中国组织工程研究 ›› 2024, Vol. 28 ›› Issue (36): 5884-5891.doi: 10.12307/2024.693
• 骨与关节综述 bone and joint review • 上一篇 下一篇
经皮椎体成形后邻近椎体压缩骨折的危险因素
柳栋元,关海山,史浩冉,刘晓亮,周浩盛
- 山西医科大学第二附属医院骨科,山西省太原市 030001
-
收稿日期:2023-10-08接受日期:2023-11-29出版日期:2024-12-28发布日期:2024-02-28 -
通讯作者:关海山,主任医师,山西医科大学第二医院骨科,山西省太原市 030001 -
作者简介:柳栋元,男,1999 年生,山西省运城市人,汉族,山西医科大学在读硕士,主要从事脊柱外科方面研究。
Risk factors for adjacent vertebral compression fractures after percutaneous vertebroplasty
Liu Dongyuan, Guan Haishan, Shi Haoran, Liu Xiaoliang, Zhou Haosheng
- Department of Orthopedics, Second Hospital of Shanxi Medical University, Taiyuan 030001, Shanxi Province, China
-
Received:2023-10-08Accepted:2023-11-29Online:2024-12-28Published:2024-02-28 -
Contact:Guan Haishan, Chief physician, Department of Orthopedics, Second Hospital of Shanxi Medical University, Taiyuan 030001, Shanxi Province, China -
About author:Liu Dongyuan, Master candidate, Department of Orthopedics, Second Hospital of Shanxi Medical University, Taiyuan 030001, Shanxi Province, China
摘要:
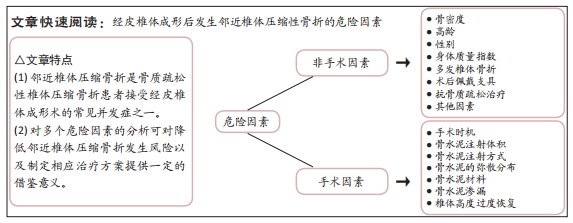
文题释义:
经皮椎体成形术:是指在X射线透视下,使用穿刺针经皮肤穿刺,通过椎弓根建立工作通道,向伤椎内注入骨水泥以达到增强椎体强度和稳定性、防治椎体塌陷、有效恢复椎体高度目的的治疗骨质疏松压缩性椎体骨折的一种脊柱外科微创技术,具有简单易施行、开放创伤小、镇痛速度快及手术疗效好的优点。邻近椎体压缩骨折:是指骨质疏松性椎体压缩骨折患者在接受经皮椎体成形术治疗后,由于存在某些危险因素,导致手术椎体相邻节段椎体的再次骨折,引起患者腰背部疼痛,降低生活质量,是经皮椎体成形术的常见并发症之一。
背景:经皮椎体成形术是治疗骨质疏松性椎体压缩骨折应用最广泛的方法,多数研究认为经皮椎体成形术会增加继发性邻近椎体压缩骨折的概率。然而,对于经皮椎体成形术后引起的邻椎再骨折相关危险因素仍然存在争议。
目的:归纳并总结骨质疏松性椎体压缩骨折患者行经皮椎体成形术后邻近椎体再发骨折的影响因素,为降低其发生风险以及制定相应治疗方案提供一定的参考。方法:以“骨质疏松症,骨折,经皮椎体成形术,邻近椎体压缩骨折,危险因素”为中文检索词,以“osteoporosis,osteoporotic vertebral compression fractures,percutaneous vertebroplasty,adjacent vertebral compression fractures,risk factors”为英文检索词,应用计算机检索中国知网、万方医学网、维普、PubMed、Springer、ScienceDirect及Elsevier数据库收录的相关文献。检索时限重点为2018年1月至2023年9月,同时纳入少数经典远期文献。通过阅读文题和摘要进行筛选,最终纳入83篇文献进行综述。
