[1] MONT MA, CHERIAN JJ, SIERRA RJ, et al. Nontraumatic Osteonecrosis of the Femoral Head: Where Do We Stand Today? A Ten-Year Update. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2015;97(19):1604-1627.
[2] ZHAO DW, YU M, HU K, et al. Prevalence of Nontraumatic Osteonecrosis of the Femoral Head and its Associated Risk Factors in the Chinese Population: Results from a Nationally Representative Survey. Chin Med J (Engl). 2015;128(21):2843-2850.
[3] 王平, 张会敏, 李刚.鹿角多肽对骨髓间充质干细胞的影响[J].中华中医药杂志,2018,33(12):5644-5647.
[4] RICHTER JF, SCHMAUDER R, KRUG SM, et al. A novel method for imaging sites of paracellular passage of macromolecules in epithelial sheets. J Control Release. 2016;229:70-79.
[5] WANG P, SUN T, LI G, et al. The Separation of Antler Polypeptide and Its Effects on the Proliferation and Osteogenetic Differentiation of Bone Marrow Mesenchymal Stem Cells.Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2020;2020:1294151.
[6] 国家药典委员会. 中国药典[M]. 北京: 中国医药科技出版社, 2020.
[7] 陈方,吴铁,崔燎.维甲酸致小鼠骨质疏松模型的量效关系及骨药理作用探讨[J].中国药理学通报,2002,18(6):681-684.
[8] 孙铁锋,王平. 鹿角胶-壳聚糖细胞支架修复大鼠股骨头缺血性坏死[J].中成药,2015,37(11):2337-2341.
[9] 杨帆,刘红梅,吉红玉.鹿角胶临床应用及其用量探究[J].长春中医药大学学报,2021,37(3):512-515.
[10] 黄思敏,吴雨蒙,张丽,等.甘草附子汤对大鼠骨关节炎及关节软骨蛋白质组学的影响[J].中国中药杂志,2021,46(3):661-669.
[11] YUN C, QIAN W, WU J, et al. Pilose antler peptide promotes osteoblast proliferation, differentiation and mineralization via the insulin signaling pathway. Exp Ther Med. 2020;19(2):923-930.
[12] 刘小元,李蕾,张凯,等. 骨髓间充质干细胞膜片复合3D打印马鹿角粉/丝素蛋白/聚乙烯醇支架的体内成骨[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2021,25(34):5420-5426.
[13] CHEN R, MIAN M, FU M, et al. Degeneration By Inhibition Of TGF-beta Signaling In A Mouse Model Of Osteoarthritis. Am J Pathol. 2015; 185(11):2875-2885.
[14] CHEN G, DENG C, LI YP, et al. TGF-beta and BMP signaling in osteoblast differentiation and bone formation. Int J Biol Sci. 2012;8(2):272-288.
[15] SHI L, SUN W, GAO F, et al. Heterotopic ossification related to the use of recombinant human BMP-2 in osteonecrosis of femoral head. Medicine (Baltimore). 2017;96(27):e7413.
[16] 杨武斌. 鹿角胶对hBMP7基因转染的骨髓间充质干细胞的成骨性诱导[D]. 济南:山东中医药大学, 2015.
[17] LEMMA S, SBOARINA M, PORPORATO P, et al. Energy metabolism in osteoclast formation and activity. Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 2016;79: 168-180.
[18] WANG C, SILVERMAN RM, SHEN J, et al. Distinct metabolic programs induced by TGF-β1 and BMP2 in human articular chondrocytes with osteoarthritis. J Orthop Translat. 2018;12:66-73.
[19] CHEN L, HUANG M, TAN J, et al. PI3K/AKT pathway involvement in the osteogenic effects of osteoclast culture supernatants on preosteoblast cells.Tissue Eng Part A. 2013;19(19-20):2226-2232.
[20] ZHANG D, WANG J, ZHOU C, et al. Zebrafish akt2 is essential for survival, growth, bone development, and glucose homeostasis. Mech Dev. 2017;143:42-52.
