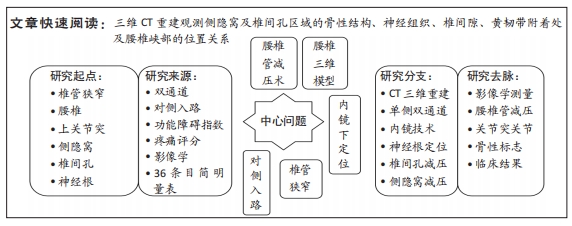
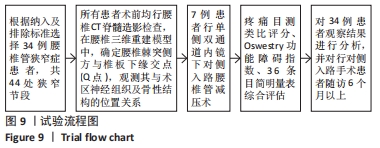
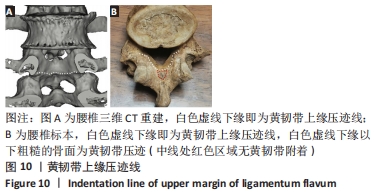
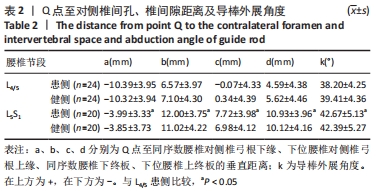
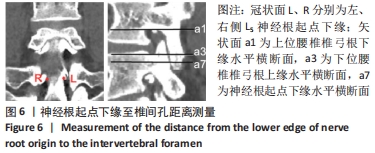
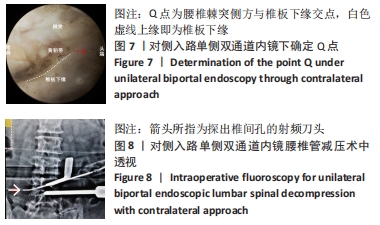
[1] 林博颖,沈茂.内镜下腰椎椎间融合:单侧椎弓根螺钉联合对侧椎板关节突螺钉固定的生物力学稳定性[J].中国组织工程研究,2022, 26(3):329-333.
[2] ARABMOTLAGH M, SELLEI RM, VINAS-RIOS JM, et al. Classification and diagnosis of lumbar spinal stenosis. Orthopade. 2019;48(10):816-823.
[3] LAI MKL, CHEUNG PWH, CHEUNG JPY. A systematic review of developmental lumbar spinal stenosis. Eur Spine J. 2020;29(9):2173-2187.
[4] LU HG, PAN XK, HU MJ, et al. Percutaneous Transforaminal Endoscopic Decompression for Lumbar Lateral Recess Stenosis. Front Surg. 2021;8: 631419.
[5] BURKHARDT BW, OERTEL JM. Is Decompression and Partial Discectomy Advantageous Over Decompression Alone in Microendoscopic Decompression Of Monosegmental Unilateral Lumbar Recess Stenosis? Int J Spine Surg. 2021;15(1):94-104.
[6] WANG Y, DENG M, WU H, et al. Short-term effectiveness of precise safety decompression via double percutaneous lumbar foraminoplasty and percutaneous endoscopic lumbar decompression for lateral lumbar spinal canal stenosis: a prospective cohort study. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2021;22(1):80.
[7] WILTSE LL, SPENCER CW. New uses and refinements of the paraspinal approach to the lumbar spine. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 1988;13(6):696-706.
[8] YANG CC, YEH KT, LIU KC, et al. Ameliorated Full-Endoscopic Transforaminal Decompression for L5-S1 Foraminal and Extraforaminal Stenosis. Clin Spine Surg. 2021;34(6):197-205.
[9] 毕经纬,李瑞,孙宁,等.单侧双通道内镜与椎间孔镜治疗腰椎管狭窄症的比较[J].中国微创外科杂志,2022,22(2):102-107.
[10] 田大胜,刘建军,朱斌,等.单边双通道内镜技术治疗腰椎间盘突出症和腰椎椎管狭窄症[J].中华骨科杂志,2020,40(17):1155-1164.
[11] LEE HG, KANG MS, KIM SY, et al. Dural Injury in Unilateral Biportal Endoscopic Spinal Surgery. Global Spine J. 2021;11(6):845-851.
