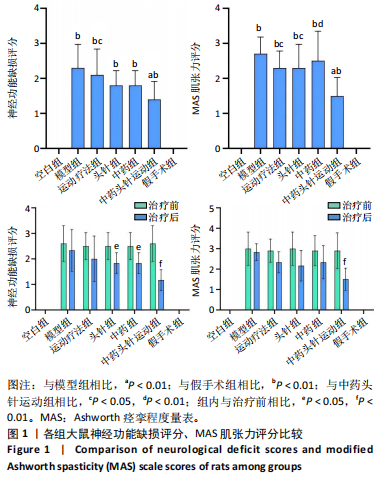
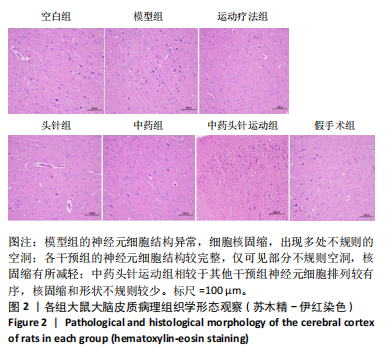
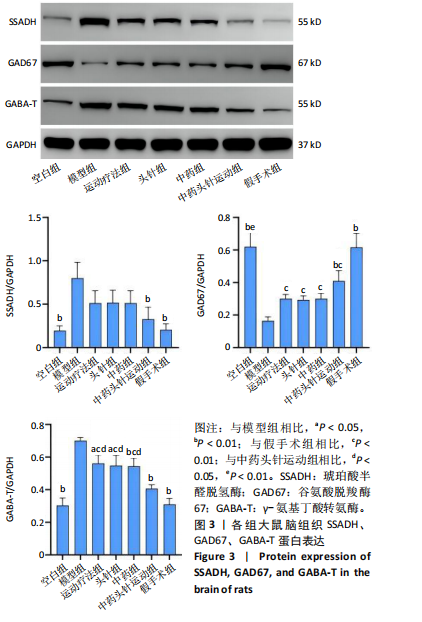
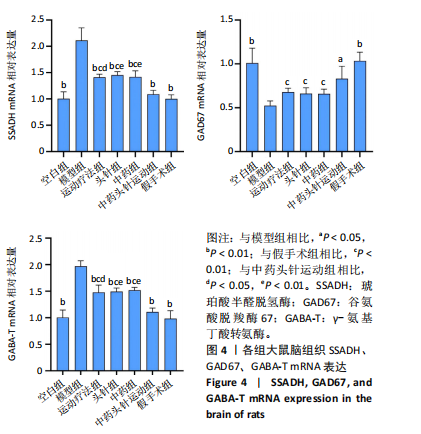
[1] FESKE SK. Ischemic Stroke. Am J Med. 2021;134(12):1457-1464.
[2] Corbyn Z. Statistics: a growing global burden. Nature. 2014;510(7506): S2-3.
[3] LIU S, ZHANG C S, CAI Y, et al. Acupuncture for Post-stroke Shoulder-Hand Syndrome: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Front Neurol. 2019;10:433.
[4] DOUSSOULIN A, RIVAS C, BACCO J, et al. Prevalence of Spasticity and Postural Patterns in the Upper Extremity Post Stroke. J Stroke Cerebrovasc Dis. 2020;29(11):105253.
[5] BURRIDGE JH, WOOD DE, HERMENS HJ, et al. Theoretical and methodological considerations in the measurement of spasticity. Disabil Rehabil. 2005;27(1-2):69-80.
[6] CHEN C, ZHOU X, HE J, et al. The Roles of GABA in Ischemia-Reperfusion Injury in the Central Nervous System and Peripheral Organs. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2019;2019:4028394.
[7] SCHNORBUSCH K, LEMBRECHTS R, PINTELON I, et al. GABAergic signaling in the pulmonary neuroepithelial body microenvironment: functional imaging in GAD67-GFP mice. Histochem Cell Biol. 2013; 140(5):549-566.
[8] 张威, 丁明俊, 耿罗娜. 互动式头针对脑卒中后痉挛性偏瘫患者平衡能力及运动功能的影响[J]. 陕西中医,2021,42(1):115-117.
[9] 甘俊鹤, 王峰, 崔向武. 互动式头针辅助治疗脑卒中后下肢痉挛临床研究[J]. 新中医,2023,55(13):160-164.
[10] 哈斯, 于立鹏, 莎琪尔. 益脑复健胶囊联合曲克芦丁脑蛋白水解物对急性脑梗死患者的治疗效果[J]. 慢性病学杂志,2022,23(5):704-707.
[11] LI Y, ZHANG J. Animal models of stroke. Animal Model Exp Med. 2021; 4(3):204-219.
[12] 中国针灸学会. 实验动物常用穴位名称与定位第2部分:大鼠[J]. 针刺研究,2021,46(4):351-352.
[13] LONGA EZ, WEINSTEIN PR, CARLSON S, et al. Reversible middle cerebral artery occlusion without craniectomy in rats. Stroke. 1989;20(1):84-91.