[21] PARK HH, HAN MH, CHOI H, et al. Mitochondria damaged by Oxygen Glucose Deprivation can be Restored through Activation of the PI3K/Akt Pathway and Inhibition of Calcium Influx by Amlodipine Camsylate. Sci Rep. 2019;9(1):15717.
[22] ZHANG Z, ZHANG X, ZHAO D, et al. TGFβ1 promotes the osteoinduction of human osteoblasts via the PI3K/AKT/mTOR/S6K1 signalling pathway. Mol Med Rep. 2019;19(5):3505-3518.
[23] 瞿麟平. ATP在高糖引起肾脏系膜细胞TGF-β1增加中的作用[D].上海:复旦大学,2008.
[24] 吴惠春,李曼,周振华,等. PI3K/PKB信号通路在TGF-β_1诱导人肝星状细胞表达骨桥蛋白中的作用[J].中国病理生理杂志,2015, 31(1):93-97.
[25] LINDERT U, CABRAL WA, AUSAVARAT S, et al. MBTPS2 mutations cause defective regulated intramembrane proteolysis in X-linked osteogenesis imperfecta. Nat Commun. 2016;7:11920.
[26] LI L, ZHAO D, ZHENG W, et al. A novel missense mutation in P4HB causes mild osteogenesis imperfecta. Biosci Rep. 2019;39(4): BSR20182118.
[27] ZENG Y , ZHANG L , ZHU W , et al. Network based subcellular proteomics in monocyte membrane revealed novel candidate genes involved in osteoporosis. Osteoporos Int. 2017;28(10):3033-3042.
[28] DUBON MJ, YU J, CHOI S,et al. Transforming growth factor β induces bone marrow mesenchymal stem cell migration via noncanonical signals and N-cadherin. J Cell Physiol. 2018;233(1):201-213.
[29] 王永会. 钙粘蛋白与胶原微环境对MSC成软骨早期分化的影响[D].南宁:广西医科大学,2019.
[30] XIANG L, ZHENG J, ZHANG M, et al. FOXQ1 promotes the osteogenic differentiation of bone mesenchymal stem cells via Wnt/β-catenin signaling by binding with ANXA2.Stem Cell Res Ther. 2020;11(1):403.
[31] ZHOU X, WU LF, WANG WY, et al. Anxa2 attenuates osteoblast growth and is associated with hip BMD and osteoporotic fracture in Chinese elderly. PLoS One. 2018;13(3):e0194781.
[32] MIDWOOD KS, CHIQUET M, TUCKER RP, et al.Tenascin-C at a glance.J Cell Sci. 2016;129(23):4321-4327.
[33] 刘洋. 不同界面处理对腱-骨愈合影响及TNC作用机制初步研究[D].重庆:中国人民解放军陆军军医大学,2017.
[34] GUO Y, YAN B, GUI Y, et al. Physiology and role of PCSK9 in vascular disease: Potential impact of localized PCSK9 in vascular wall. J Cell Physiol. 2021;236(4):2333-2351.
[35] DEMERS A, SAMAMI S, LAUZIER B, et al. PCSK9 induces CD36 degradation and affects long-chain fatty acid uptake and triglyceride metabolism in adipocytes and in mouse liver. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2015;35(12):2517-2525.
[36] JANG YJ, AN SY, KIM JH. Identification of MFGE8 in mesenchymal stem cell secretome as an anti-fibrotic factor in liver fibrosis. BMB Rep. 2017; 50(2):58-59.
[37] 祝皓. 痹肿消汤及其有效成分阿魏酸干预胶原诱导性关节炎大鼠的定量蛋白质组学研究[D].长沙:中南大学,2014.
[38] Gemert VY, Kozijn AE, Pouwer MG, et al. Novel high-intensive cholesterol-lowering therapies do not ameliorate knee OA development in humanized dyslipidemic mice.Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2021;S1063-4584.
[39] 李晶, 李娜, 律广富, 等. 鹿角胶对环磷酰胺所致血虚模型小鼠的影响[J].吉林中医药,2014,34(10):973-975.