[12] GATAM AR, GATAM L, MAHADHIPTA H, et al. Unilateral Biportal Endoscopic Lumbar Interbody Fusion: A Technical Note and an Outcome Comparison with the Conventional Minimally Invasive Fusion. Orthop Res Rev. 2021;13:229-239.
[13] JIANG HW, CHEN CD, ZHAN BS, et al. Unilateral biportal endoscopic discectomy versus percutaneous endoscopic lumbar discectomy in the treatment of lumbar disc herniation: a retrospective study. J Orthop Surg Res. 2022;17(1):30.
[14] KIM JY, KIM HS, JEON JB, et al. The Novel Technique of Uniportal Endoscopic Interlaminar Contralateral Approach for Coexisting L5-S1 Lateral Recess, Foraminal, and Extraforaminal Stenosis and Its Clinical Outcomes. J Clin Med. 2021;10(7):1364.
[15] JHA RT, SYED HR, CATALINO M, et al. Contralateral Approach for Minimally Invasive Treatment of Upper Lumbar Intervertebral Disc Herniation: Technical Note and Case Series. World Neurosurg. 2017; 100:583-589.
[16] HWANG JH, PARK WM, PARK CW. Contralateral Interlaminar Keyhole Percutaneous Endoscopic Lumbar Surgery in Patients with Unilateral Radiculopathy. World Neurosurg. 2017;101:33-41.
[17] HUA W, WANG B, KE W, et al. Comparison of lumbar endoscopic unilateral laminotomy bilateral decompression and minimally invasive surgery transforaminal lumbar interbody fusion for one-level lumbar spinal stenosis. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2020;21(1):785.
[18] HUA W, WANG B, KE W, et al. Comparison of Clinical Outcomes Following Lumbar Endoscopic Unilateral Laminotomy Bilateral Decompression and Minimally Invasive Transforaminal Lumbar Interbody Fusion for One-Level Lumbar Spinal Stenosis With Degenerative Spondylolisthesis. Front Surg. 2021;7:596327.
[19] AKBARY K, KIM JS, PARK CW, et al. Biportal Endoscopic Decompression of Exiting and Traversing Nerve Roots Through a Single Interlaminar Window Using a Contralateral Approach: Technical Feasibilities and Morphometric Changes of the Lumbar Canal and Foramen. World Neurosurg. 2018;117:153-161.
[20] ALIMI M, NJOKU IJR, CONG GT, et al. Minimally invasive foraminotomy through tubular retractors via a contralateral approach in patients with unilateral radiculopathy. Neurosurgery. 2014;10 Suppl 3:436-447.
[21] KHALSA SS, KIM HS, SINGH R, et al. Radiographic outcomes of endoscopic decompression for lumbar spinal stenosis. Neurosurg Focus. 2019;46(5):E10.
[22] 刘金玉,丁宇,蒋强,等. 全内镜下腰椎板开窗减压有限元模拟建模及生物力学变化[J]. 中国组织工程研究,2020,24(27): 4291-4296.
[23] KIM J, HEO DH, LEE DC, et al. Biportal endoscopic unilateral laminotomy with bilateral decompression for the treatment of cervical spondylotic myelopathy. Acta Neurochir (Wien). 2021;163(9):2537-2543.
[24] KIM JS, PARK CW, YEUNG YK, et al. Unilateral Bi-portal Endoscopic Decompression via the Contralateral Approach in Asymmetric Spinal Stenosis: A Technical Note. Asian Spine J. 2021;15(5):688-700.
[25] AKBARY K, KIM JS, PARK CW, et al. Biportal Endoscopic Decompression of Exiting and Traversing Nerve Roots Through a Single Interlaminar Window Using a Contralateral Approach: Technical Feasibilities and Morphometric Changes of the Lumbar Canal and Foramen. World Neurosurg. 2018;117:153-161.
[26] KIM HS, PATEL R, PAUDEL B, et al. Early Outcomes of Endoscopic Contralateral Foraminal and Lateral Recess Decompression via an Interlaminar Approach in Patients with Unilateral Radiculopathy from Unilateral Foraminal Stenosis. World Neurosurg. 2017;108: 763-773.
