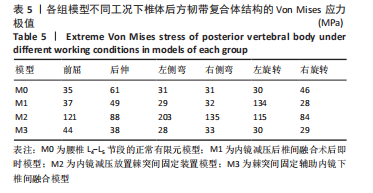
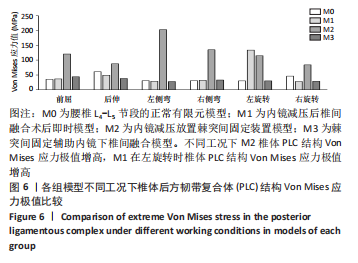
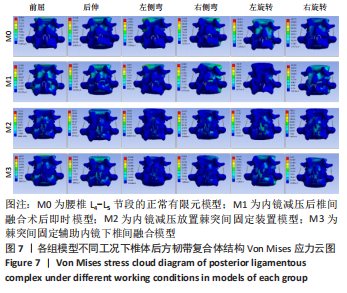
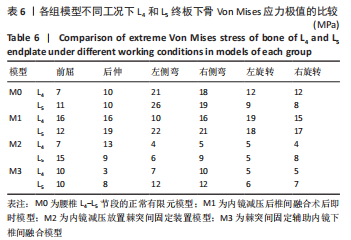
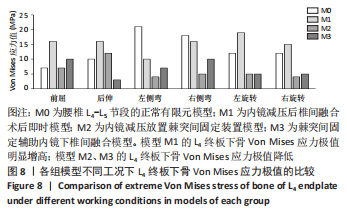
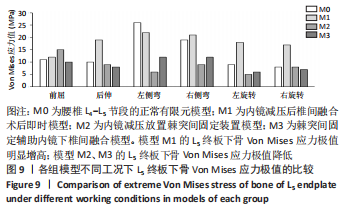
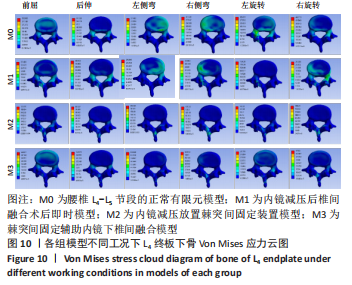
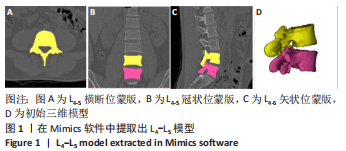
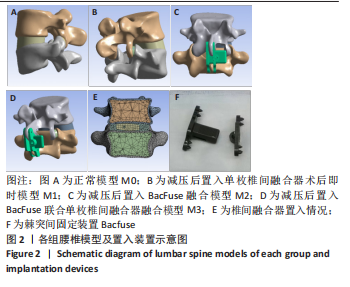
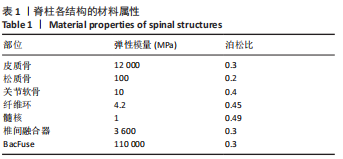
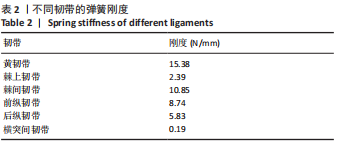
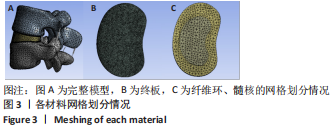
[1] 李嘉睿,燕杨,武晓刚,等. 单边双通道内镜下腰椎椎间融合的生物力学分析[J]. 中国组织工程研究,2023,27(34):5523-5529.
[2] 曹雅雯,张丹. Schizas形态学分型和硬膜囊面积测量对腰椎管狭窄症的诊断效能[J]. 承德医学院学报,2022,39(6):469-473.
[3] 胡前芹,谢水华,孙雷,等. 单侧双通道内镜技术治疗腰椎管狭窄的临床疗效分析[J]. 实用骨科杂志,2022,28(6):533-536.
[4] 李锦军,张体栋,陈浩,等. BacFuse固定融合术治疗老年腰椎退行性滑脱[J]. 中国矫形外科杂志,2017,25(21):1933-1937.
[5] 苏楠,杨雍,王炳强,等. Bacfuse棘突间撑开装置是否为高龄腰椎管狭窄症患者的又一选择[J]. 北京医学,2016,38(7):643-647.
[6] 牛海明,王庆春,徐新宇. 采用微创腰椎椎间融合联合椎弓根钉棒固定治疗腰椎滑脱症的临床疗效[J]. 骨科临床与研究杂志,2022, 7(2):98-103,110.
[7] 陈道裕,李进,俞涛,等. 经皮腰椎全内镜下单侧入路双侧减压治疗单节段腰椎椎管狭窄症的临床疗效分析[J]. 中国骨与关节杂志, 2022,11(9):659-663.
[8] 闫志刚,王元利,施建锋,等. 椎间孔镜联合棘突间融合治疗老年人腰椎管狭窄症伴不稳[J]. 中国骨伤,2021,34(3):249-254.
[9] 张睿,吴思滨,张金虎. 腰后路减压植骨融合内固定术治疗老年性多节段腰椎管狭窄症的临床观察[J]. 中国医学创新,2023,20(1): 35-38.
