中国组织工程研究 ›› 2022, Vol. 26 ›› Issue (11): 1641-1647.doi: 10.12307/2022.345
• 骨组织构建 bone tissue construction • 下一篇
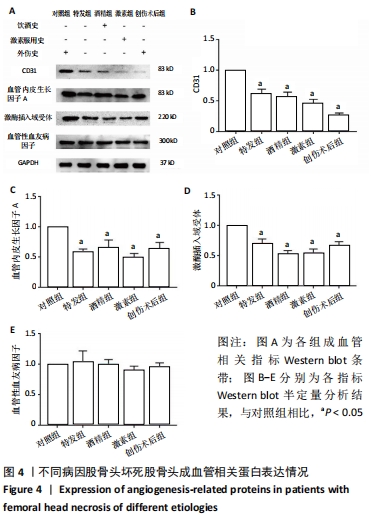
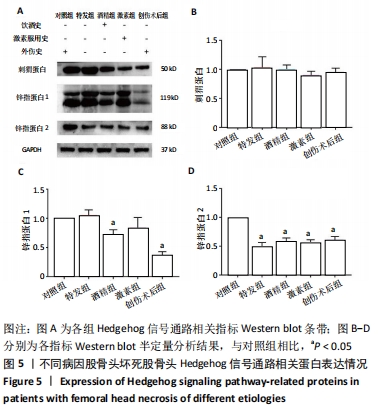
不同病因股骨头坏死样本成骨与成血管相关指标蛋白表达的差异
骆 帝1,2,梁学振1,2,刘金豹2,李嘉程2,阎博昭2,许 波2,李 刚1,2
- 1山东中医药大学附属医院,山东省济南市 250014;2山东中医药大学,山东省济南市 250355
Difference in osteogenesis- and angiogenesis-related protein expression in femoral head samples from patients with femoral head necrosis of different etiologies
Luo Di1, 2, Liang Xuezhen1, 2, Liu Jinbao2, Li Jiacheng2, Yan Bozhao2, Xu Bo2, Li Gang1, 2
- 1Affiliated Hospital of Shandong University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Jinan 250014, Shandong Province, China; 2Shandong University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Jinan 250355, Shandong Province, China
摘要:

文题释义:
股骨头坏死:是指由于不同病因破坏了股骨头血液供应,导致股骨头发生部分或完全性缺血,骨结构成分包括骨细胞、骨髓造血细胞及脂肪细胞坏死的病理过程。常见的类型有:激素性股骨头坏死、酒精性股骨头坏死、创伤性股骨头坏死。
免疫蛋白印迹法:是分子生物学、生物化学和免疫遗传学中常用的一种实验方法。其基本原理是通过特异性抗体对凝胶电泳处理过的细胞或生物组织样品进行着色,通过分析着色位置和着色深度获得特定蛋白质在所分析细胞或组织中表达情况的信息。
背景:股骨头坏死病因与发病机制尚不明确,急待开展深入研究加以探索。
目的:检测全髋关节置换后坏死股骨头样本中坏死区骨组织Hedgehog信号通路、成骨与成血管相关标志物的蛋白表达情况,尝试探究酒精、激素与创伤等不同因素致病的机制,为后续临床对股骨头坏死的防治提供理论支持。
方法:收集山东中医药大学附属医院在2017年12月至2019年12月接受全髋关节置换后的股骨头坏死与股骨颈骨折患者的股骨头样本,挑选符合纳入标准的股骨头按病因分别归入对照组、特发组、酒精组、激素组以及创伤术后组,采用Western blot法检测不同病因坏死骨组织中Hedgehog信号通路、成骨与成血管相关指标的蛋白表达情况。
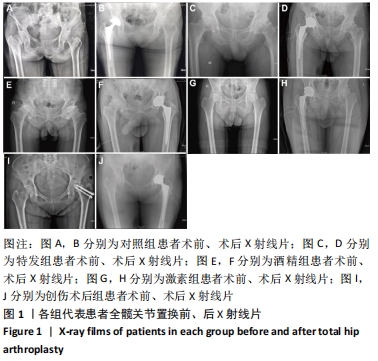
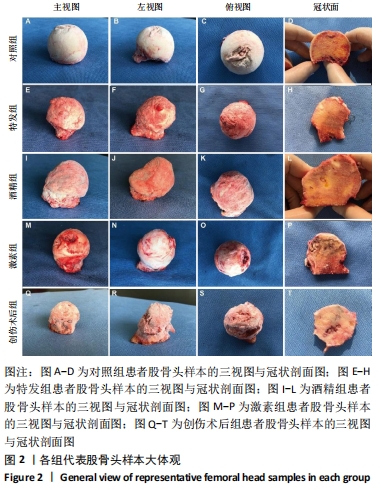
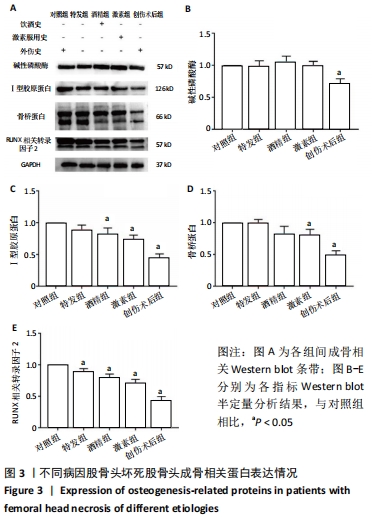
结果与结论:①通过观察各组股骨头样本的大致形态与冠状面,发现不同病因股骨头坏死患者股骨头样本在大致形态与剖面具有较为相似的病理表现,同时有相似的坏死和修复的组织学特征;②Western blot结果示,在不同病因股骨头坏死患者股骨头样本中成骨相关指标碱性磷酸酶、Ⅰ型胶原蛋白、骨桥蛋白及RUNX2,成血管相关指标CD31、血管内皮生长因子A与激酶插入域受体、血管性血友病因子,以及Hedgehog信号通路指标刺猬蛋白、锌指蛋白1、锌指蛋白2的蛋白表达水平相较于对照组均出现了不同程度的改变;③结果证明股骨头坏死的发生发展与成骨、成血管以及Hedgehog信号通路之间或存在着密切关联,而更深层机制则有待进一步研究。
缩略语:RUNX相关转录因子2:runt-related transcription factor 2,RUNX2;激酶插入域受体:kinase insert domain receptor,KDR
https://orcid.org/0000-0002-3231-8879 (骆帝)
中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:组织构建;骨细胞;软骨细胞;细胞培养;成纤维细胞;血管内皮细胞;骨质疏松;组织工程
中图分类号: