中国组织工程研究 ›› 2025, Vol. 29 ›› Issue (11): 2377-2384.doi: 10.12307/2025.373
• 组织构建综述 tissue construction review • 上一篇 下一篇
运动疗法通过机械-化学偶联治疗慢性非特异性下背痛
张佳乐,王富森,邱镇锐,樊鑫铭,邹吉龙,毕郑刚,孙佳冰
- 哈尔滨医科大学附属第一医院骨科,黑龙江省哈尔滨市 150001
-
收稿日期:2024-04-10接受日期:2024-06-01出版日期:2025-04-18发布日期:2024-08-12 -
通讯作者:孙佳冰,主任医师,教授,博士生导师,哈尔滨医科大学附属第一医院骨科,黑龙江省哈尔滨市 150001 -
作者简介:张佳乐,男,1998年生,黑龙江省肇东市人,汉族,硕士,主要从事脊柱外科研究。 -
基金资助:2023年哈尔滨医科大学研究生科研和实践创新项目(YJSCX2023-209HYD),项目负责人:张佳乐,课题名称:计算机辅助工程技术在腰椎退行性疾病治疗中的应用
Exercise therapy for the treatment of chronic nonspecific lower back pain through mechanical-chemical coupling
Zhang Jiale, Wang Fusen, Qiu Zhenrui, Fan Xinming, Zou Jilong, Bi Zhenggang, Sun Jiabing
- Department of Orthopedics, The First Affiliated Hospital of Harbin Medical University, Harbin 150001, Heilongjiang Province, China
-
Received:2024-04-10Accepted:2024-06-01Online:2025-04-18Published:2024-08-12 -
Contact:Sun Jiabing, Chief physician, Professor, Doctoral supervisor, Department of Orthopedics, The First Affiliated Hospital of Harbin Medical University, Harbin 150001, Heilongjiang Province, China -
About author:Zhang Jiale, Master, Department of Orthopedics, The First Affiliated Hospital of Harbin Medical University, Harbin 150001, Heilongjiang Province, China -
Supported by:2023 Harbin Medical University Postgraduate Research and Practice Innovation Program, No. YJSCX2023-209HYD (to ZJL)
摘要:
文题释义:
运动疗法:通过某些运动方式使患者获得局部或全身运动功能、感觉功能恢复的训练方法。
慢性非特异性下背痛:腰痛持续 > 3个月且无特定的原因。
背景:目前运动疗法是非药物治疗腰痛的有效方法,运动疗法可通过骨骼和肌肉之间的机械-化学偶联维持腰椎的稳定,但目前尚无关于运动疗法通过机械-化学偶联缓解慢性非特异性下背痛之间研究进展及最佳治疗方案的明确阐述。
目的:综述运动疗法时椎旁肌通过机械-化学偶联影响腰椎稳定性进而缓解慢性非特异性下背痛的相关研究进展,以及目前运动疗法治疗慢性非特异性下背痛的最佳方案。
方法:在万方数据库、中国知网、维普、Web of Science和PubMed数据库进行文献检索,以“慢性非特异性下背痛,腰椎稳定,椎旁肌,运动疗法”为中文检索词,以“chronic nonspecific low back pain,lumbar stabilization,paravertebral muscle,exercise therapy”为英文检索词,检索各数据库建库至2024年1月发表的相关文献,最终纳入93篇文献进行归纳总结。
结果与结论:运动疗法可以通过适当的机械刺激作用于椎旁肌和骨骼并使其产生相应的变化。运动疗法主要通过机械-化学偶联方式来提高椎旁肌的质量,进而维持腰椎稳定,从而更好地缓解慢性非特异性下背痛,是慢性非特异性下背痛的重要干预措施。但是,对于运动疗法通过腰椎稳定来治疗慢性非特异性下背痛的确切有效方案尚无明确报道。个体化运动方案的制定对于慢性非特异性下背痛的治疗和预后尤为重要。同一个体的肌肉质量与骨骼质量是密切相关的,影像学评估椎旁肌的质量和体积对于疾病的发现和干预具有重要意义。
https://orcid.org/0009-0005-3561-6619(张佳乐)
中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:组织构建;骨细胞;软骨细胞;细胞培养;成纤维细胞;血管内皮细胞;骨质疏松;组织工程
中图分类号:
引用本文
张佳乐, 王富森, 邱镇锐, 樊鑫铭, 邹吉龙, 毕郑刚, 孙佳冰. 运动疗法通过机械-化学偶联治疗慢性非特异性下背痛[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2025, 29(11): 2377-2384.
Zhang Jiale, Wang Fusen, Qiu Zhenrui, Fan Xinming, Zou Jilong, Bi Zhenggang, Sun Jiabing. Exercise therapy for the treatment of chronic nonspecific lower back pain through mechanical-chemical coupling[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(11): 2377-2384.

