中国组织工程研究 ›› 2023, Vol. 27 ›› Issue (4): 547-551.doi: 10.12307/2023.246
• 数字化骨科 digital orthopedics • 上一篇 下一篇
机器人辅助髓芯减压植骨治疗ARCO Ⅱ期股骨头坏死
李 辉1,2,张 堃2,郝阳泉2,冯 磊2,杨 治2,许 鹏2,鲁 超2
- 1陕西中医药大学,陕西省咸阳市 712000;2西安交通大学附属红会医院,陕西省西安市 710000
Robot-assisted core decompression and bone grafting for ARCO II osteonecrosis of the femoral head
Li Hui1, 2, Zhang Kun2, Hao Yangquan2, Feng Lei2, Yang Zhi2, Xu Peng2, Lu Chao2
- 1Shaanxi University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Xianyang 712000, Shaanxi Province, China; 2Honghui Hospital, Xi’an Jiaotong University, Xi’an 710000, Shaanxi Province, China
摘要:
文题释义:
股骨头坏死:又称股骨头缺血性坏死,是股骨头血供中断或受损导致股骨头结构改变进而发生股骨头塌陷,引起患者关节疼痛、关节功能障碍的疾病,是骨科领域常见的难治性疾病。
ARCO分期:是1991年ARCO委员会在综合Ficat分期、Steinberg分期和日本骨坏死研究会分期后制定的分期系统,是一种更加全面、实用的分期方式,在疾病诊断、评估治疗效果和预后各方面具有较高的价值。
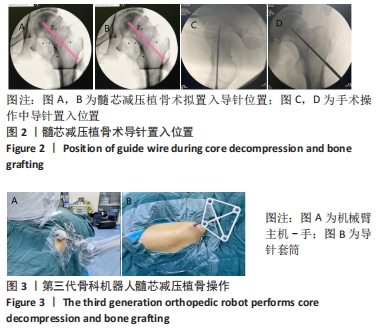
背景:髓芯减压植骨是ARCOⅡ期股骨头坏死的主要保髋术式之一,但传统手术方式存在透视时间长、出血量大等缺点。
目的:分析机器人辅助下进行髓芯减压植骨术治疗ARCO Ⅱ期股骨头坏死的临床治疗特点,为股骨头坏死保髋治疗提供新思路。
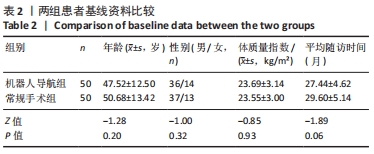
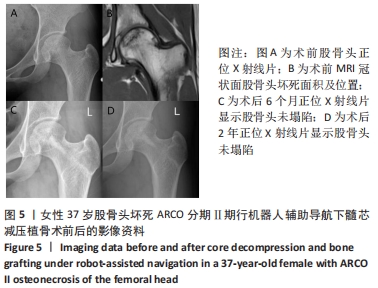
方法:回顾性分析2017年6月到2019年12月于西安交通大学附属红会医院骨坏死与关节重建科因股骨头坏死行髓芯减压植骨治疗的100例患者资料,其中骨科机器人导航辅助下髓芯减压植骨患者50例,男性36例,女性14例,年龄30-74(47.52±12.50)岁,设为机器人导航组;常规髓芯减压植骨患者50例,男性37例,女性13例,年龄28-77(50.68±13.60)岁,设为常规手术组;所有手术均为同一名术者操作完成。记录两组患者术前、末次随访Harris评分、术后目测类比疼痛评分、股骨头塌陷情况、术中各操作透视次数、术中出血量和手术时间。
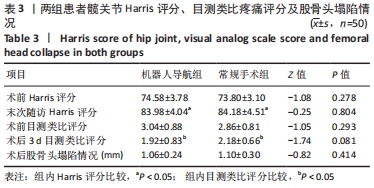
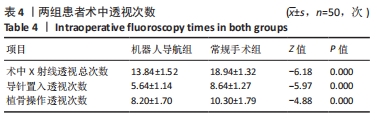
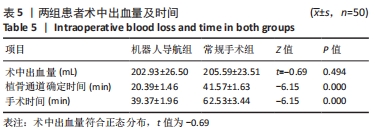
结果与结论:①所有患者获得随访,随访时间为20-38(28.53±0.50)个月;②机器人导航组患者术中X射线透视总次数、导针置入透视次数、植骨操作透视次数、植骨通道确定时间、手术时间分别为(13.84±1.52)次、(5.64±1.14)次、(8.20±1.70)次、(20.39±1.46) min和(39.37±1.96) min,均少于常规手术组上述各项指标的相应值[(18.94±1.32)次、(8.64±1.27)次、(10.30±1.79)次、(41.57±1.63) min和(62.53±3.44) min,均P < 0.05];③两组在末次Harris评分、术后目测类比疼痛评分、股骨头塌陷情况和术中出血量之间比较差异无显著性意义(P > 0.05);④结果说明,骨科机器人导航辅助下进行髓芯减压植骨治疗ARCO Ⅱ期股骨头坏死可明显提高髓芯减压植骨操作的精准度,减少术中透视次数,缩短手术时间,降低术后并发症出现的概率。
https://orcid.org/0000-0001-8665-0116 (李辉)
中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:人工关节;骨植入物;脊柱;骨折;内固定;数字化骨科;组织工程
中图分类号: