585-1595.
[23] SALVATORE G, BERTON A, GIAMBINI H, et al. Biomechanical effects of metastasis in the osteoporotic lumbar spine: A Finite Element Analysis. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2018;19(1):1-8.
[24] EOM J, BAYOME M, PARK JH, et al. Displacement and stress distribution of the maxillofacial complex during maxillary protraction using palatal plates: A three-dimensional finite element analysis. Korean J Orthod. 2018;48(5):304-315.
[25] GUO ZH, YAN YQ, TANG Y, et al. Finite element optimization analysis of minimally invasive screw treatment for Sanders typeⅡcalcaneal fracture. Zhongguo Gu Shang. 2021;34(2):137-142.
[26] ALSAYEDNOOR J, METCALF L, ROCHESTER J, et al. Comparison of HR-pQCT-and microCT-based finite element models for the estimation of the mechanical properties of the calcaneus trabecular bone. Biomech Model Mechanobiol. 2018;17(6):1715-1730.
[27] LEE DC, BATISTA PM, MEYERMANN K, et al. Traumatic thoracolumbar projectile with concomitant vertebral body and aortic injury. J Vasc Surg Cases Innov Tech. 2020;6(4):490-492.
[28] FAN K, CAO X, ZHANG X, et al. Research on effect of lumbar motion angle on stress of lumbar intervertebral disc and vertebral body based on finite element analysis. Basic Clin Pharmacol Toxicol. 2019;125: 27-28.
[29] 马朋朋,蔡明,张春林,等. 三维有限元建模分析椎体成形术后骨水泥体积对邻近椎体骨折发生的影响[J]. 中国数字医学,2020, 15(7):92-94.
[30] 邬超,高明杰,王建忠,等. 有限元法分析Lenke 3型青少年特发性脊柱侧凸胸-腰椎的应力及位移变化[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2021,25(33):5273-5280.
[31] 闫惠淳,李晶,柳大为,等. 舌侧矫治器预置转矩弓丝对上前牙牙周膜应力影响的三维有限元研究[J]. 中华口腔正畸学杂志,2020, 27(3):154-157.
[32] 王江南,黄干,葛绍勇,等. 椎体压缩性骨折患者PVP术后相邻新发椎体压缩骨折Nomogram模型构建[J]. 中国骨与关节杂志,2020, 9(6):471-478.
[33] 逯登鹏,尚大财,尚晋. 胸腰椎损伤分类与严重度评分联合载荷分享评分对胸腰椎椎体骨折微创手术治疗患者近期预后的评价研究[J]. 中国骨与关节杂志,2022,11(2):147-151.
[34] 姚龚,沈忆新,李敏,等.骨水泥不同弥散方式对椎体成形术后生物力学影响的有限元分析[J].中国骨伤,2021,34(8):732-737.
[35] 秦大平,张晓刚,权祯,等.不同方法治疗骨质疏松性胸腰椎压缩骨折椎体力学稳定性变化差异的有限元分析[J].中华中医药杂志, 2021,36(8):4886-4895.
[36] 范智荣. 椎体后凸成型术后椎体高度与邻近椎体生物力学变化的有限元研究[D].广州:广州中医药大学,2021.
[37] 曾锦源,谢昀,陈春永,等.骨折复位程度和骨水泥注入量对PKP术后邻近椎体应力影响的有限元分析[J].中国骨与关节损伤杂志, 2023,38(7):698-702.
[38] ROCHA ROMERO A, HERNÁNDEZ-PORRAS BC, PLANCARTE-SANCHEZ R, et al. Risk of new fractures in vertebroplasty for multiple myeloma. A retrospective study. Pain Med. 2020;21(11):3018-3023.
[39] 赵研,宋启春,李东,等.骨质疏松性椎体压缩骨折不同骨水泥分布的临床观察及生物力学的有限元分析[J].创伤外科杂志,2022, 24(11):818-824+836.
[40] CHEVALIER Y, PAHR D, CHARLEBOIS M, et al. Cement distribution, volume, and compliance in vertebroplasty: some answers from an anatomy-based nonlinear finite element study. Spine. 2008;33(16): 1722-1730.
[41] 钱程,蒋涛.有限元分析法在椎体成形术中的应用进展[J].中国医药导报,2022,19(20):37-40+57.
|