2.2 椎旁肌与腰椎稳定性 腰椎的稳定往往与腰椎稳定系统中椎旁肌的质量相关,关于激活腰椎椎旁肌来维持腰椎的稳定,最早由约瑟夫·普拉提于1900年代初期提出,随着时代的发展,椎旁肌的作用也逐渐深入。激活椎旁核心肌能够增强老年人的肌肉力量[17]、降低跌倒风险[14],并且提高躯干和肢体的协调性[15],进而提高老年人的生活质量[16]。腰椎失稳通常是慢性非特异性下背痛发生的原因,因此,了解椎旁肌解剖结构与腰椎稳定性是治疗慢性非特异性下背痛的关键。
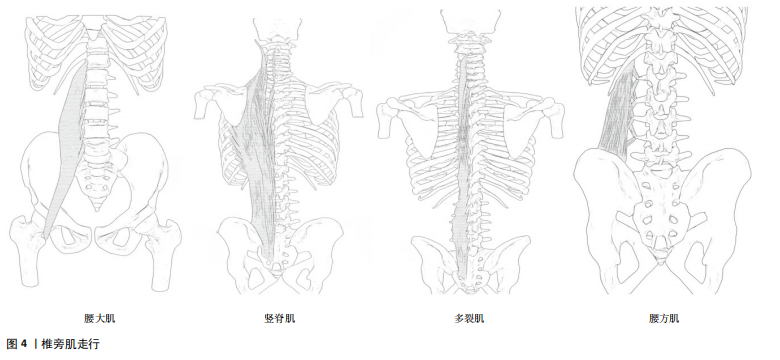
2.2.1 椎旁肌的解剖及作用 椎旁肌主要包括腰大肌、竖脊肌、多裂肌和腰方肌,如图4所示。椎旁肌的功能取决于其解剖结构,各椎旁肌之间相互协同发挥作用,共同维持腰椎的稳定。腰大肌是位于腰椎椎体两侧的长肌[18],其功能与躯干侧屈及前屈有关。在评估腰大肌的指标中,腰大肌横截面积可作为肌肉减少症的可靠指标之一[19],
腰大肌指数常被用来预测腰背部肌肉退行性变和骨密度[20-22]。竖脊肌位于脊柱的两侧[23],它与躯干侧屈和脊柱后伸密切相关,是维持脊柱稳定性及人体直立姿势的重要结构。多裂肌是唯一从腰骶部覆盖整条脊柱的位于脊柱最内侧的肌肉[24],是腰椎最强的稳定器[25]。腰方肌是一种位于腰部侧面的肌肉[26],具有伸展、侧屈躯干和稳定腰椎的作用[27]。
2.2.2 腰椎稳定性的概述 稳定的脊柱是保护椎管内神经结构、防止早期脊柱机械性恶化的基本要求[28],脊柱稳定性是指在静态和主动运动状态下脊柱保持相对中立位置的能力[28]。PANJABI[7]提出脊柱的稳定由被动支持系统、主动支持系统以及神经控制系统共同维持,其中被动支持系统由脊椎骨、韧带、椎间盘、筋膜等组成,主要提供内源性稳定;主动支持系统包括核心肌群与肌腱,主要提供外源性稳定;神经控制系统主要控制、协调主被动系统,以上任一系统受损均可导致脊柱失稳[7]。
腰椎的核心稳定性指肢体运动过程中保持稳定腰椎位置的能力[29]。维持腰椎的稳定除了需要骨性结构支撑,还需要主动系统中核心肌群的支持[30-31],椎旁肌主要通过抵抗静态和运动过程中腰椎的剪切力来维持腰椎的稳定,在主动系统维持腰椎稳定过程中起着至关重要的作用[32]。
2.3 椎旁肌的影像学评估 椎旁肌附着在脊柱上,可直接影响腰椎的稳定性,椎旁肌的体积和质量是评估肌肉力量和功能的重要因素。研究表明,计算机断层扫描(CT)可以通过定量测量椎旁肌的横截面积和脂肪浸润程度来评估椎旁肌的体积和质量[33],进而评估椎旁肌的力量和功能,从而评估腰椎的稳定性[34]。
2.3.1 椎旁肌的横截面积 椎旁肌体积常与肌肉减少症以及肌肉萎缩相关[34]。研究表明,椎旁肌体积在腰椎稳定方面与其横截面积呈正比[33],因此可应用CT水平位上的椎旁肌横截面积评估腰椎的稳定性。有学者发现,在L3
椎体层面的骨骼肌总面积与全身椎旁肌体积相关性最高,并且不受年龄、种族、性别、身高、体质量等影响[35],因此,在影像学中利用CT水平位L3水平椎旁肌横截面积对椎旁肌体积进行评估已经极为普遍[35-36]。
2.3.2 椎旁肌的脂肪浸润及功能性横截面积 椎旁肌质量通常与椎旁肌脂肪浸润相关[34]。椎旁肌脂肪浸润是指脂肪浸润椎旁肌的横截面积,在影像学中经脂肪浸润后肌肉密度减低表现为CT值衰减,因此可用CT水平位测量的肌肉密度来衡量双侧椎旁肌的脂肪浸润程度,其单位为Hounsfield(HU)值[37]。有学者认为脂肪浸润是肌肉萎缩的征兆,但研究发现脂肪取代肌肉后肌肉的横截面积不会受到显著影响[38]。因此,为降低肌肉脂肪变性对测量结果的影响,有学者提出功能性横截面积,功能性横截面积指不包括脂肪变性的肌肉横截面积。研究表明,腰椎骨密度与腰大肌和多裂肌的功能性横截面积相关性较强,而与竖脊肌的功能性横截面积相关性较弱[39],这可能与多裂肌独特的解剖结构有关。遗传学研究已证实,椎旁肌维生素D受体基因中FoKI的多态性与椎旁肌功能性横截面积有关[40]。因此,可以用椎旁肌功能性横截面积与脂肪浸润来评估椎旁肌的质量。
2.4 椎旁肌的质量和体积对腰椎稳定性的影响 椎旁肌为适应环境的变化会产生相应的改变来维持腰椎的稳定,腰椎稳定是保持人体正常生理活动所必须的。椎旁肌的质量和体积的改变可以导致许多疾病,例如唐氏综合征、腰椎滑脱、腰椎术后邻椎病、骨质疏松、腰椎间盘退行性变等,使腰椎失稳,进而引发腰痛。
2.4.1 椎旁肌与唐氏综合征患者的腰椎稳定相关 研究发现唐氏综合征患者的腰大肌和竖脊肌肌肉质量较正常人更好[41],但是绝大多数患者的多裂肌发生萎缩[42]。因为腰大肌和竖脊肌在维持腰椎前凸中发挥重要作用[43],所以唐氏综合征患者具有较大的腰椎前凸角,而较大的前凸角会使腰椎进行代偿性改变,这主要表现在L4椎体代偿性向前移动,使腰椎失稳产生滑脱[44]。然而有学者发现,在腰椎滑脱患者中患有唐氏综合征的腰椎滑脱程度较轻[41],这可能因为腰大肌和竖脊肌肌肉质量足以代偿多裂肌萎缩所带来的影响,进而增强了脊柱的稳定性。
2.4.2 椎旁肌与腰椎滑脱相关 腰椎滑脱的主要原因之一是椎旁肌的脂肪浸润[45]。研究表明,椎旁肌脂肪浸润的病理机制可能是腰椎稳定性降低导致椎旁肌内部机械刺激丢失,使Wnt通路抑制脂肪的作用降低,椎旁肌脂肪生成增多,此时腰大肌中脂肪生成性启动子高表达,使脂肪进一步沉积[46]。椎旁肌经脂肪浸润后功能性横截面积减少、肌肉力量下降,进而脊柱的稳定性下降导致腰椎滑脱[47]。
2.4.3 椎旁肌与邻椎病相关 椎旁肌是腰椎融合术后预防邻椎病发生的重要结构[48],可以为融合部位提供充足的血运,从而加速骨融合[49]。腰椎融合术后邻椎病的发生与下腰段多裂肌横截面积、脂肪浸润和骨密度密切相关,术前椎旁肌横截面积较小是融合术后发生邻椎病的危险因素[48],更进一步的研究发现,L3-L4水平上多裂肌横截面积小、L4-L5和L5-S1水平多裂肌脂肪浸润程度高以及骨密度低是腰椎融合术后邻椎病的重要危险因素[50-51]。
2.4.4 骨质疏松与椎旁肌的关系 骨质疏松与椎旁肌质量存在一定的相关性[39,52]。在骨质疏松进展过程中,骨细胞数量减少,其分泌的胰岛素样生长因子1减少[53],相应的胰岛素样生长因子1/磷脂酰肌醇3-激酶/蛋白激酶B通路活性下调[54],导致椎旁肌中Ⅰ型和Ⅱ型肌纤维萎缩,但Ⅱ型肌纤维萎缩更为明显。萎缩的椎旁肌纤维使椎旁肌质量降低[54]。也有研究表明,骨密度与椎旁肌的脂肪浸润之间存在显著的相关性[55-56]。因此,骨质疏松可导致椎旁肌萎缩和脂肪浸润增加,进而影响腰椎的稳定。
2.4.5 腰椎间盘退行性变与椎旁肌相关 腰椎间盘退行性变的常见症状为腰痛[57],腰痛常常与椎旁肌的脂肪浸润相关[58],那么腰椎间盘退行性变与椎旁肌的脂肪浸润是否存在相关性呢?对此,有学者进一步研究发现,腰椎退行性变后产生炎症反应使椎旁肌重塑,椎旁肌中炎症递质失调和炎性细胞因子参与椎旁肌的脂肪浸润[59],因此,腰椎间盘退行性变与椎旁肌脂肪浸润之间存在一定的相关性[60]。有学者研究发现,腰椎间盘退行性变程度与多裂肌脂肪浸润程度呈正相关,比腰椎间盘退行性变程度与竖脊肌和腰大肌脂肪浸润程度的相关性更高[61]。也有学者认为腰椎间盘退行性变时脊柱损伤信号会抑制神经肌肉控制系统,即相应的神经支配减少[62],椎旁肌的神经支配减少会导致椎旁肌功能性横截面积减少和椎旁肌脂肪浸润增多,此时椎旁肌的内分泌功能减弱[63]。椎旁肌的这种病理改变增加了间盘、韧带及小关节的压力,使腰椎退行性变进一步加重[64],从而影响脊柱的运动和稳定性。
腰椎稳定的目的是适应机体和环境的需要,这种适应表现为椎旁肌和骨骼应对机械刺激时保持的动态平衡。在脊柱稳定系统中,适当的机械刺激可以促进骨骼和肌肉的再生和修复。当机体受到机械刺激时,物理信号会转化为生化信号促进肌肉和骨骼适应性重塑,当刺激趋于稳定时,适应性重塑也会达到新的稳定状态来维持脊柱的稳定[65]。相反,当机械刺激减少时会导致肌肉萎缩和骨质流失,进而导致腰椎的稳定性降低,因此持续适当的机械刺激是维持脊柱稳定的驱动因素。
2.5 机械-化学偶联是椎旁肌和骨骼之间的桥梁 适当的机械刺激在促进椎旁肌增加肌肉质量和体积的同时也增强骨质,使椎旁肌和骨骼共同维持腰椎的稳定[9]。椎旁肌作为强大的成骨刺激器可分泌肌因子促进成骨,骨骼通过分泌骨因子也可促进肌肉的生成和修复[66]。目前认为椎旁肌和骨骼通过物理力(机械刺激)与它们分泌的骨因子以及肌因子(化学刺激)之间相互作用,即机械-化学偶联[65,67],最终使组织和个体产生适应性变化,进而提高肌肉质量和抗骨折能力,从而增强脊柱的稳定性。
研究表明,适当的机械振动对于维持肌肉质量和提高骨量具有一定意义[9]。机械刺激信号可以促进肌肉形变和骨小管网络中的液体流动来刺激骨骼和肌肉[68],相应受体接收到机械刺激后通过一系列黏附分子在细胞间传递信息,接收到信息的细胞通过处理DNA调节元件、适应性转录和翻译来增多细胞分泌蛋白和细胞骨架蛋白,从而促使细胞骨架变硬。细胞的这种改变在椎旁肌和骨骼上表现为肌肉质量和骨质的增加,为持续应对机械刺激做准备。机械刺激也可以传至核膜和核孔结构,使分子进出细胞核发生变化,甚至核内染色体也会出现富集及结构的改变[69]。骨细胞经机械刺激后分泌的NO和前列腺素2对成骨细胞成骨有促进作用,从而预防骨质疏松[70]。因此,适当的机械刺激可以改善肌肉质量和预防骨质疏松。