[40] 李辉, 陈俊宇, 杨擎, 等.鹿角胶对脑缺血大鼠脑组织的保护作用及机制[J].中国老年学杂志,2016,36(16):3895-3897.
|
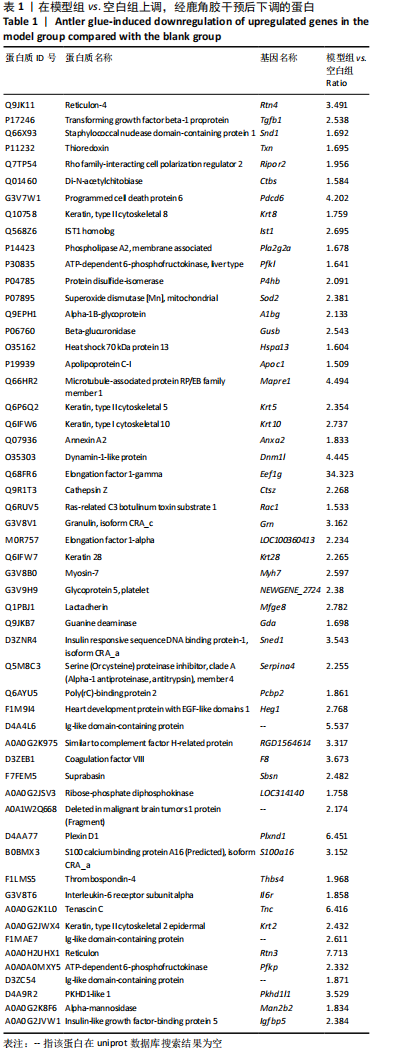
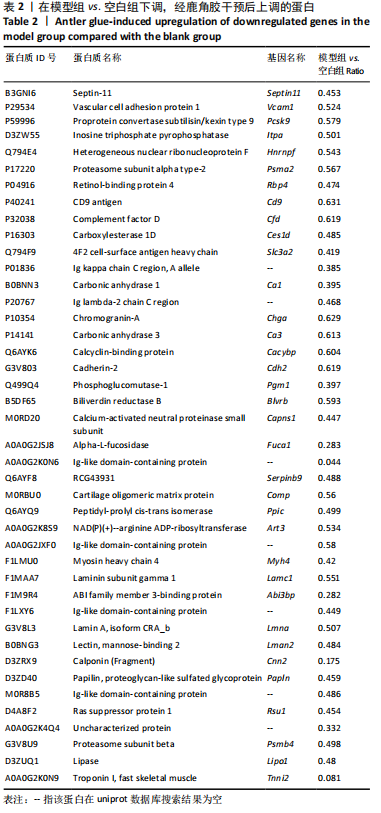
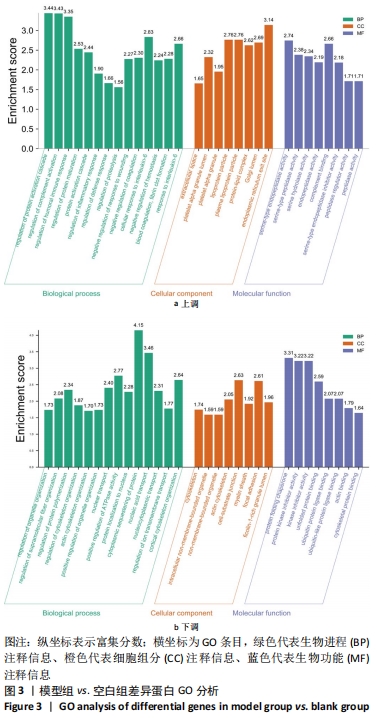
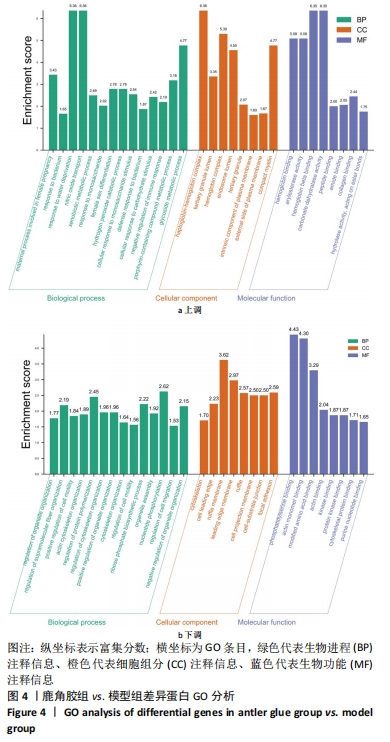
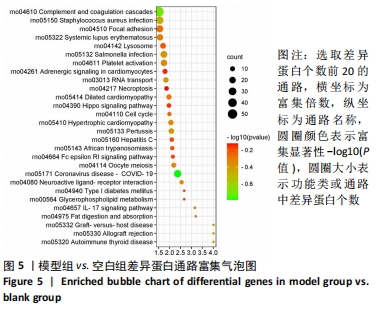
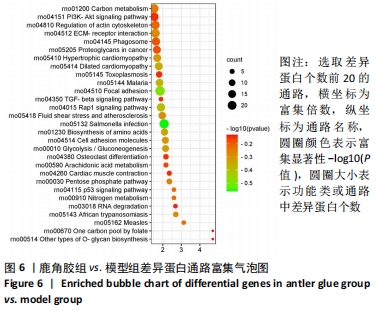
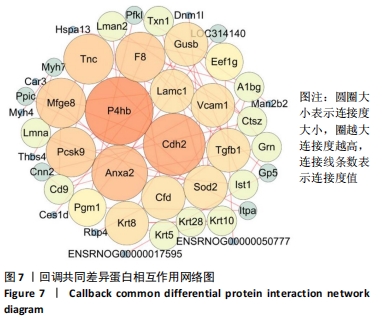

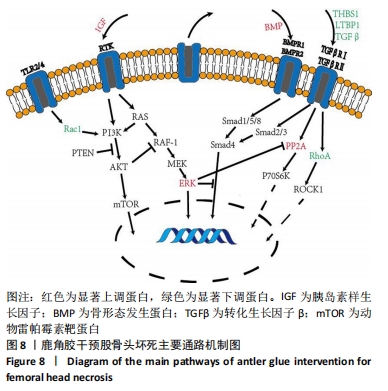 通过对回调的共同差异表达蛋白功能富集发现,蛋白质二硫键异构酶(P4HB)、钙黏蛋白2(CDH2)、膜联蛋白A2(ANXA2)、前蛋白转化酶枯草杆菌蛋白酶9型(PCSK9)、乳脂球-表皮生长因子8(MFGE8)等连接度较高。