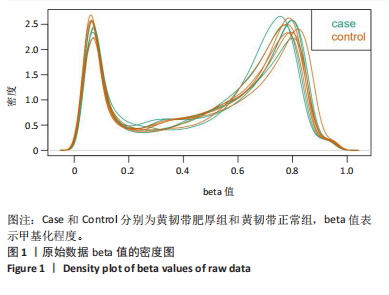
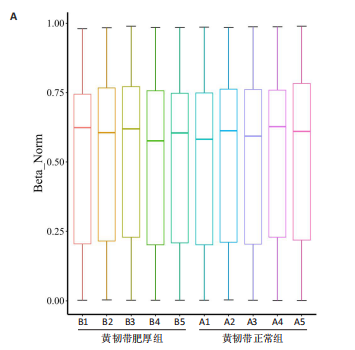
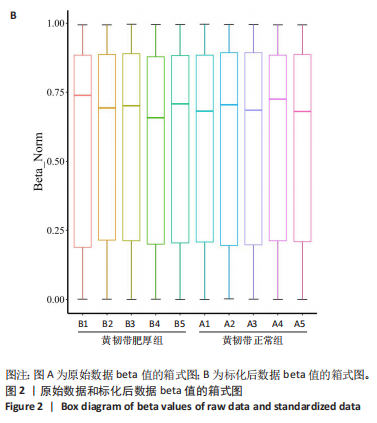
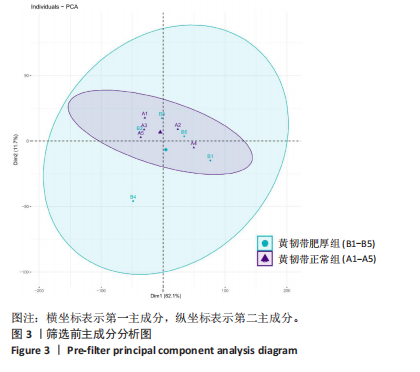
[1] KATZ JN, ZIMMERMAN ZE, MASS H, et al. Diagnosis and Management of Lumbar Spinal Stenosis: A Review. JAMA. 2022;327(17):1688-1699.
[2] BYVALTSEV VA, KALININ AA, HERNANDEZ PA, et al. Molecular and Genetic Mechanisms of Spinal Stenosis Formation: Systematic Review. Int J Mol Sci. 2022;23(21):13479.
[3] KWON WK, HAM CH, CHOI H, et al. Elucidating the effect of mechanical stretch stress on the mechanism of ligamentum flavum hypertrophy: Development of a novel in vitro multi-torsional stretch loading device. PLoS One. 2022;17(10):e0275239.
[4] HAYASHI F, MORIMOTO M, HIGASHINO K, et al. Myofibroblasts are increased in the dorsal layer of the hypertrophic ligamentum flavum in lumbar spinal canal stenosis. Spine J. 2022;22(4):697-704.
[5] KIM J, KWON WK, CHO H, et al. Ligamentum flavum hypertrophy significantly contributes to the severity of neurogenic intermittent claudication in patients with lumbar spinal canal stenosis. Medicine (Baltimore). 2022;101(36):e30171.
[6] MEHROTRA A, SINGH K, KANJILAL S, et al. Expanding the Horizons of Minimally Invasive Spine Surgery: Experience of the Destandau Technique for the Treatment of Multiple Spinal Diseases. World Neurosurg. 2024;181:e970-e977.
[7] BURILE G, JAWADE S, SETH N. The Scope of Physiotherapy Rehabilitation in Compressive Myelopathy Managed by Spinal Fusion: A Case Report. Cureus. 2023;15(11):e48290.
[8] KURZ E, SCHENK P, BRAKOPP F, et al. Muscle activity and rehabilitation in spinal stenosis (MARSS) after conservative therapy and surgical decompression with or without fusion: Protocol for a partially randomized patient preference trial on rehabilitation timing. Contemp Clin Trials Commun. 2024;38:101273.
[9] SOBAŃSKI D, STASZKIEWICZ R, STACHURA M, et al. Presentation, Diagnosis, and Management of Lower Back Pain Associated with Spinal Stenosis: A Narrative Review. Med Sci Monit. 2023;29:e939237.
[10] WANG S, QU Y, FANG X, et al. Decorin: a potential therapeutic candidate for ligamentum flavum hypertrophy by antagonizing TGF-β1. Exp Mol Med. 2023;55(7):1413-1423.
[11] SUN C, ZHANG H, WANG X, et al. Ligamentum flavum fibrosis and hypertrophy: Molecular pathways, cellular mechanisms, and future directions. FASEB J. 2020;34(8):9854-9868.