腰椎的骨骼为椎旁肌提供附着点,椎旁肌为腰椎提供稳定性,骨骼和椎旁肌之间一直以来被认为是机械偶联的关系[9],进一步的研究发现二者间也有化学偶联的关系[11,71],但新的研究发现这二者之间还可以通过机械-化学偶联相互作用[10]。近年来肌肉和骨骼被命名为“内分泌器官”,肌肉分泌的产物被称为肌因子[11]。肌肉分泌的生长因子如碱性成纤维细胞生长因子2、胰岛素样生长因子1对骨骼的形成及重塑具有一定作用[72]。碱性成纤维细胞生长因子2可通过抑制骨骼和肌肉中生长抑素和硬化蛋白的表达对骨骼和肌肉进行调控[73]。运动后肌肉胰岛素样生长因子1 mRNA迅速升高,外周血胰岛素样生长因子1蛋白于24 h后显著增高[74],从而调节骨骼的代谢。骨骼的产物被称为骨因子[11],骨特异性分泌产物也可以影响肌肉量、肌肉的生成与再生,由骨细胞产生的硬化蛋白和Dickkopf相关蛋白1作为成骨性Wnt信号传导抑制剂在促进骨代谢的同时还可以下调椎旁肌质量[71]。研究表明,适当的机械刺激可以下调血清中硬化蛋白和Dickkopf相关蛋白1的水平[10],进一步验证了适当的机械刺激与骨代谢抑制以及肌肉质量增加具有一定的相关性。当骨骼和肌肉细胞受到机械刺激后钙离子内流,诱导含有肌因子和骨因子的囊泡释放[75],肌因子与骨因子以此参与运动和损伤后的肌肉和骨组织再生[76-77]。因此,腰椎的骨骼和椎旁肌之间通过机械-化学偶联方式调节肌肉质量和抗骨折能力,进而增强腰椎的稳定性。
骨骼与椎旁肌可以通过机械-化学偶联的机制相互作用,椎旁肌的肌肉细胞经机械刺激后分泌的胰岛素样生长因子1、碱性成纤维细胞生长因子2对骨骼的形成及重塑具有一定作用,椎旁肌引起的机械张力也会启动成骨活动,骨细胞会对机械刺激作出反应[78]。由骨细胞产生的物质,如硬化蛋白和Dickkopf相关蛋白1在调控骨代谢的同时也调节椎旁肌质量,骨钙素也对椎旁肌的肌肉数量有直接影响[79]。因此,不同个体椎旁肌的质量差异会导致骨骼质量和形状差异,不同个体的骨骼质量也会导致椎旁肌体积和质量的差异[80]。
2.6 运动疗法维持腰椎稳定缓解腰痛 目前的研究已经证实,椎旁肌与骨骼之间是通过机械-化学偶联相互作用来维持腰椎的稳定性[10]。腰椎失稳后椎间盘、韧带及小关节受到的机械刺激进一步增大,椎旁肌和骨骼产生适应性改变以应对这种变化,这种适应性改变会使腰椎病变进一步加重,腰椎稳定性也会随之下降[64]。若不加干预如此循环将会导致疾病进展加快,腰痛症状更加明显。因此,及时对疾病进行干预和治疗不仅有利于维持腰椎的稳定性,而且有利于缓解腰痛症状,甚至是改善患者的预后。
积极运动是干预和治疗腰痛的最常见方法之一[81]。研究发现,通过对核心肌肉进行训练可以刺激椎旁肌进而增加肌肉的质量和体积[82],椎旁肌的质量和体积决定其肌肉力量和抗疲劳程度,当减少对核心肌肉的机械刺激时,肌肉的力量和抗疲劳程度降低,相应的椎旁肌神经激活降低[83],从而降低腰椎的稳定性。当肌肉持续受到超负荷的机械刺激时,肌肉的疲劳程度增加,椎旁肌的质量和体积降低,进而降低腰椎稳定性[84]。因此,对椎旁肌进行适当的机械刺激(即运动疗法)对于维持腰椎的稳定性、缓解腰痛具有重要临床治疗意义。
运动疗法在循证医学上被认为是慢性非特异性下背痛的重要干预措施[13],其主要目的是恢复和增强椎旁肌质量,进而改善椎旁肌维持腰椎的稳定。与非运动疗法相比,运动疗法可更好地缓解慢性非特异性下背痛[12],在慢性非特异性下背痛发生的早期,进行运动疗法不仅可以减轻疼痛、降低致残的概率[85],而且可以更快地恢复腰椎的稳定,从而改善患者生活质量[86]。但是对于运动疗法的最佳运动方案尚无明确阐述。
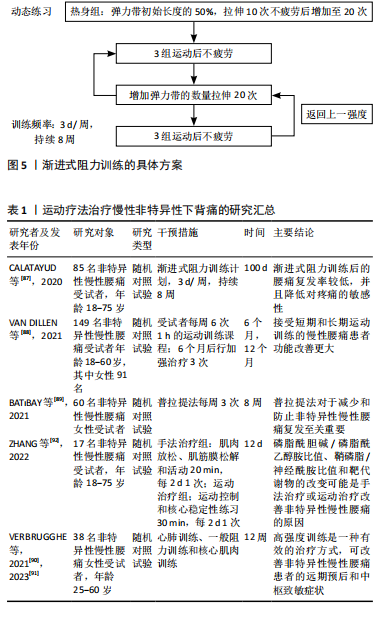
近年来对运动疗法最佳运动方案的研究较多,如表1。CALATAYUD等[87]通过核心肌肉动态训练和平板支撑来研究渐进式阻力训练对疼痛复发和身体功能的有效性,渐进式阻力训练的具体方案见图5,此方案考虑到了个体化的差异,结果显示经过渐进式阻力训练的患者慢性非特异性下背痛加重和复发率较低,并且可降低疼痛的敏感度。VAN DILLEN等[88]同样认为运动疗法应根据个体差异进行调整,个体化运动疗法可在短期和长期带来更好的预后。BAT?BAY等[89]发现应用Pilates法(3次/周、持续8周)治疗慢性腰痛可减少慢性腰痛的复发,能够增加核心肌肉的活动,增强肌肉质量并维持腰椎稳定[90]。VERBRUGGHE等[90]认为运动疗法中的高强度训练可以在降低致残率的同时改善慢性非特异性下背痛患者的中枢性致敏症状[91],高强度训练包括心肺训练、一般阻力训练和核心肌肉训练,具体方案见表2,同样是根据个人体质不同来制定相应的运动治疗方案。运动疗法治疗和改善慢性非特异性下背痛患者预后的机制不仅限于改善椎旁肌的稳定性,其机制也与脂质组学、代谢组学机制有关。ZHANG等[92]发现经运动疗法治疗后,慢性非特异性下背痛患者磷脂酰胆碱/磷脂酰乙醇胺(PC/PE)比值降低、鞘磷脂/神经酰胺(SM/Cer)比值升高。PC/PE的比值降低可显著抑制炎症反应,同时SM/Cer比值升高可通过抑制蛋白激酶C参与炎症反应的相关通路,使腰痛得到缓解[93]。这一发现从脂质组学和代谢组学上揭示了运动疗法治疗慢性非特异性下背痛的机制。以上提出的运动方案都是根据患者自身所能耐受的最大运动量来对慢性非特异性下背痛进行治疗,表明个体化的治疗方案对于慢性非特异性下背痛的治疗和预后是尤为重要的。
综上所述,腰椎稳定是保持人体正常生理活动所必须的。各个椎旁肌相互作用共同为腰椎的稳定提供外源性支持,椎旁肌质量和体积的改变可使腰椎失稳。慢性非特异性下背痛的非药物治疗首选运动疗法,适当机械刺激经机械-化学偶联方式改善腰椎椎旁肌和骨骼的质量使腰椎稳定,从而达到缓解慢性非特异性下背痛的目的。

| [1] BALAGUÉ F, MANNION AF, PELLISÉ F, et al. Non-specific low back pain. Lancet. 2012;379(9814):482-491. [2] HOY D, MARCH L, BROOKS P, et al. The global burden of low back pain: estimates from the global burden of disease 2010 study. Ann Rheum Dis. 2014;73:968-974. [3] NIU S, YANG H, GAO J, et al. Correlation between sagittal parameters and disability of patients with nonspecific chronic low back pain: a cross-sectional study of 435 subjects. Spine J. 2024;24(4):634-643. [4] MALFLIET A, ICKMANS K, HUYSMANS E, et al. Best evidence rehabilitation for chronic pain part 3: low Back pain. J Clin Med. 2019; 8(7):1063. [5] National Research Council (US) and Institute of Medicine (US) Panel on Musculoskeletal Disorders and the Workplace. Musculoskeletal Disorders and the Workplace: Low Back and Upper Extremities. Washington (DC): National Academies Press (US);2001. [6] PANJABI MM. Panjabi-1992-the stabilizing system of the spine. Part II. Neutral zone and instability hypothesis. J Spinal Disord. 1992;5:390-396. discussion: 397. [7] PANJABI MM. The stabilizing system of the spine. Part I. Function, dysfunction, adaptation, and enhancement. J Spinal Disord. 1992;5(4): 383-389. [8] CHOLEWICKI J, MCGILL SM. Mechanical stability of the in vivo lumbar spine: implications for injury and chronic low back pain. Clin Biomech (Bristol, Avon). 1996;11(1):1-15. [9] STOLZENBERG N, BELAVY D L, RAWER R, et al. Whole-body vibration versus proprioceptive training on postural control in post-menopausal osteopenic women. Gait Posture. 