结果与结论:①骨质疏松性椎体压缩骨折是骨质疏松症最常见的并发症之一,使老年患者致残和死亡的风险显著增加。经皮椎体成形术是治疗骨质疏松性椎体压缩骨折切实有效的方法。②随着经皮椎体成形术的普及,继发椎体压缩性骨折也逐渐增多,以邻近椎体压缩骨折最为常见。③以往的研究仅讨论了骨密度、多发椎体骨折、身体质量指数、年龄、性别、骨水泥的用量、骨水泥渗漏及抗骨质疏松治疗等因素对经皮椎体成形术后继发邻近椎体压缩骨折的影响,而对于椎体骨折数量、手术时机、手术方式、骨水泥材料、骨水泥弥散分布、伤椎恢复高度和术后佩戴支具等方面总结的尚不全面,并且对危险因素引起邻椎骨折的具体机制分析也较为少见。④文章结果表明,骨密度过低、高龄、围绝经期女性、多发椎体骨折、伤椎高度的过度恢复、骨水泥渗漏、合并基础疾病及不良的生活习惯是经皮椎体成形术后继发邻近椎体压缩骨折的危险因素,保持正常的身体质量指数、早期手术、双侧经皮椎体成形术、使用新型骨水泥材料、适宜的骨水泥注射体积、均匀的骨水泥弥散分布、规律抗骨质疏松治疗和术后佩戴支具是经皮椎体成形术后继发邻近椎体压缩骨折的保护因素。
https://orcid.org/0009-0001-0122-3703 (柳栋元)
中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:人工关节;骨植入物;脊柱;骨折;内固定;数字化骨科;组织工程
中图分类号:
引用本文
柳栋元, 关海山, 史浩冉, 刘晓亮, 周浩盛. 经皮椎体成形后邻近椎体压缩骨折的危险因素[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2024, 28(36): 5884-5891.
Liu Dongyuan, Guan Haishan, Shi Haoran, Liu Xiaoliang, Zhou Haosheng. Risk factors for adjacent vertebral compression fractures after percutaneous vertebroplasty[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(36): 5884-5891.
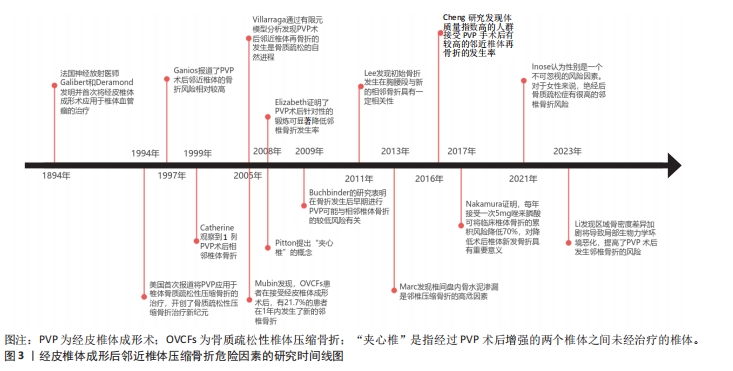
2.2 影响经皮椎体成形后邻近椎体压缩骨折的非手术因素
2.2.1 骨密度 是指单位面积(面积密度,g/cm2)或单位体积(体积密 度,g/cm3)所含的骨量,是判断骨代谢的重要指标。刘畅等[12]应用受试者工作特征曲线分析了骨密度T-值与椎体成形术后疗效的关系,该分析的诊断准确度值为0.809,敏感度和特异度分别为0.721和 0.836,这提示骨密度T-值在邻近椎体压缩骨折危险因素的研究中具有较高的价值和意义。CHEN等[13]对110例接受经皮椎体成形术治疗的OVCFs患者进行了为期3年的随访,研究根据有无继发椎体骨折分为2组,即骨折组和非骨折组,每组均包含55例患者,两组脊柱椎体T-值平均值分别为为-3.54和-4.25(P < 0.01),这表明椎体骨密度T-值降低会增加椎体成形术后邻近椎体压缩骨折的发生风险。PARK等[8]通过实验也得出了类似的结论。