[12] WU L, MUNAKOMI S, CRUZ R. Lumbar Spinal Stenosis. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing, 2024.
[13] ZHAO R, DONG J, LIU C, et al. Thrombospondin-1 promotes mechanical stress-mediated ligamentum flavum hypertrophy through the TGFβ1/Smad3 signaling pathway. Matrix Biol. 2024;127:8-22.
[14] WEISKIRCHEN R, WEISKIRCHEN S, TACKE F. Organ and tissue fibrosis: Molecular signals, cellular mechanisms and translational implications. Mol Aspects Med. 2019;65:2-15.
[15] LIN Z, ZHOU P, VON GISE A, et al. Pi3kcb links Hippo-YAP and PI3K-AKT signaling pathways to promote cardiomyocyte proliferation and survival. Circ Res. 2015;116(1):35-45.
[16] ARCERI L, NGUYEN TK, GIBSON S, et al. Cannabinoid Signaling in Kidney Disease. Cells. 2023;12(10):1419.
[17] GOLOSOVA D, LEVCHENKO V, KRAVTSOVA O, et al. Acute and long-term effects of cannabinoids on hypertension and kidney injury. Sci Rep. 2022;12(1):6080.
[18] TAHAMTAN A, SAMIEIPOOR Y, NAYERI FS, et al. Effects of cannabinoid receptor type 2 in respiratory syncytial virus infection in human subjects and mice. Virulence. 2018;9(1):217-230.
[19] GHALLAB A, SEDDEK A. PPARG as therapeutic target for antifibrotic therapy. EXCLI J. 2020;19:227-229.
[20] LU C, LIU Z, ZHANG H, et al. Proliferation effect of ligamentum flavum cells induced by transforming growth factor β 1 and its effect on connective tissue growth factor. Zhongguo Xiu Fu Chong Jian Wai Ke Za Zhi. 2019;33(7):883-888.
[21] SABBAH DA, HAJJO R, SWEIDAN K. Review on Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor (EGFR) Structure, Signaling Pathways, Interactions, and Recent Updates of EGFR Inhibitors. Curr Top Med Chem. 2020;20(10):815-834.
[22] NEEDHAM SR, ZANETTI-DOMINGUES LC, HIRSCH M, et al. Structure-function relationships and supramolecular organization of the EGFR (epidermal growth factor receptor) on the cell surface. Biochem Soc Trans. 2014;42(1):114-119.
[23] KIM BJ, HUR JW, PARK JS, et al. Expression of matrix metalloproteinase-2 and -9 in human ligamentum flavum cells treated with tumor necrosis factor-α and interleukin-1β. J Neurosurg Spine. 2016;24(3):428-435.
[24] WEBSTER JD, VUCIC D. The Balance of TNF Mediated Pathways Regulates Inflammatory Cell Death Signaling in Healthy and Diseased Tissues. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2020;8:365.
[25] SUN C, WANG Z, TIAN JW, et al. Leptin-induced inflammation by activating IL-6 expression contributes to the fibrosis and hypertrophy of ligamentum flavum in lumbar spinal canal stenosis. Biosci Rep. 2018;38(2):BSR20171214.
[26] PARNELL J, MARTIN N, DEDEK A, et al. Cannabinoid CB1 Receptor Expression and Localization in the Dorsal Horn of Male and Female Rat and Human Spinal Cord. Can J Pain. 2023;7(2):2264895.
[27] 薛翠华,高振军,李秋萍,等.塞来昔布对大鼠重症急性胰腺炎血清TNF-α,IL-1β,IL-6及IL-8水平的影响[J].江苏大学学报(医学版), 2009,19(6):496-498,504.
[28] GOPAL D, HO AL, SHAH A, et al. Molecular basis of intervertebral disc degeneration. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2012;760:114-133.
[29] CALDEIRA J, SANTA C, OSÓRIO H, et al. Matrisome Profiling During Intervertebral Disc Development And Ageing. Sci Rep. 2017;7(1):11629.
[30] XIE G, LIANG C, YU H, et al. Association between polymorphisms of collagen genes and susceptibility to intervertebral disc degeneration: a meta-analysis. J Orthop Surg Res. 2021;16(1):616.
[31] SOPHIA FOX AJ, BEDI A, RODEO SA. The basic science of articular cartilage: structure, composition, and function. Sports Health. 2009; 1(6):461-468.
[32] YOSHIDA M, SHIMA K, TANIGUCHI Y, et al. Hypertrophied ligamentum flavum in lumbar spinal canal stenosis. Pathogenesis and morphologic and immunohistochemical observation. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 1992; 17(11):1353-1360. |