2013;38:416-420. [10] PICKE AK, SYLOW L, MØLLER LLV, et al. Differential effects of high-fat diet and exercise training on bone and energy metabolism. Bone. 2018;116:120-134. [11] BONEWALD LF. Use it or lose it to age: A review of bone and muscle communication. Bone. 2019;120:212-218. [12] SEARLE A, SPINK M, HO A, et al. Exercise interventions for the treatment of chronic low back pain: a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomised controlled trials. Clin Rehabil. 2015;29(12):1155-1167. [13] HRKAĆ A, BILIĆ D, ČERNY-OBRDALJ E, et al. Comparison of supervised exercise therapy with or without biopsychosocial approach for chronic nonspecific low back pain: a randomized controlled trial. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2022;23(1):966. [14] BARKER AL, TALEVSKI J, BOHENSKY MA, et al. Feasibility of Pilates exercise to decrease falls risk: A pilot randomized controlled trial in community-dwelling older people. Clin Rehabil. 2016;30:984-996. [15] SOFIANIDIS G, DIMITRIOU AM, HATZITAKI V. A comparative study of the effects of pilates and Latin dance on static and dynamic balance in older adults. J Aging Phys Act. 2017;25:412-419. [16] LIPOSCKI DB, DA SILVA NAGATA IF, SILVANO GA, et al. Influence of a Pilates exercise program on the quality of life of sedentary elderly people: A randomized clinical trial. J Bodyw Mov Ther. 2019;23:390-393. [17] LIMA M, SILVA B, ROCHA-RODRIGUES S, et al. The impact of an 8-week Pilates-based physical training program on functional mobility: Data from a septuagenarian group. Biomed Hum Kinet. 2021;13:11-19. [18] LIFSHITZ L, BAR SELA S, GAL N, et al. Iliopsoas the Hidden Muscle: Anatomy, Diagnosis, and Treatment. Curr Sports Med Rep. 2020;19(6): 235-243. [19] CAWTHON PM. Assessment of lean mass and physical performance in sarcopenia. J Clin Densitom. 2015;18:467-471. [20] KAJIKI Y, TSUJI H, MISAWA H, et al. Psoas muscle index predicts osteoporosis and fracture risk in individuals with degenerative spinal disease. Nutrition. 2022;93:111428. [21] KURUMISAWA S, KAWAHITO K. The psoas muscle index as a predictor of long-term survival after cardiac surgery for hemodialysis-dependent patients. J Artif Organs. 2019;22:214-221. [22] LEE D, KANG M. Correlation between psoas muscle index and degeneration of spinal back muscle in patients with back pain. Healthcare. 2021;9:1189. [23] BUSTAMI FM. A new description of the lumbar erector spinae muscle in man. J Anat. 1986;144:81-91. [24] MACINTOSH JE, VALENCIA F, BOGDUK N, et al. The morphology of the human lumbar multifidus. Clin Biomechan. 1986;1(4):196-204. [25] KIM CW, GOTTSCHALK LJ, ENG C, et al. The multifidus muscle is the strongest stabilizer of the lumbar spine. Spine J. 2007;7:76S. [26] GRZONKOWSKA M, BAUMGART M, BADURA M, et al. Quantitative anatomy of the growing quadratus lumborum in the human foetus. Surg Radiol Anat. 2018;40(1):91-98. [27] BORDONI B, VARACALLO M. Anatomy, Abdomen and Pelvis, Quadratus Lumborum. 2023 Jul 17. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2024. [28] IZZO R, GUARIERI G, GUGLIELMI G, et al. Biomechanics of the spine. Part I: spinal stability. Eur J Radiol. 2013;82(1):118-126. [29] VASSELEN O, UNSGAARD-TONDEL M, WESTAD C, et al. Effect of core stability exercises on feed-forward activation of deep abdominal muscles in chronic low back pain: a randomized controlled trial. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2012;37(13):1101-1108. [30] HEBERT JJ, KOPPENHAVER SL, MAGEL JS, et al. The relationship of transversus abdominis and lumbar multifidus activation and prognostic factors for clinical success with a stabilization exercise program: a cross-sectional study. Arch Phys Med Rehabil. 2010;91(1):78-85. [31] HODGES PW, GANDEVIA SC. Changes in intra-abdominal pressure during postural and respiratory activation of the human diaphragm. J App1 Physiol (1985). 2000;89(3):967-976. [32] WONG C. Mechanism of right thoracic adolescent idiopathic scoliosis at risk for progression; a unifying pathway of development by normal growth and imbalance. Scoliosis. 