然而,近年来人们逐渐认识到双能X射线吸收测定法的缺点,退行性疾病,包括骨赘、骨质硬化和严重的椎间盘突出会显著影响骨密度测量结果的准确性,除了使用T-值反映骨密度外,术前CT成像中测量的Hounsfield单位(HU)值也被推荐作为反映患者骨密度和相关骨折风险的可靠指标,提供了更有价值的诊断信息。在一项回顾性研究中,CHENG等[14]得出结论,低HU值是椎体成形术后邻近椎体继发性压缩骨折的一个独立危险因素。LI等[15]构建了腰椎有限元模型,分别测量相邻椎体从上终板到下终板的各个横向平面的HU值,将这些平面的最高和最低HU值之间的差值作为HU值的最大差异,即骨密度的区域差异,以此来评估相邻节段椎体的刚度差异。随着相邻松质骨HU值的最大差异的增加,会使椎体局部生物力学环境发生变化,导致椎体成形术后继发邻近椎体压缩骨折的风险升高。因此,对于接受经皮椎体成形术治疗的胸腰椎椎体骨质疏松性椎体压缩骨折患者,可以定期测量其相邻松质骨T-值及HU值的最大差异,以更好地预测邻近椎体压缩骨折的发生风险。
2.2.2 高龄 国内外研究表明,高龄是椎体成形术后继发邻椎骨折的独立危险因素[10]。这可能是因为接受椎体成形术治疗的高龄OVCFs患者吸收的钙逐渐减少,但排出的钙却日益增加,使得血钙降低,引起继发性甲状旁腺激素水平升高,最终导致钙离子在骨骼中沉积减少,骨量流失[16];另一方面,老年人通常会合并不同程度的营养不良,对伤害应激反应能力下降,导致了自身修复能力降低及脊柱承受力低下,跌倒率升高,这使得椎体成形术后邻椎再骨折风险显著增加[17]。LI等[18]的研究共纳入了412例患者,其中邻近椎体压缩骨折组(n=68)患者的平均年龄为(71.8±6.7)岁,非邻近椎体压缩骨折组(n=322)患者的平均年龄为(69.5±7.2)岁,两组患者年龄差异有显著性意义(P < 0.05)。随着年龄每增加1岁,再骨折发生率就增加1.996倍[19]。因此,在初次OVCFs治疗期间应密切关注高龄患者,椎体成形术后的健康管理和营养补充是一种潜在有效的邻近椎体压缩骨折的预防策略。
2.2.3 性别 邻近椎体压缩骨折发病率与患者性别显著相关,研究发现,女性尤其是绝经后妇女椎体成形术后更容易发生邻近椎体再骨折[20]。根据2018年中国骨质疏松症的流行病学调查统计数据,50岁以上的人群中,患有骨质疏松症的比例为19.2%。具体而言,男性患病率为6.0%,而女性的患病率则为32.1%,女性患病率明显高于男性。造成这种差异的原因主要与女性围绝经期生理特征有关,在这一时期,女性卵巢功能开始衰退,体内雌激素水平逐渐降低,使得破骨细胞活性增强而刺激成骨作用减弱,钙磷沉积减少,导致骨量降低,骨微结构破坏,骨脆性增加,较同年龄段男性骨质疏松更为严重,这使得绝经后女性椎体成形术后发生邻近椎体继发骨折的概率显著提高。ZHANG等[7]对2 216例行经皮椎体成形术的老年患者进行回顾性分析发现,有227例(占总数的10.2%)患者在12-24周随访中继发邻近节段椎体骨折,其中女性203例,占邻近椎体压缩骨折患者总数的89.4%,远远高于男性的10.6%。因此,对于高龄女性患者来说,需要告知其术后邻近椎体压缩骨折风险高,应缩短复查间期,延长复查时间,若再次出现腰背部疼痛不适及活动受限,应该尽快就诊。
2.2.4 身体质量指数 体质量指数对于接受经皮椎体成形术OVCFs患者术后邻近椎体再骨折发生率的影响目前仍未有定论。有研究发现,椎体成形术后邻近椎体继发骨折组体质量指数为(21.55±2.20) kg/m2,而无骨折组为(22.61±2.64) kg/m2,差异有显著性意义(P < 0.05),这表明低身体质量指数将导致OVCFs患者椎体成形术后邻近椎体再骨折[9]。这可能是因为低身体质量指数患者肌肉和脂肪的分解代谢增加,导致平衡和行走能力下降,更易跌倒,并且通常低身体质量指数患者的骨密度和维生素D水平也较低,抗骨折能力较弱,在相同的外界条件下更容易发生邻近椎体的骨折。但也有研究认为高身体质量指数人群椎体会受到更高的应力,在接受椎体成形手术后有较高邻近椎体压缩骨折的发生率[21]。REN等[22]的研究发现椎体成形术后邻近椎体继发骨折组和无骨折组身体质量指数平均值分别为23.7 kg/m2和21.6 kg/m2,组间比较差异有显著性意义(P=0.01),故其认为高身体质量指数是椎体成形术后继发邻近椎体压缩骨折的危险因素。总之,身体质量指数过低或过高都会增加罹患椎体成形术后邻椎再骨折风险,故保持适宜的身体质量指数和健康的营养状态对于降低邻近椎体压缩骨折的发生率有着积极意义。
2.2.5 多发椎体骨折 李春涛等[23]指出,伤椎数量越多,在椎体成形术后对邻椎负荷的影响越大,继发邻近椎体压缩性骨折的发生率就越高。初始多个椎体骨折的OVCFs患者接受经皮椎体成形术后邻近椎体压缩骨折发生风险是单个椎体骨折患者的1.92倍[24]。夹心椎(即通过椎体成形术后增强的2个椎体之间未经治疗的椎体)是经皮椎体成形术的一种特殊类型邻椎,其上下终板均与强化椎相邻,由Pitton于2008年率先提出这一概念。既往研究认为,由于其头、尾两端椎体的强化和垂直弹性的丧失,应力会向夹心椎上下终板显著集中,对夹心椎产生更大的压力负荷,因此夹心椎相较于普通多个椎体骨折更易继发邻椎的再骨折,是邻近椎体压缩骨折的重要风险因素[5]。刘进等[25]的研究证明,普通邻椎再骨折的相对危险度是非邻椎的2.239倍,而夹心椎相对于非邻椎来说更易继发再骨折,其相对危险度为非邻椎的3.688倍,被骨水泥填充的相邻两个椎体形成的夹心椎再骨折的发生率要高于普通邻椎。另外,CHIU等[26]的一项回顾性研究发现1 347例OVCFs患者中,椎体成形术后夹心椎骨折发生率达到了惊人的21.3%,研究还指出,夹心椎继发骨折的平均时间为术后1.5个月。此外,男性患者比女性患者发生夹心椎骨折的概率更高。因此,对于初始多个椎体骨折尤其是存在“夹心椎”患者,必须提前告知椎体成形术后继发邻近椎体压缩骨折风险较高,督促患者术后早期复查。
2.2.6 术后佩戴支具 椎体成形术后常规佩戴支具能够限制腰背部的活动,从而减少椎体压力,有效恢复压缩椎体高度。此外,支具还可以缓解术后残留疼痛,辅助患者早期进行功能锻炼,显著降低邻椎再骨折的风险,提高预后水平。支具佩戴时间与邻近椎体压缩骨折的发生风险具有一定的相关性。GUO等[27]发现与未佩戴支具组相比,佩戴支具组的目测类比评分(visual analogue scale,VAS)、功能障碍指数(oswestry disability index,ODI)和日本骨科协会(Japanese Orthopaedic Association,JOA)评分显著增加(P < 0.05),邻近椎体压缩骨折发生率也要低于未佩戴支具组(P < 0.05),除此之外,还发现软支具组和硬支具组再骨折发生率无显著性差异(P > 0.05),但软支具组JOA评分改善优于硬支具组(P < 0.05)。姜天淇等[28]的一项回顾性研究共纳入了178 例OVCFs患者,出现邻近椎体继发骨折29例,该研究多元Logistic回归分析结果显示,术后支具佩戴时间< 2个月是邻近椎体压缩骨折的危险因素之一。因此,作者建议,椎体成形术后患者应至少规律佩戴支具2个月,从而恢复脊柱的功能性与稳定性,减少邻近椎体压缩骨折的发生。但值得注意的是,支具佩戴时间的延长可能会带来腰背部肌力下降、压疮、接触性皮炎等不良反应,甚至可能增加再骨折率,故椎体成形术后支具佩戴的最佳时间仍是一个应当讨论和研究的问题。