[14] MESEGUER-HENAREJOS AB, SÁNCHEZ-MECA J, LÓPEZ-PINA JA, et al. Inter- and intra-rater reliability of the Modified Ashworth Scale: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Eur J Phys Rehabil Med. 2018; 54(4):576-590.
[15] CHENG H, FANG X, LIAO L, et al. Prevalence and factors influencing the occurrence of spasticity in stroke patients: a retrospective study. Neurol Res. 2023;45(2):166-172.
[16] NAM KE, LIM SH, KIM JS, et al. When does spasticity in the upper limb develop after a first stroke? A nationwide observational study on 861 stroke patients. J Clin Neurosci. 2019;66:144-148.
[17] HOTTER B, PADBERG I, LIEBENAU A, et al. Identifying unmet needs in long-term stroke care using in-depth assessment and the Post-Stroke Checklist - The Managing Aftercare for Stroke (MAS-I) study. Eur Stroke J. 2018;3(3):237-245.
[18] SCHINWELSKI MJ, SITEK EJ, WĄŻ P, et al. Prevalence and predictors of post-stroke spasticity and its impact on daily living and quality of life. Neurol Neurochir Pol. 2019;53(6):449-457.
[19] LIU C, LI R, SONG X, et al. Effect of catgut implantation at acupoints on GABA(B) and mGluR1 expressions in brain stem of rats with spasticity after stroke. J Tradit Chin Med. 2014;34(5):566-571.
[20] WU C, QIN X, DU H, et al. The immunological function of GABAergic system. Front Biosci (Landmark Ed). 2017;22(7):1162-1172.
[21] MAZZOLI R, PESSIONE E. The Neuro-endocrinological Role of Microbial Glutamate and GABA Signaling. Front Microbiol. 2016;7:1934.
[22] WANG H, LIU S, WANG H, et al. The effect of propofol postconditioning on the expression of K(+)-Cl(-)-co-transporter 2 in GABAergic inhibitory interneurons of acute ischemia/reperfusion injury rats. Brain Res. 2015;1597:210-219.
[23] 毛雪莲, 秦思, 金荣疆, 等. 电针对脑卒中肢体痉挛大鼠γ-氨基丁酸代谢酶的影响[J].中国康复医学杂志,2018,33(1):22-28.
[24] PEARL PL, PARVIZ M, VOGEL K, et al. Inherited disorders of gamma-aminobutyric acid metabolism and advances in ALDH5A1 mutation identification. Dev Med Child Neurol. 2015;57(7):611-617.
[25] 于波, 张勇. 中医综合康复疗法治疗中风病的研究概述与问题探讨[J]. 中国康复医学杂志,2015,30(1):73-75.
[26] ZANON MA, PACHECO RL, LATORRACA COC, et al. Neurodevelopmental Treatment (Bobath) for Children With Cerebral Palsy: A Systematic Review. J Child Neurol. 2019;34(11):679-686.
[27] BHUSARI N, SALPHALE VG, DEODHE NP. Implementation of the Gamut of Physiotherapy Maneuvers in Restoration and Normalization of Functional Potencies in a Patient With a Hemorrhagic Stroke: A Case Report. Cureus. 2022;14(12):e33035.
[28] YU S, FETTERS L. Commentary on “Effects of constraint-induced movement therapy on gait, balance, and functional locomotor mobility”. Pediatr Phys Ther. 2012;24(1):69.
[29] 李薇, 林丹, 邹忆怀, 等. 头针治疗缺血性脑卒中后偏瘫机制研究进展[J]. 中国中医药信息杂志,2021,28(5):128-132.
[30] 王建华. 益脑复健胶囊治疗脑梗塞36例[J]. 中国民间疗法, 2002(10):38.
[31] 张君宇, 韩为, 金子开, 等.“通督调神”针法结合康复训练对缺血性脑卒中后下肢运动功能恢复的影响[J]. 康复学报,2022,32(5): 401-406+418.
[32] 章春霞, 张绍华, 王玉龙, 等.互动式头针对卒中后认知功能和运动功能的影响[J].上海针灸杂志,2021,40(7):801-806.
[33] 郭斌, 岳增辉, 谢志强, 等. 基于神经兴奋-抑制因子(Glu-GABA)受体含量及表达观察电针对于脑卒中痉挛状态大鼠黑质纹状体的影响实验研究[J]. 时珍国医国药,2020,31(5):1268-1270.
[34] 毛雪莲, 秦思, 金荣疆, 等. 电针对脑卒中肢体痉挛大鼠γ-氨基丁酸代谢酶的影响[J]. 中国康复医学杂志,2018,33(1):22-28.
[35] 李婧雯,胡延超,王艺莹,等.督脉电针对脑卒中肢体痉挛大鼠大脑皮层中谷氨酸脱羧酶67和γ-氨基丁酸转氨酶表达的影响[J].针刺研究,2022,47(8):703-709.
|