2015;10:2. [33] BECKER L, LI Z, WANG Z, et al. Adolescent idiopathic scoliosis is associated with muscle area asymmetries in the lumbar spine. Eur Spine J. 2023;32(11):3979-3986. [34] AMINI B, BOYLE SP, BOUTIN RD, et al. Approaches to Assessment of Muscle Mass and Myosteatosis on Computed Tomography: A Systematic Review. J Gerontol A Biol Sci Med Sci. 2019;74(10):1671-1678. [35] EBADI M, WANG CW, LAI JC, et al. From the Fitness, Life Enhancement, and Exercise in Liver Transplantation (FLEXIT) Consortium. Poor performance of psoas muscle index for identification of patients with higher waitlist mortality risk in cirrhosis. J Cachexia Sarcopenia Muscle. 2018;9(6):1053-1062. [36] DERSTINE BA, HOLCOMBE SA, GOULSON RL, et al. Quantifying sarcopenia reference values using lumbar and thoracic muscle areas in a healthy population. J Nutr Health Aging. 2017;21(10):180-185. [37] YAJIMA T, ARAO M, YAJIMA K. Psoas muscle index and psoas muscle density as predictors of mortality in patients undergoing hemodialysis. Sci Rep. 2022;12(1):10496. [38] TEICHTAHL AJ, URQUHART DM, WANG Y, et al. Fat infiltration of paraspinal muscles is associated with low back pain, disability, and structural abnormalities in community-based adults. Spine J. 2015;15: 1593-1601. [39] KIM M, CHON J, LEE SA, et al. Does Unilateral Lumbosacral Radiculopathy Affect the Association between Lumbar Spinal Muscle Morphometry and Bone Mineral Density? Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2021;18(24):13155. [40] KAWAO N, KAJI H. Interactions between muscle tissues and bone metabolism. J Cell Biochem. 2015;116:687-695. [41] OHYAMA S, AOKI Y, INOUE M, et al. The Quantity and Quality of Lumbar Muscles and Lumbopelvic Parameters in Patients With Degenerative Spondylolisthesis. Cureus. 2021;13(10):e18428. [42] WANG G, KARKI SB, XU S, et al. Quantitative MRI and X-ray analysis of disc degeneration and paraspinal muscle changes in degenerative spondylolisthesis. J Back Musculoskelet Rehabil. 2015;28:277-285. [43] XIA W, FU H, ZHU Z, et al. Association between back muscle degeneration and spinal-pelvic parameters in patients with degenerative spinal kyphosis. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2019;20:454. [44] SCHULLER S, CHARLES YP, STEIB JP. Sagittal spinopelvic alignment and body mass index in patients with degenerative spondylolisthesis. Eur Spine J. 2011;20:713-719. [45] GARCÍA-RAMOS CL, VALENZUELA-GONZÁLEZ J, BAEZA-ÁLVAREZ VB, et al. Lumbar degenerative spondylolisthesis II: treatment and controversies. Acta Ortop Mex. 2020;34(6):433-440. [46] CAO B, ZUO Y, XU Y, et al. Correlation between fat infiltration of paraspinal muscle and L4 degenerative lumbar spondylolisthesis in asymptomatic adults. Asian J Surg. 2023;46(2):834-840. [47] ZUO YQ, GAO ZH, WANG Z, et al. Utility of multidetector computed tomography quantitative measurements in identifying sarcopenia: a propensity score matched study. Skeletal Radiol. 2022;51(6):1303-1312. [48] CHANG MY, PARK Y, HA JW, et al. Paraspinal lean muscle mass measurement using spine MRI as a predictor of adjacent segment disease after lumbar fusion: a propensity score-matched case-control analysis. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2019;212(6):1310-1317. [49] BAWA M, SCHIMIZZI AL, LEEK B, et al. Paraspinal muscle vasculature contributes to posterolateral spinal fusion. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2006; 31:891-896. [50] GONG Z, LI D, ZOU F, et al. Low lumbar multifidus muscle status and bone mineral density are important risk factors for adjacent segment disease after lumbar fusion: a case-control study. J Orthop Surg Res. 2022;17(1):490. [51] CHEN M, ZHANG P, LAI J, et al. A correlation study of preoperative lumbar paraspinal muscle quality and L5-S1 lumbar foraminal stenosis degeneration after L4-5 TLIF. J Orthop Surg Res. 2023;18(1):731. [52] KHALID SI, NUNNA RS, MAASARANI S, et al. Association of Osteopenia and Osteoporosis with Higher Rates of Pseudarthrosis and Revision Surgery in Adult Patients Undergoing Single-Level Lumbar Fusion. Neurosurg. Focus. 2020;49:1-7. [53] TAGLIAFERRI C, WITTRANT Y, DAVICCO MJ, et al. Muscle and bone, two interconnected tissues. Ageing Res Rev. 2015;21:55-70. [54] TERRACCIANO C, CELI M, LECCE D, et al. Differential features of muscle fiber atrophy in osteoporosis and osteoarthritis. Osteoporos. Int. 2013; 24:1095-1100. [55] JEON I, KIM S W, YU D. Paraspinal muscle fatty degeneration as a predictor of progressive vertebral collapse in osteoporotic vertebral compression fractures. Spine J. 2022;22(2):313-320. [56] LI X, ZHANG Y, XIE Y, et al. Correlation Between Bone Mineral Density (BMD) and Paraspinal Muscle Fat Infiltration Based on QCT: A Cross-Sectional Study. Calcif Tissue Int. 2022;110(6):666-673. [57] KOS N, GRADISNIK L, VELNAR T. A brief review of the degenerative intervertebral disc disease. Med Arch. 2019;73(6):421-424. [58] OZCAN-EKSI EE, EKSI MS, TURGUT VU, et al. Reciprocal relationship between multifidus and psoas at L4–L5 level in women with low back pain. Br J Neurosurg. 2021;35(2):220-228. [59] HODGES PW, JAMES G, BLOMSTER L, et al. Can proinflammatory cytokine gene expression explain multifidus muscle fiber changes after an intervertebral disc lesion? Spine (Phila Pa 1976) 2014;39(13):1010-1017. [60] SUN D, LIU P, CHENG J, et al. Correlation between intervertebral disc degeneration, paraspinal muscle atrophy, and lumbar facet joints degeneration in patients with lumbar disc herniation. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2017;18(1):167. [61] SHI L, YAN B, JIAO Y, et al. Correlation between the fatty infiltration of paraspinal muscles and disc degeneration and the underlying mechanism. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2022;23(1):509. [62] RUSSO M, DECKERS K, ELDABE S, et al. Muscle Control and Non-specific Chronic Low Back Pain. Neuromodulation. 2018;21(1):1-9. [63] HAMRICK MW, MCGEE-LAWRENCE ME, FRECHETTE DM. Fatty Infiltration of Skeletal Muscle: Mechanisms and Comparisons with Bone Marrow Adiposity. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2016;7:69. [64] KIRKALDY-WILLIS WH, WEDGE JH, YONG-HING K, et al. Pathology and pathogenesis of lumbar spondylosis and stenosis. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 1978;3(4):319-328. [65] HERRMANN M, ENGELKE K, EBERT R, et al. Interactions between Muscle and Bone-Where Physics Meets Biology. Biomolecules. 2020; 10(3):432. [66] LAURITZEN HPMM, BRANDAUER J, SCHJERLING P, et al. Contraction and AICAR StimulateIL-6 Vesicle Depletion From Skeletal Muscle Fibers In Vivo. Diabetes. 2013;62:3081-3092. [67] MIKOLAJEWICZ N, SEHAYEK S, WISEMAN PW, et al. Transmission of Mechanical Information by Purinergic Signaling. Biophys J. 2019;116: 2009-2022. [68] NACHURY MV, MICK D. Establishing and regulating the composition of cilia for signal transduction. Nat Rev Mol Cell Boil. 2019;20:389-405. [69] DONNALOJA F, JACCHETTI E, SONCINI M, et al. Mechanosensing at the Nuclear Envelope by Nuclear Pore Complex Stretch Activation and Its Effect in Physiology and Pathology. Front Physiol. 2019;10:896. [70] ROCHEFORT GY, PALLU S, BENHAMOU CL. Osteocyte: the unrecognized side of bone tissue. Osteoporos Int. 2010;21:1457-1469. [71] KIM JA, ROH E, HONG SH, et al. Association of serum sclerostin levels with low skeletal muscle mass: The Korean Sarcopenic Obesity Study (KSOS). Bone. 2019;128:115053. [72] YAKAR S, ROSEN CJ, BEAMER WG, et al. Circulating levels of IGF-1 directly regulate bone growth and density. J Clin Invest. 2002;110(6): 771-781. [73] ADHIKARY S, CHOUDHARY D, TRIPATHI AK, et al. FGF-2 targets sclerostin in bone and myostatin in skeletal muscle to mitigate the deleterious effects of glucocorticoid on musculoskeletal degradation. Life Sci. 2019; 229:261-276. [74] ANNIBALINI G, CONTARELLI S, LUCERTINI F, et al. Muscle and Systemic Molecular Responses to a Single Flywheel Based Iso-Inertial Training Session in Resistance-Trained Men. Front. Physiol. 2019;10:554. [75] MORRELL AE, BROWN GN, ROBINSON ST, et al. Mechanically induced Ca2+ oscillations in osteocytes release extracellular vesicles and enhance bone formation. Bone Res.2018;6:6. [76] BITTEL DC, JAISWAL JK. Contribution of Extracellular Vesicles in Rebuilding Injured Muscles. Front Physiol. 2019;10:828. [77] MURRAY LM, KRASNODEMBSKAYA A. Concise Review: Intercellular Communication Via Organelle Transfer in the Biology and Therapeutic Applications of Stem Cells. Stem Cells. 2018;37:14-25. [78] LI J, WANG Y, ZHANG X, et al. Associations of muscle size and fatty infiltration with bone mineral density of the proximal femur bone. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2022;13:990487. [79] FERNANDEZ-REAL JM, IZQUIERDO M, ORTEGA F, et al. The relationship of serum osteocalcin concentration to insulin secretion, sensitivity, and disposal with hypocaloric diet and resistance training. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2009;94(1):237-245. [80] GIRGIS CM, MOKBEL N, DIGIROLAMO DJ. Therapies for musculoskeletal disease: can we treat two birds with one stone? Curr Osteoporos Rep. 2014;12(2):142-153. [81] AIRAKSINEN O, BROX JI, CEDRASCHI C, et al. Chapter 4. European guidelines for the management of chronic nonspecific low back pain. Eur Spine J. 2006;15(Suppl. 2):S192-S300. [82] WANG XQ, ZHENG JJ, YU ZW, et al. A meta-analysis of core stability exercise versus general exercise for chronic low back pain. PLoS One. 2012;7:e52082. [83] BOGDANIS GC. Effects of physical activity and inactivity on muscle fatigue. Front Physiol.2012;3:142. [84] KRAVITZ E, MOORE ME, GLAROS A. Paralumbar muscle activity in chronic low back pain. Arch Phys Med Rehabil. 1981;62(4):172-176. [85] HAYDEN JA, ELLIS J, OGILVIE R, et al. Exercise therapy for chronic low back pain. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2021;9(9):CD009790. [86] OWEN PJ, MILLER CT, MUNDELL NL, et al. Which specific modes of exercise training are most effective for treating low back pain? Network meta-analysis. Br J Sports Med. 2020;54(21):1279-1287. [87] CALATAYUD J, GUZMÁN-GONZÁLEZ B, ANDERSEN LL, et al. Effectiveness of a Group-Based Progressive Strength Training in Primary Care to Improve the Recurrence of Low Back Pain Exacerbations and Function: A Randomised Trial. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2020;17(22):8326 [88] VAN DILLEN LR, LANIER VM, STEGER-MAY K, et al. Effect of Motor Skill Training in Functional Activities vs Strength and Flexibility Exercise on Function in People With Chronic Low Back Pain: A Randomized Clinical Trial. JAMA Neurol. 2021;78(4):385-395. [89] BATıBAY S, KÜLCÜ DG, KALEOĞLU Ö, et al. Effect of Pilates mat exercise and home exercise programs on pain, functional level, and core muscle thickness in women with chronic low back pain. J Orthop Sci. 2021;26(6):979-985. [90] VERBRUGGHE J, HANSEN D, DEMOULIN C, et al. High Intensity Training Is an Effective Modality to Improve Long-Term Disability and Exercise Capacity in Chronic Nonspecific Low Back Pain: A Randomized Controlled Trial. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2021;18(20):10779. [91] VERBRUGGHE J, AGTEN A, STEVENS S, et al. High intensity training improves symptoms of central sensitization at six-month follow-up in persons with chronic nonspecific low back pain: Secondary analysis of a randomized controlled trial. Braz J Phys Ther. 2023;27(2):100496. [92] ZHANG Z, ZHANG C, LI Y, et al. Lipid and metabolic alteration involvement in physiotherapy for chronic nonspecific low back pain. Lipids Health Dis. 2022;21(1):125. [93] PANG Z, ZHOU G, EWALD J, et al. Using MetaboAnalyst 5.0 for LC-HRMS spectra processing, multi-omics integration and covariate adjustment of global metabolomics data. Nat Protoc. 2022;17(8):1735-1761. |
| [1] | 王 娟, 王广兰, 左会武. 运动疗法对前交叉韧带重建后康复疗效影响的网状Meta分析[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2025, 29(8): 1714-1726. |
| [2] | 朱传喜, 邱 龙, 李凌絮, 汲广成 . 中药结合头针运动疗法改善缺血性脑卒中大鼠肢体痉挛[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2025, 29(35): 7571-7577. |