2.2.7 抗骨质疏松治疗 OVCFs患者早期和针对性抗骨质疏松治可以显著增加骨密度,有效恢复术后功能,提高生活质量,在预防邻近椎体压缩骨折中起着关键作用。一项回顾性队列研究纳入了2015-2019年期间接受椎体成形术治疗症状性OVCFs的2 202例住院患者,其中362例术后新发椎体骨折患者(16.43%)为骨折组,其他1 840例术后无新发椎体骨折患者为非骨折组,骨折组患者接受规律抗骨质疏松治疗的比例(21.3%)明显低于非骨折组(39.7%),这说明规律抗骨质疏松治疗是有效避免OVCFs 患者椎体成形术后再次发生椎体压缩骨折的保护性因素[29]。通过多因素Logistic回归分析,JI等[30]研究发现,椎体成形术后是否规律使用抗骨质疏松药物治疗的两组间比较差异具有显著性意义,这证实了术后规律抗骨质疏松治疗可以有效降低邻近椎体的骨折风险。HEINI等[31]通过对比接受抗骨质疏松治疗与未接受抗骨质疏松治疗的OVCFs患者发现,后者椎体成形术后邻近椎体压缩骨折的发生率是前者的4倍。目前,钙剂、维生素D、维生素K2、骨吸收抑制剂(如双膦酸盐类、降钙素和选择性雌激素受体调节剂)及骨形成促进剂(特立帕肽)等药物在常规临床实践中用于治疗骨质疏松。NAKAMURA等[32]发现,唑来膦酸作为第三代双膦酸盐制剂,每年服用5 mg可将临床新发椎体骨折的累积风险降低70%。根据椎体成形术后是否采用唑来膦酸联合维生素K2对OVCFs患者进行抗骨质疏松治疗,HUANG等[33]将患者分为实验组和对照组,并发现实验组的邻近椎体压缩骨折发生率明显低于对照组(P < 0.05),这表明唑来膦酸联合维生素K2方案可以用于OVCFs患者经皮椎体成形术后的抗骨质疏松治疗,疗效肯定,安全系数高。SU等[34]发现32例OVCFs患者接受经皮椎体成形术新发相邻椎体压缩性骨折,使用特立帕肽抗骨质疏松治疗18个月后腰椎骨密度增加26.32%,骨吸收抑制剂治疗18个月后增加4.62%。一项为期1年的前瞻性研究表明,特立帕肽联合阿仑膦酸钠的短序治疗能够有效地提高骨密度,降低经皮椎体成形术后骨质疏松患者的再骨折率,是预防邻近椎体压缩骨折的有效策略[11]。此外,有研究发现,骨形成促进剂同骨吸收抑制剂相比较,在降低邻近椎体压缩骨折的发生风险方面表现出更大的优势[35]。对于患有严重骨质疏松症的老年患者,必须仔细评估经皮椎体成形术后继发邻近椎体压缩骨折的风险,并应接受骨质减少或骨质疏松症的最佳医疗管理。
2.2.8 其他因素 合并高血压、糖尿病、慢性阻塞性肺疾病、自身免疫性疾病、既往骨折病史等基础疾病及有吸烟、饮酒等不良生活习惯的OVCFs患者在接受椎体成形术后,发生邻近椎体压缩骨折的概率将会明显提升,而户外活动及腰背肌锻炼是邻近椎体压缩骨折的保护因素。高血压一方面会明显促进心脑血管意外的发生,从而增加患者跌倒发生邻椎再骨折的风险,另一方面,高血压疾病患者,通常会伴有同型半胱氨酸水平的增高,GAO等[36]认为高水平的同型半胱氨酸可能会对患者注射骨水泥后的恢复能力产生不利影响,降低手术疗效。糖尿病患者椎体成形术后保持良好的血糖水平对于防止新骨折的发生至关重要,高血糖会导致全身代谢紊乱,既往实验表明,糖尿病可通过破坏成骨平衡,形成炎症和活性氧微环境,干扰钙、磷等矿物质代谢,抑制骨微血管血供,加剧骨代谢和骨质疏松,增加再骨折率[37]。LI等[18]进行的一项回顾性研究,发现邻近椎体压缩骨折组与非邻近椎体压缩骨折组在慢性阻塞性肺疾病方面存在显著性差异(P < 0.05),邻近椎体压缩骨折组慢性阻塞性肺疾病患者比例多于非邻近椎体压缩骨折组。自身免疫性疾病患者通常会将糖皮质激素作为一线治疗用药,一项前瞻性实验纳入了141例接受椎体成形术治疗OVCFs患者,其中70例服用糖皮质激素,71例未服用,经过2年的随访发现,有31例服用糖皮质激素和16例未服用糖皮质激素的患者出现了新的椎体骨折,累计发病率分别为44.3%和22.5%,表明与未接受糖皮质激素治疗的OVCFs患者相比,接受治疗的患者邻近椎体压缩骨折风险增加了1倍[38]。