[1] BIRKNES JK, WHITE AP, ALBERT TJ, et al. Adult degenerative scoliosis: a review. Neurosurgery. 2008;63(3 Suppl):94-103.
[2] YıLMAZ H, ZATERI C, KUSVURAN OZKAN A, et al. Prevalence of adolescent idiopathic scoliosis in Turkey: an epidemiological study. Spine J. 2020;20(6):947-955.
[3] VAN ROYEN BJB. Understanding the Lenke Classification for Adolescent Idiopathic Scoliosis (AIS). Curr Probl Diagn Radiol. 2023;52(4):233-236.
[4] NEGRINI S, DONZELLI S, AULISA AG, et al. 2016 SOSORT guidelines: orthopaedic and rehabilitation treatment of idiopathic scoliosis during growth. Scoliosis Spinal Disord. 2018;13:3.
[5] PAPALIODIS DN, BONANNI PG, ROBERTS TT, et al. Computer Assisted Cobb Angle Measurements: A novel algorithm. Int J Spine Surg. 2017; 11(3):21.
[6] DA SILVEIRA GE, ANDRADE RM, GUILHERMINO GG, et al. The Effects of Short- and Long-Term Spinal Brace Use with and without Exercise on Spine, Balance, and Gait in Adolescents with Idiopathic Scoliosis. Medicina (Kaunas). 2022;58(8):1024.
[7] RICHARDS BS, BERNSTEIN RM, D’AMATO CR, et al. Standardization of criteria for adolescent idiopathic scoliosis brace studies: SRS Committee on Bracing and Nonoperative Management. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2005;30(18):2068-2075; discussion 2076-2077.
[8] KING HA, MOE JH, BRADFORD DS, et al. The selection of fusion levels in thoracic idiopathic scoliosis. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1983;65(9):1302-1313.
[9] CUMMINGS RJ, LOVELESS EA, CAMPBELL J, et al. Interobserver reliability and intraobserver reproducibility of the system of King et al. for the classification of adolescent idiopathic scoliosis. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1998;80(8):1107-1111.
[10] LENKE LG, BETZ RR, BRIDWELL KH, et al. Intraobserver and interobserver reliability of the classification of thoracic adolescent idiopathic scoliosis. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1998;80(8):1097-1106.
[11] LENKE LG, BETZ RR, HARMS J, et al. Adolescent idiopathic scoliosis: a new classification to determine extent of spinal arthrodesis. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2001;83(8):1169-1181.
[12] DICKSON RA. The etiology and pathogenesis of idiopathic scoliosis. Acta Orthop Belg. 1992;58 Suppl 1:21-25.
[13] HOSSEINPOUR-FEIZI H, SOLEIMANPOUR J, SALES JG, et al. Lenke and King classification systems for adolescent idiopathic scoliosis: interobserver agreement and postoperative results. Int J Gen Med. 2011;4:821-825.
[14] SAEEDI M, KAMYAB M, BABAEE T, et al. The effects of bracing on sagittal spinopelvic parameters and Cobb angle in adolescents with idiopathic scoliosis: A before-after clinical study. Turk J Phys Med Rehabil. 2020;66(4):452-458.
[15] MAC-THIONG JM, LABELLE H, DE GUISE JA. Comparison of sacropelvic morphology between normal adolescents and subjects with adolescent idiopathic scoliosis. Stud Health Technol Inform. 2006;123:195-200.
[16] NASH CL JR, MOE JH. A study of vertebral rotation. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1969;51(2):223-229.
[17] LANG C, HUANG Z, ZOU Q, et al. Coronal deformity angular ratio may serve as a valuable parameter to predict in-brace correction in patients with adolescent idiopathic scoliosis. Spine J. 2019;19(6):1041-1047.
[18] WANG XB, LENKE LG, THUET E, et al. Deformity Angular Ratio Describes the Severity of Spinal Deformity and Predicts the Risk of Neurologic Deficit in Posterior Vertebral Column Resection Surgery. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2016;41(18):1447-1455.
[19] SANDERS AE, ANDRAS LM, IANTORNO SE, et al. Clinically Significant Psychological and Emotional Distress in 32% of Adolescent Idiopathic Scoliosis Patients. Spine Deform. 2018;6(4):435-440.
[20] WANG H, LI T, YUAN W, et al. Mental health of patients with adolescent idiopathic scoliosis and their parents in China: a cross-sectional survey. BMC Psychiatry. 2019;19(1):147.
[21] KIM W, PORRINO JA, HOOD KA, et al. Clinical Evaluation, Imaging, and Management of Adolescent Idiopathic and Adult Degenerative Scoliosis. Curr Probl Diagn Radiol. 2019;48(4):402-414.
[22] KUZNIA AL, HERNANDEZ AK, LEE LU. Adolescent Idiopathic Scoliosis: Common Questions and Answers. Am Fam Physician. 2020;101(1):19-23.
[23] MA Q, WANG L, ZHAO L, et al. Coronal Balance vs. Sagittal Profile in Adolescent Idiopathic Scoliosis, Are They Correlated? Front Pediatr. 2020;7:523.
[24] ZHANG C, WANG Y, YU J, et al. Analysis of sagittal curvature and its influencing factors in adolescent idiopathic scoliosis. Medicine (Baltimore). 2021;100(23):e26274.
[25] PESENTI S, POMERO V, PROST S, et al. Curve location influences spinal balance in coronal and sagittal planes but not transversal trunk motion in adolescents with idiopathic scoliosis: a prospective observational study. Eur Spine J. 2020;29(8):1972-1980.
[26] MOHANTY SP, PAI KANHANGAD M, GULLIA A. Curve severity and apical vertebral rotation and their association with curve flexibility in adolescent idiopathic scoliosis. Musculoskelet Surg. 2021;105(3):303-308.
[27] MILLNER PA, DICKSON RA. Idiopathic scoliosis: biomechanics and biology. Eur Spine J. 1996;5(6):362-373.
[28] CHENG JC, CASTELEIN RM, CHU WC, et al. Adolescent idiopathic scoliosis. Nat Rev Dis Primers. 2015;1:15030.
[29] HAN SM, YANG C, WEN JX, et al. Morphology and deformity of the shoulder and pelvis in the entire spine radiographs of adolescent idiopathic scoliosis. Quant Imaging Med Surg. 2023;13(5):3266-3278.
[30] KIM SB, HEO YM, HWANG CM, et al. Reliability of the EOS Imaging System for Assessment of the Spinal and Pelvic Alignment in the Sagittal Plane. Clin Orthop Surg. 2018;10(4):500-507.
[31] MERRILL RK, KIM JS, LEVEN DM, et al. Differences in Fundamental Sagittal Pelvic Parameters Based on Age, Sex, and Race. Clin Spine Surg. 2018;31(2):E109-E114.
[32] WANG G, LI Y, LIU P, et al. Pelvic incidence correlates to sagittal spinal morphology in lenke 5 adolescent idiopathic scoliosis and influences the proximal junctional kyphosis rate after correction surgery. Eur Spine J. 2021;30(9):2457-2466.
[33] BRINK RC, VAVRUCH L, SCHLÖSSER TPC, et al. Three-dimensional pelvic incidence is much higher in (thoraco)lumbar scoliosis than in controls. Eur Spine J. 2019;28(3):544-550.
[34] MIYAZAKI M, ISHIHARA T, ABE T, et al. Analysis of reciprocal changes in upper cervical profiles after posterior spinal fusion with the simultaneous double rod rotation technique for adolescent idiopathic scoliosis. Orthop Traumatol Surg Res. 2020;106(7):1275-1279.
[35] SCHLÖSSER TP, ABELIN-GENEVOIS K, HOMANS J, et al. Comparison of different strategies on three-dimensional correction of AIS: which plane will suffer? Eur Spine J. 2021;30(3):645-652.
[36] KARAM M, VERGARI C, SKALLI W, et al. Assessment of the axial plane deformity in subjects with adolescent idiopathic scoliosis and its relationship to the frontal and sagittal planes. Spine Deform. 2022; 10(3):509-514.
[37] GUM JL, ASHER MA, BURTON DC, et al. Transverse plane pelvic rotation in adolescent idiopathic scoliosis: primary or compensatory? Eur Spine J. 2007;16(10):1579-1586.
[38] QIU XS, ZHANG JJ, YANG SW, et al. Anatomical study of the pelvis in patients with adolescent idiopathic scoliosis. J Anat. 2012;220(2):173-178.
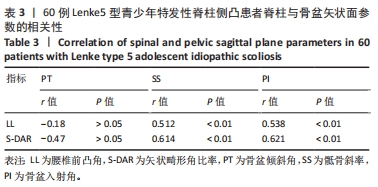
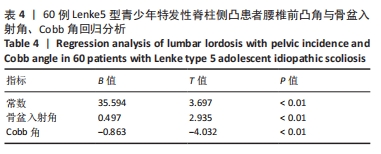
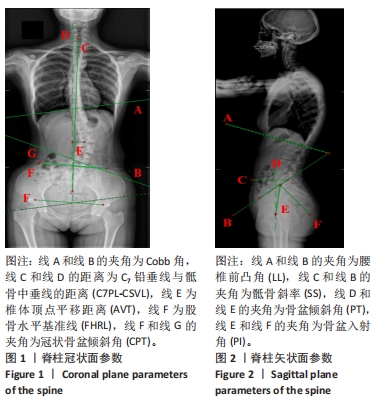
|