| [3] | 吴 悦, 任 爽, 黄红拾, 代瑞兰, 敖英芳, 苟 波. 运动疗法激活臀肌改善青年男性膝前痛患者的下肢肌力[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2025, 29(18): 3798-3803. |
| [4] | 梁佳佳, 孙姣姣, 刘文洁, 邢 政, 李 奇, 李庆雯, 褚晓蕾. 肌电生物反馈疗法与脊髓损伤患者运动功能的恢复[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2025, 29(14): 3002-3010. |
| [5] | 吴 菁, 姚英策, 杨晓巍, 薛博士, 赵建斌, 杨 辰, 栾天峰, 周志鹏. 肌力训练与神经肌肉电刺激干预髌股关节痛患者下肢功能和生物力学的变化[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2024, 28(9): 1365-1371. |
| [6] | 张锦璞, 王军利, 张思奇, 陈家豪, 杨秋实. 运动干预纤维肌痛综合征有效性的Meta分析[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2024, 28(32): 5210-5216. |
| [7] | 李 超, 张佩佩, 徐朦婷, 李琳琳, 丁江涛, 刘西花, 毕鸿雁. 肌骨超声评价呼吸训练改善慢性非特异性下背痛患者多裂肌的形态学改变[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2023, 27(9): 1417-1421. |
| [8] | 周劲衍, 钟远鸣, 李智斐, 许 伟, 张家立, 梁梓扬. 压力生物反馈训练治疗颈椎病[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2023, 27(31): 5052-5057. |
| [9] | 孙晓蕾, 张晓辉, 林佳声, 廖八根. 器具辅助松解结合特定运动治疗RigoA型脊柱侧凸:改善躯干旋转角及减轻背部疼痛[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2023, 27(18): 2871-2877. |
| [10] | 宋校能, 胡玲慧, 黄德胜, 周绪昌, 吴 伟. 运动防治膝骨关节炎的关键因素及注意事项[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2020, 24(2): 289-295. |
| [11] | 刘 辉, 刘 波, 张 鑫, 赵卫侠, 严 攀, 敬竹子, 梁俊豪, 沈 海. 开链和闭链训练治疗膝关节半月板损伤[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2020, 24(11): 1733-1737. |
| [12] | 甘东浩,乔全来,陈德强,谭国庆,薛海鹏,徐展望. Waveflex半刚性内固定治疗腰椎间盘突出症的生物力学优势[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2019, 23(36): 5830-5835. |
| [13] | 马钧峰,汪 伟,王紫括,江泽华,龙明星,袁建军,朱如森,胡 炜,张学利. 腰椎MRI评价椎间小关节积液与退变性腰椎滑脱稳定性的相关性[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2019, 23(24): 3845-3851. |
| [14] | 姜 勇,郑益丽,徐盛嘉. 生物力学背景下物理疗法的研究与进展[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2019, 23(12): 1936-1942. |
| [15] | 刘 潇,刘耀升,刘蜀彬. 有限元法分析腰椎融合与非融合后的应力分布[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2018, 22(3): 409-414. |
一直以来椎旁肌和骨骼之间被认为是机械偶联的关系[9],但新的研究发现,骨骼和椎旁肌之间还可以通过机械-化学偶联的方式相互作用[10]。经研究发现,椎旁肌和骨骼经机械刺激后会像内分泌器官一样分泌化学物质来调节骨骼和肌肉的代谢、生成和修复[11],但是,目前尚无椎旁肌通过机械-化学偶联与骨骼相互作用来维持腰椎稳定性进而缓解腰痛的明确阐述。
运动疗法可以通过适当的机械刺激作用于椎旁肌和骨骼并使其产生相应的变化。运动疗法主要通过机械-化学偶联的方式来提高椎旁肌的质量,进而维持腰椎稳定,从而更好地缓解慢性非特异性下背痛[12],是慢性非特异性下背痛的重要干预措施[13],但目前运动疗法的具体方案尚无明确的阐述。因此,该文就运动疗法通过机械-化学偶联来影响腰椎稳定性进而影响慢性非特异性下背痛的相关研究进展,以及目前运动疗法治疗慢性非特异性下背痛的最佳方案进行综述,为后续进一步探索慢性非特异性下背痛的治疗方案提供新的思路。
中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:组织构建;骨细胞;软骨细胞;细胞培养;成纤维细胞;血管内皮细胞;骨质疏松;组织工程
1.1 资料来源
1.1.1 检索人及检索时间 由第一作者在2024年1月进行检索。
1.1.2 检索文献时限 各数据库建库至2024年1月。
1.1.3 检索数据库 万方数据库、中国知网、维普、Web of Science和PubMed数据库。
1.1.4 检索词 中文检索词为“慢性非特异性下背痛,腰椎稳定,椎旁肌,运动疗法”,英文检索词为“chronic nonspecific low back pain,lumbar stabilization,paravertebral muscle,exercise therapy”。
1.1.5 检索文献类型 包括综述、研究原著与荟萃分析。
1.1.6 手工检索情况 无。
1.1.7 检索策略 英文数据库检索策略图见图1。
1.1.8 检索文献量 初步检索到14 367篇文献,其中中文6 810篇、英文7 557篇,包括万方数据库1 076篇、中国知网3 255篇、Web of Science数据库2 355篇、PubMed数据库5 202篇、维普数据库2 479篇。
1.2 入组标准
1.2.1 纳入标准 文献内容与慢性非特异性下背痛和运动疗法相关;文章内容涉及椎旁肌功能与腰椎稳定性;文章内容涉及骨骼、肌肉和腰椎稳定的机械、化学通路。
1.2.2 排除标准 不符合研究目的文章;重复发表的文章;质量和可信度低的文章;无参考意义的文章。
1.3 文献质量评估及数据提取 数据库共检索到14 367篇,排除重复及年代久远的研究,按照纳入和排除标准进行筛选,初筛后纳入230篇文献,经过仔细阅读文章内容后最终纳入93篇文献,均来自于PubMed数据库。文献筛选流程图见图2。
3.1 既往该领域研究的贡献和存在的问题 慢性非特异性下背痛是常见的骨骼肌肉疾病,具有患病率高、预后差等特点,随着人口老龄化的进一步加剧,慢性非特异性下背痛的发生率逐年上升,严重影响患者的生活质量,因此,对于慢性非特异性下背痛的防治变得尤为重要。随着对慢性非特异性下背痛认识的深入,研究人员发现腰椎稳定与慢性非特异性下背痛存在一定关联,并且运动疗法对于其治疗的报道也得到证实。但是,对于运动疗法通过腰椎稳定来治疗慢性非特异性下背痛的确切有效方案尚无明确报道。
3.2 作者综述区别于他人他篇的特点 尽管现有的研究已证实运动疗法对于慢性非特异性下背痛的治疗是有效的,但未明确指出具体的治疗方案。区别于既往的研究,该文将机械-化学偶联与椎旁肌的稳定性和运动疗法相结合,探讨了在某些常见疾病当中肌肉与骨骼之间的相互作用,归纳了运动疗法治疗慢性非特异性下背痛的效果和预后,提出按照个体化方式制定具体的运动方案对于获得更好的预后是必要的。
3.3 综述的局限性 ①国内外关于运动疗法的具体方案尚无明确的阐述,大多数关于运动疗法治疗慢性非特异性下背痛相关研究的临床样本量较有限,并且随访时间较短,因此还需要更大的样本量及更久的随访时间进一步验证运动疗法的结果;②腰椎椎旁肌质量的影像学评估方法仅限于水平位的横截面积,利用某一层面横截面积来评估椎旁肌整体质量缺少确切的观测指标。
3.4 综述的重要意义 该文总结了椎旁肌肌肉和骨骼之间的机械-化学偶联在运动疗法中的相关研究进展,表明腰椎的稳定对于缓解慢性非特异性下背痛是必要的,阐述了个体化运动疗法对慢性非特异性下背痛的临床治疗具有重要作用,为防治慢性非特异性下背痛提供一定的理论参考,有望为降低慢性非特异性下背痛的致残率并获得更好的预后提供新的思路。
中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:组织构建;骨细胞;软骨细胞;细胞培养;成纤维细胞;血管内皮细胞;骨质疏松;组织工程
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||