中国组织工程研究 ›› 2023, Vol. 27 ›› Issue (13): 1981-1986.doi: 10.12307/2023.238
• 骨与关节生物力学 bone and joint biomechanics • 上一篇 下一篇
脊柱内镜下椎板开窗减压与单侧入路双侧减压治疗腰椎管狭窄症的生物力学稳定性及有限元分析
张晗硕1,2,3,丁 宇1,2,3,蒋 强3,卢正操3 ,练诗林3,李土胜3
- 1安徽医科大学海军临床学院,北京市 100048;2安徽医科大学第五临床医学院,安徽省合肥市 230032;3解放军总医院第六医学中心中医医学部骨伤科,北京市 100048
Biomechanical stability and finite element analysis of endoscopic LOVE decompression technique and endoscopic unilateral laminotomy for bilateral decompression technique for lumbar spinal stenosis
Zhang Hanshuo1, 2, 3, Ding Yu1, 2, 3, Jiang Qiang3, Lu Zhengcao3, Lian Shilin3, Li Tusheng3
- 1Navy Clinical College, Anhui Medical University, Beijing 100048, China; 2The Fifth School of Clinical Medicine, Anhui Medical University, Hefei 230032, Anhui Province, China; 3Orthopedics of TCM Senior Department, the Sixth Medical Center of PLA General Hospital, Beijing 100048, China
摘要:
文题释义:
全脊柱内镜下椎板开窗减压:为传统开放手术的内镜化及微创化,可在较短时间内完成骨性椎管、盘黄间隙、神经根管及侧隐窝扩大成形,一期完成椎间隙平面、上位椎板黄韧带止点、下位椎弓根层面及侧隐窝全椎管减压,实现了多平面、立体椎管减压,适用于重度、中央型椎管狭窄,小切口下解除硬膜囊和神经根靶点压迫,有效缓解患者临床症状,降低医源性不稳的发生,确保临床疗效,患者生活质量大幅改善。
脊柱内镜下单侧入路双侧减压:在脊柱内镜下利用水介质冲洗下获得清晰视野,相对开放手术安全性和精确性更高,可首先经全脊柱内镜下椎板开窗进行单侧减压,而后倾斜套管在棘突基底部潜行到对侧进行减压,其主要适用于单纯中央型椎管狭窄、中央型椎管狭窄伴侧隐窝狭窄、单侧或双侧侧隐窝狭窄等。
背景:全脊柱内镜下椎板开窗减压及脊柱内镜下单侧入路双侧减压手术作为后路脊柱内镜下治疗腰椎管狭窄症的前沿高精技术,临床疗效较好,但目前鲜有生物力学及有限元分析的相关研究报道。
目的:分析全脊柱内镜下椎板开窗减压及脊柱内镜下单侧入路双侧减压对内镜下治疗腰椎管狭窄症生物力学的影响,验证该两种手术方式治疗腰椎管狭窄症的可靠性和有效性。
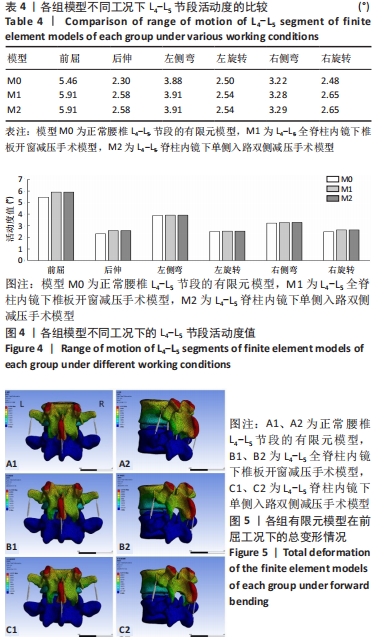
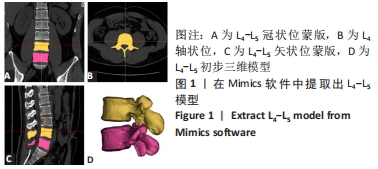
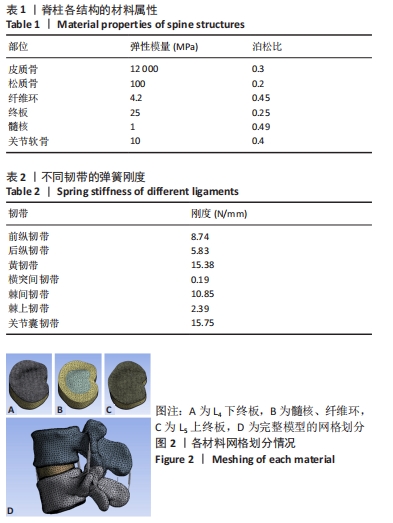
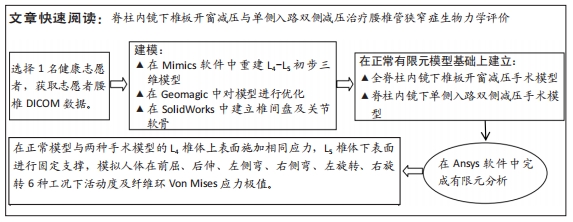
方法:取1名健康志愿者的腰椎CT图像,利用Mimics、Geomagic、Solidworks、Ansys软件建立正常腰椎L4-L5节段的有限元模型M0,在此基础上分别建立全脊柱内镜下椎板开窗减压手术模型M1与脊柱内镜下单侧入路双侧减压手术模型M2,在3组模型的L4椎体上表面施加相同应力,L5椎体下表面进行固定支撑,分析在前屈、后伸、左侧弯、右侧弯、左旋转、右旋转6种工况下的整体关节活动度及纤维环Von Mises应力极值。
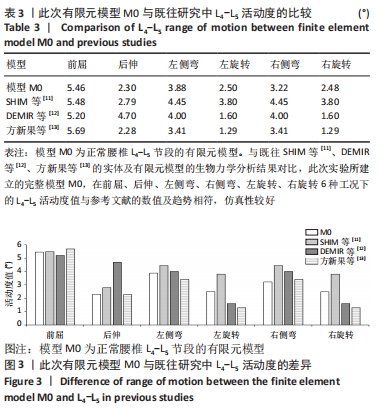
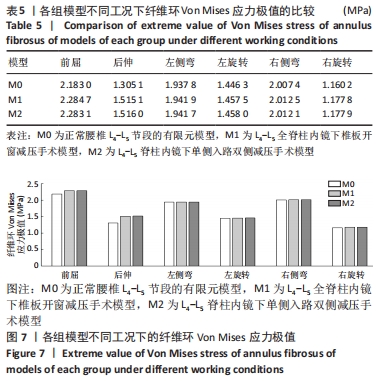
结果与结论:①与模型M0相比,模型M1在前屈、后伸、左侧弯、左旋转、右侧弯、右旋转下的整体关节活动度分别增加8.24%,12.17%,0.77%,1.60%,1.86%,6.85%,模型M2在前屈、后伸、左侧弯、左旋转、右侧弯、右旋转下的整体关节活动度分别增加8.24%,12.17%,0.77%,1.60%,2.17%,6.85%;与模型M1相比,模型M2在右侧弯下的活动度整体关节稍增加,其余工况未见明显增加与趋势的改变;②与模型M0相比,模型M1在前屈、后伸、左侧弯、左旋转、右侧弯、右旋转下的纤维环Von Mises 应力极值分别增加4.65%,16.09%,0.21%,0.77%,0.25%,1.51%,模型M2在前屈、后伸、左侧弯、左旋转、右侧弯、右旋转下的纤维环Von Mises 应力极值分别增加4.58%,16.15%,0.20%,0.80%,0.23%,1.52%;模型M1与模型M2不同工况下的纤维环Von Mises 应力极值变化趋势不明显;③结果显示,全脊柱内镜下椎板开窗减压及脊柱内镜下单侧入路双侧减压治疗腰椎管狭窄症后,其责任节段稳定性较好。
https://orcid.org/0000-0002-1482-3329(张晗硕)
中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:人工关节;骨植入物;脊柱;骨折;内固定;数字化骨科;组织工程
中图分类号: