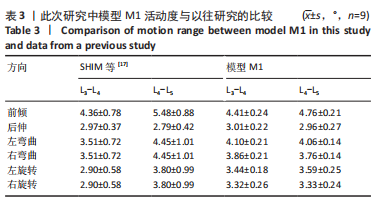
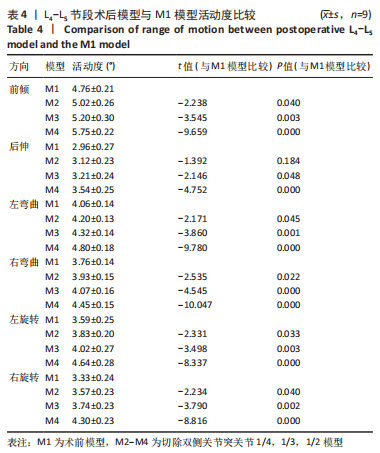
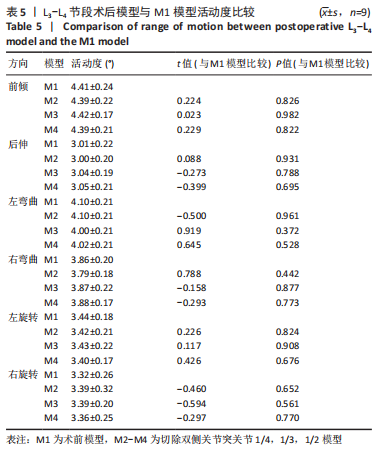
[1] KATZ JN, ZIMMERMAN ZE, MASS H, et al. Diagnosis and Management of Lumbar Spinal Stenosis: A Review. JAMA. 2022;327(17):1688-1699.
[2] LURIE J, TOMKINS-LANE C. Management of lumbar spinal stenosis. BMJ. 2016;352:h6234.
[3] HEO DH, CHOI WS, PARK CK, et al. Minimally Invasive Oblique Lumbar Interbody Fusion with Spinal Endoscope Assistance: Technical Note. World Neurosurg. 2016;96:530-536.
[4] HE J, XIAO S, WU Z, et al. Microendoscopic discectomy versus open discectomy for lumbar disc herniation: a meta-analysis. Eur Spine J. 2016;25(5):1373-1381.
[5] SAIRYO K, CHIKAWA T, NAGAMACHI A. State-of-the-art transforaminal percutaneous endoscopic lumbar surgery under local anesthesia: Discectomy, foraminoplasty, and ventral facetectomy. J Orthop Sci. 2018;23(2):229-236.
[6] 庹伟,周霖,刘德森,等.单侧双通道内镜技术治疗腰椎管狭窄的初步研究[J].中国微创外科杂志,2021,21(1):56-60.
[7] SIEPE CJ, SAUER D, MICHAEL MAYER H. Full endoscopic, bilateral over-the-top decompression for lumbar spinal stenosis. Eur Spine J. 2018;27(Suppl 4):563-565.
[8] DAVID T. Long-term results of one-level lumbar arthroplasty: minimum 10-year follow-up of the CHARITE artificial disc in 106 patients. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2007;32(6):661-666.
[9] AHUJA S, MOIDEEN AN, DUDHNIWALA AG, et al. Lumbar stability following graded unilateral and bilateral facetectomy: A finite element model study. Clin Biomech (Bristol, Avon). 2020;75:105011.
[10] ZENG ZL, ZHU R, WU YC, et al. Effect of Graded Facetectomy on Lumbar Biomechanics. J Healthc Eng. 2017;2017:7981513.
[11] SHI Y, XIE YZ, ZHOU Q, et al. The biomechanical effect of the relevant segments after facet-disectomy in different diameters under posterior lumbar percutaneous endoscopes: a three-dimensional finite element analysis. J Orthop Surg Res. 2021;16(1):593.
[12] 刘昌震,孙宁,朱锴,等.三维CT评估单孔分体内镜治疗L4/5滑脱症椎间融合术的安全性[J].中国组织工程研究,2023,27(18): 2884-2891.
[13] CAO L, LIU Y, MEI W, et al. Biomechanical changes of degenerated adjacent segment and intact lumbar spine after lumbosacral topping-off surgery: a three-dimensional finite element analysis. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2020;21(1):104.
[14] 张晗硕,丁宇,蒋强,等.脊柱内镜下椎板开窗减压与单侧入路双侧减压治疗腰椎管狭窄症的生物力学稳定性及有限元分析[J].中国组织工程研究,2023,27(13):1981-1986.
[15] MIELE VJ, PANJABI MM, BENZEL EC. Anatomy and biomechanics of the spinal column and cord. Handb Clin Neurol. 2012;109:31-43.
[16] 代云磊,魏亚,吴昌兵,等.有限元模拟脊柱内镜下椎间孔成形对腰椎生物力学的影响[J].西安交通大学学报(医学版),2022,43(1): 127-132.
[17] SHIM CS, PARK SW, LEE SH, et al. Biomechanical evaluation of an interspinous stabilizing device, Locker. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2008; 33(22):E820-827.
[18] STORZER B, SCHNAKE KJ. Microscopic bilateral decompression by unilateral approach in spinal stenosis. Eur Spine J. 2016;25 Suppl 2: 270-271.
[19] JAUMARD NV, WELCH WC, WINKELSTEIN BA. Spinal facet joint biomechanics and mechanotransduction in normal, injury and degenerative conditions. J Biomech Eng. 2011;133(7):071010.
[20] REED WR, LONG CR, PICKAR JG. Effects of unilateral facet fixation and facetectomy on muscle spindle responsiveness during simulated spinal manipulation in an animal model. J Manipulative Physiol Ther. 2013;36(9):585-594.
[21] STEIB K, PROESCHOLDT M, BRAWANSKI A, et al. Predictors of facet joint syndrome after lumbar disc surgery. J Clin Neurosci. 2012;19(3):418-422.
[22] ADAMS MA, HUTTON WC, STOTT JR. The resistance to flexion of the lumbar intervertebral joint. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 1980;5(3):245-253.
[23] LI XR, YU J, ZHANG W, et al. Biomechanical Model Study of the Effect of Partial Facetectomy on Lumbar Stability Under Percutaneous Endoscopy. World Neurosurg. 2020;139:e255-e264.
[24] DESMOULIN GT, PRADHAN V, MILNER TE. Mechanical Aspects of Intervertebral Disc Injury and Implications on Biomechanics. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2020;45(8):E457-E464.
[25] DELGADO-LÓPEZ PD, CASTILLA-DÍEZ JM. Impact of obesity in the pathophysiology of degenerative disk disease and in the morbidity and outcome of lumbar spine surgery. Neurocirugia. 2018;29(2):93-102.
[26] 郭小惠,宋西正,韩枕学,等.可控压缩应力轴向诱导山羊椎间盘退变模型构建及评价[J].医用生物力学,2021,36(2):224-230.
[27] RUBERTÉ LM, NATARAJAN RN, ANDERSSON GB. Influence of single-level lumbar degenerative disc disease on the behavior of the adjacent segments--a finite element model study. J Biomech. 2009;42(3):341-348.
|