有既往骨折病史患者,相较于无骨折病史患者的骨强度较低,因此更易继发邻近椎体骨折。一项回顾性研究共纳入了204例OVCFs患者,分为2组,术后再骨折组共有33例患者,其中24例有既往骨折病史,而非骨折组共有171例患者,既往有骨折病史的仅有62例,骨折组既往骨折病史的比例是非骨折组的2倍,通过多因素Logistic回归分析发现,有既往骨折病史是OVCFs患者发生邻近椎体压缩骨折的单危险因素和独立危险因素(OR=2.532)[39]。COSTA-RODRIGUES等[40]通过对15 907份血液样本进行基因测试,结果表明烟草会使椎体成形术后邻近椎体骨折风险增加,主要是由于烟草中的有害物质会导致DNA甲基化,从而影响骨组织的再生和转化,导致或加重骨质疏松症,引起椎体的再骨折。但这种影响是可逆的,KIYOTA等[41]研究证实,吸烟引起的骨稳态破坏在戒烟后可以逐渐恢复。既往研究显示乙醇会影响骨骼重塑过程,从而引起骨量减少[42]。CHEN等[43]研究发现大多数继发椎体骨折患者的户外活动时间处于低水平。有研究表明,每天户外活动少于0.5 h的邻近椎体压缩骨折发生风险比超过0.5 h的风险增加1.73倍[44]。术后腰背肌锻炼可以改善体质,减轻疼痛,促进椎体高度恢复,它还可以帮助维持骨密度,从而显著降低邻椎再骨折的风险[45]。因此,保持身体健康,摒弃不良生活习惯,戒烟禁酒,降低基础病的发病率,并进行中高水平的户外活动及腰背肌锻炼有利于减少经皮椎体成形术后引起的邻近椎体再骨折事件。
2.3 影响经皮椎体成形后邻近椎体压缩骨折的手术因素
2.3.1 手术时机 有研究表明,骨质疏松性压缩骨折后的手术时机与相邻椎体再骨折的发生密切相关[46]。GAO等[36]通过研究证明损伤至手术时间超过7 d是中老年OVCFs患者接受经皮椎体成形术治疗后发生邻近椎体压缩骨折的独立危险因素。HE等[47]进行的一项回顾性队列研究纳入了早期椎体成形术手术组(≤21 d)的118例患者和晚期椎体成形术手术组的72例患者(> 21 d),随访时间至少为4年,发现早期手术时机组的邻近椎体再骨折率显著低于晚期手术时机组。而YANG等[48]认为OVCFs发生后30 d内进行椎体成形术可能与胸腰段相邻骨折的风险较低有关。如今关于骨质疏松导致胸腰椎椎体压缩骨折后,接受经皮椎体成形术治疗的最佳时间仍尚未有定论。
2.3.2 骨水泥注射体积 关于骨水泥注射体积对邻椎继发骨折的影响,国内外学者有不同的看法。MA等[49]认为骨水泥注射量不足会使骨水泥在骨折椎体中发生不均匀扩散,导致内部结构不稳定,从而改变椎弓根直径的比例以及椎体的前后高度,使脊柱生物力学发生改变,增加术后邻近椎体压缩骨折的风险。一项回顾性研究将接受椎体成形术治疗的76例OVCFs患者分为2组,其中26例患者存在邻近椎体继发骨折,骨折组骨水泥注射量为(3.61±1.52) mL,未骨折组包括50例患者,骨水泥注射量为(4.96±1.62) mL,组间差异有显著性意义(P=0.001),因此骨水泥注射量低是OVCFs患者邻近椎体压缩骨折的危险因素[50]。但也有研究表明,高体积的骨水泥可能会增加伤椎的硬度,从而改变椎体表面的应力分布,导致邻椎的应力也发生改变,加速相邻椎间盘加速,进而增加相应的骨水泥渗漏和邻椎骨折的发生率[51]。LI等[52]的一项为期2年的回顾性研究表明骨水泥体积过大(> 4.5 mL)和不足(< 4 mL)均为邻近椎体继发性压缩骨折的独立危险因素。