[27] HEO DH, KIM JS, PARK CW, et al. Contralateral Sublaminar Endoscopic Approach for Removal of Lumbar Juxtafacet Cysts Using Percutaneous Biportal Endoscopic Surgery: Technical Report and Preliminary Results. World Neurosurg. 2019;122:474-479.
[28] KIM JY, HEO DH. Contralateral sublaminar approach for decompression of the combined lateral recess, foraminal, and extraforaminal lesions using biportal endoscopy: a technical report. Acta Neurochir (Wien). 2021;163(10):2783-2787.
[29] CHOI CM, CHUNG JT, LEE SJ, et al. How I do it? Biportal endoscopic spinal surgery (BESS) for treatment of lumbar spinal stenosis. Acta Neurochir (Wien). 2016;158(3):459-463.
[30] RHEE J, ANAIZI AN, SANDHU FA, et al. Minimally invasive resection of lumbar synovial cysts from a contralateral approach. J Neurosurg Spine. 2012;17(5):453-458.
[31] HWANG JH, PARK WM, PARK CW. Contralateral Interlaminar Keyhole Percutaneous Endoscopic Lumbar Surgery in Patients with Unilateral Radiculopathy. World Neurosurg. 2017;101:33-41.
[32] KIM HS, SINGH R, ADSUL NM, et al. Management of Root-Level Double Crush: Case Report with Technical Notes on Contralateral Interlaminar Foraminotomy with Full Endoscopic Uniportal Approach. World Neurosurg. 2019;122:505-507.
[33] CHAU AM, PELZER NR, HAMPTON J, et al. Lateral extent and ventral laminar attachments of the lumbar ligamentum flavum: cadaveric study. Spine J. 2014;14(10):2467-2471.
[34] PENG YX, ZHENG ZY, WANG MD WG, et al. Relationship between the location of ligamentum flavum hypertrophy and its stress in finite element analysis. Orthop Surg. 2020;12(3):974-982.
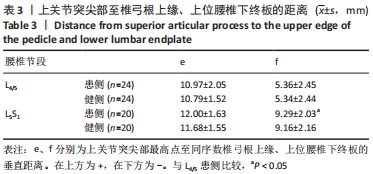
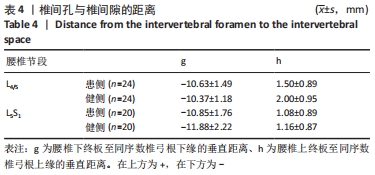
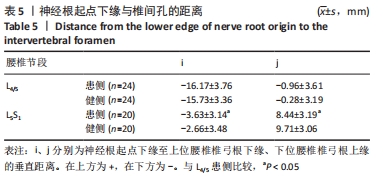
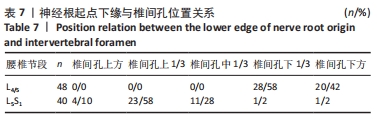
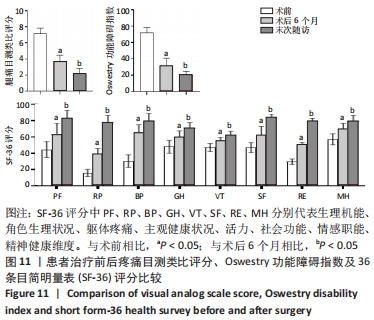
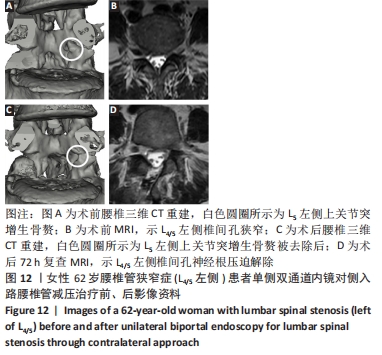
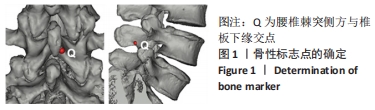
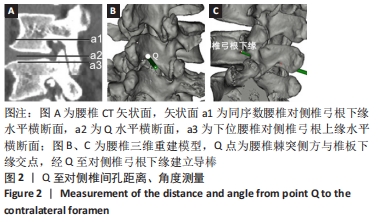
|