[10] 朱雷,于秀淳,鲁成林. 棘突间融合装置联合椎体间融合对下腰椎稳定性影响的三维有限元研究[J]. 生物骨科材料与临床研究, 2013,10(3):55-60, 插7-插8.
[11] SHEN YW, YANG Y, LIU H, et al. Biomechanical Evaluation of Intervertebral Fusion Process After Anterior Cervical Discectomy and Fusion: A Finite Element Study. Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2022;2(10): 487-493.
[12] 陈浩,张体栋,贾璞,等. BacFuse棘突间植入术和后路椎间融合固定术治疗腰椎间盘突出症的对比研究[J]. 临床和实验医学杂志, 2016,15(5):471-474.
[13] LI XF, JIN LY, LV ZD, et al. Efficacy of percutaneous transforaminal endoscopic decompression treatment for degenerative lumbar spondylolisthesis with spinal stenosis in elderly patients. Exp Ther Med. 2020;19(2):1417-1424.
[14] 曹亮亮,徐建广,梅伟. 三维有限元法分析腰骶区椎间融合联合置入棘突间动态内固定装置后腰椎的生物力学变化[J]. 中国组织工程研究,2020,24(12):1905-1910.
[15] 范威,张驰,王庆东,等. 振动载荷下不同入路腰椎椎间融合术的生物力学研究[J]. 生物医学工程学杂志,2021,38(5):877-884.
[16] LIU Z, ZHANG S, LI J, et al. Biomechanical comparison of different interspinous process devices in the treatment of lumbar spinal stenosis: a finite element analysis. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2020; 463(25):876-882.
[17] SHIM CS, PARK SW, LEE SH, et al. Biomechanical evaluation of an interspinous stabilizing device, Locker. Spine. 2008;33(22): E820-E827.
[18] DEMIR E, ELTES P, CASTRO AP, et al. Finite element modelling of hybrid stabilization systems for the human lumbar spine. Proc Inst Mech Eng H. 2020;234(12):1409-1420.
[19] 方新果, 赵改平, 王晨曦, 等. 基于 CT 图像腰椎 L4~L5 节段有限元模型建立与分析 [J]. 中国生物医学工程学报,2014,33(4):487-492.
[20] 王宪峰,牛犇,李欣,等. 改良TLIF治疗腰椎管狭窄症[J]. 中国矫形外科杂志,2019,27(13):1167-1170.
[21] SPICHER A, SCHMOELZ W, SCHMID R, et al. Functional and radiographic evaluation of an interspinous device as an adjunct for lumbar interbody fusion procedures. Biomed Tech (Berl). 2020;65(2):183-189.
[22] WEI H, TANG H, ZHANG T, et al. Preliminary efficacy of inter-spinal distraction fusion which is a new technique for lumbar disc herniation. Int Orthop. 2019;43(4):899-907.
[23] HE L, FENG H, MA X, et al. Percutaneous endoscopic posterior lumbar interbody fusion for the treatment of degenerative lumbar diseases: a technical note and summary of the initial clinical outcomes. Br J Neurosurg. 2021;47(4):192-201.
[24] KARAHALIOS DG, KAIBARA T, PORTER RW, et al. Biomechanics of a lumbar interspinous anchor with anterior lumbar interbody fusion. J Neurosurg Spine. 2010;16(17):322-331.
[25] PANCHAL R, DENHAESE R, HILL C, et al. Anterior and Lateral Lumbar Interbody Fusion With Supplemental Interspinous Process Fixation: Outcomes from a Multicenter, Prospective, Randomized, Controlled Study. Int J Spine Surg. 2018;12(2):172-184.
[26] DE KUNDER SL, RIJKERS K, CAELERS IJMH, et al. Lumbar Interbody Fusion. Spine. 2018;43(16):1161-1168.
[27] RUSTENBURG CME, FARAJ SSA, HOLEWIJN RM, et al. The biomechanical effect of single-level laminectomy and posterior instrumentation on spinal stability in degenerative lumbar scoliosis: a human cadaveric study. Neurosurg Focus. 2019;46(5):432-441.
[28] SPICHER A, SCHMOELZ W, SCHMID R, et al. Functional and radiographic evaluation of an interspinous device as an adjunct for lumbar interbody fusion procedures. Biomed Eng. 2020;65(2):183-189.
[29] MORGENSTERN R, MORGENSTERN C. Feasibility of Full Percutaneous Segmental Stabilization of the Lumbar Spine With a Combination of an Expandable Interbody Cage and an Interspinous Spacer: Preliminary Results. Int J Spine Surg. 2018;12(6):665-672.
[30] 刘立佳,陈萌萌,唐海. 棘突间固定融合装置BacFuse在退行性腰椎滑脱症的临床疗效分析[J]. 中国病案,2021,22(8):108-112.
[31] WU JC, MUMMANENI PV. Using Lumbar Interspinous Anchor with Transforaminal Lumbar Interbody Fixation. World Neurosurg. 2010; 73(5):471-472. |