P4HB是编码脯氨酰4-羟化酶膜蛋白β亚基的蛋白编码基因,可改变细胞内外的蛋白质结构,在细胞黏附和细胞迁移中发挥重要作用。P4hb基因缺失可导致增加成纤维细胞中热休克蛋白47的表达升高,导致成骨细胞功能障碍,并导致骨形成缺陷和骨脆性[25]。此外,p4hb突变还会破坏Ⅰ型胶原三螺旋结构的形成,引发骨不全症[26]。P4HB可以从血液迁移到骨骼并分化成破骨细胞,破骨细胞在骨骼维持和体内平衡方面起着关键作用[27]。
通过对回调的共同差异表达蛋白功能富集发现,蛋白质二硫键异构酶(P4HB)、钙黏蛋白2(CDH2)、膜联蛋白A2(ANXA2)、前蛋白转化酶枯草杆菌蛋白酶9型(PCSK9)、乳脂球-表皮生长因子8(MFGE8)等连接度较高。P4HB是编码脯氨酰4-羟化酶膜蛋白β亚基的蛋白编码基因,可改变细胞内外的蛋白质结构,在细胞黏附和细胞迁移中发挥重要作用。P4hb基因缺失可导致增加成纤维细胞中热休克蛋白47的表达升高,导致成骨细胞功能障碍,并导致骨形成缺陷和骨脆性[25]。此外,p4hb突变还会破坏Ⅰ型胶原三螺旋结构的形成,引发骨不全症[26]。P4HB可以从血液迁移到骨骼并分化成破骨细胞,破骨细胞在骨骼维持和体内平衡方面起着关键作用[27]。