对于最佳骨水泥注射体积,SUN等[53]认为4-6 mL体积的骨水泥可最大限度地恢复骨折和相邻椎体的正常应力分布,此时体积分数(骨折椎体内的骨水泥体积/椎体体积)达到19.78%,可以实现满意的骨水泥分布,有效减少水泥渗漏的发生。ZHOU等[54]通过回顾性研究发现较大侧骨水泥注射体积/椎体体积(LSBCV/VBV%)比值为13.82%时,邻近椎体压缩骨折的发生率显著增加。LEE等[55]的研究也得到了类似的结论。对于不同部位椎体骨折的最佳骨水泥注射体积,有研究显示在保证穿刺针穿透骨折线的前提下,胸椎中骨水泥的体积应为2.0-3.0 mL,腰椎中骨水泥体积应为3.0-4.0 mL,此时椎体成形术后邻近椎体压缩骨折的风险最低[6]。因此,在缓解伤椎后凸畸形和椎体高度方面不必追求过多的骨水泥灌注量,适宜的骨水泥注射体积对降低术后邻近椎体压缩骨折的发生风险有着十分重要的意义。
2.3.3 骨水泥注射方式 在临床实践中,经皮椎体成形术被广泛用于治疗骨质疏松性椎体压缩骨折,包括单侧经皮椎体成形术和双侧经皮椎体成形术,均被证实是治疗OVCFs的有效手术方法,可以迅速控制疼痛来提高这一患者群体的生活质量。但就不同骨水泥注射方式对邻近椎体压缩骨折风险的影响,目前国内外研究仍有着不同的结论。有学者研究发现接受单侧经皮椎体成形术的治疗组,其术后邻椎骨折发生率较接受双侧经皮椎体成形术的治疗组高[56],这可能是由于单侧经皮椎体成形术会导致椎体内骨水泥的不均匀分布,不利于椎体高度及Cobb角的恢复和维持,增加相邻椎体的进一步塌陷的风险[57]。DAI等[58]通过有限元方法比较了双侧经皮椎体成形术和单侧经皮椎体成形术之间的生物力学差异,结果表明,与单侧经皮椎体成形术相比,双侧经皮椎体成形术会在骨折区域提供更为对称的骨水泥分布,从而在恢复脊柱稳定性,减缓相邻椎间盘退变,降低邻近椎体应力,减少邻椎骨折的发生风险方面更具有生物力学优势。MO等[59]也在一项回顾性队列研究中强调了双侧经皮椎体成形术的重要性。但也有学者认为单侧经皮椎体成形术与邻近椎体压缩骨折的发生率增加无相关性,并且同双侧经皮椎体成形术相比,单侧经皮椎体成形术在缩短手术及辐射暴露时间、减少术中失血、降低骨水泥注射量以预防骨水泥渗漏和术后邻椎再骨折的发生等方面更具一定优势,治疗OVCFs表现出更好的安全性和有效性[60],故对于患者体质较差或合并肺部疾病等不能耐受较长时间俯卧的情况,为缩短治疗时间,可以采取单侧经皮椎体成形术作为首选术式。
2.3.4 骨水泥的弥散分布 椎体内骨水泥良好的弥散分布是脊柱生物力学平衡维持和骨折椎体刚度重建的关键,可以更好地缓解患者疼痛,促进椎体功能的恢复,改善生活质量,最大限度地减少邻椎继发骨折。既往研究认为,椎体成形术后骨水泥理想分布是呈现弥散型或混合型形态特征,广泛填充并充分覆盖骨折线区域,双侧均匀连续分布于椎体前柱,并同时接触上下椎板中间部[61]。目前临床上采用骨水泥分布指数(distribution index,DI)作为评价椎体成形术后骨水泥分布的参数,共分为5级[62],见表2。骨水泥分布指数的值越高,则说明骨水泥在椎体中的分布越均匀。
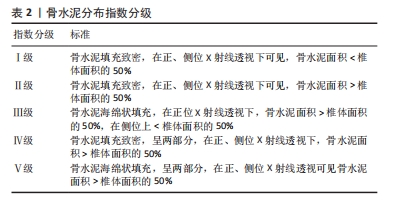
研究结果表明,实施经皮椎体成形术治疗骨质疏松性椎体压缩骨折的患者骨水泥分布指数偏低与术后邻椎继发骨存在一定的的关联[63]。椎体成形术所使用的高硬度骨水泥会导致强化椎头尾两端节段椎体、椎间盘及小关节应力的改变,而骨水泥的不均匀分布会使这种应力改变更为显著,从而增加了邻近椎体骨折的发生风险[64]。ZHOU等[65]的研究发现椎体成形术后的邻椎再骨折主要发生在Ⅳ和Ⅴ型患者中。蒋学国[66]对162例行椎体成形术的OVCFs患者随访1年以上发现,共有19例发生邻椎骨折,发生率为 11.7%。经过分析,发现骨水泥分布指数为Ⅰ级发生邻近椎体再骨折的患者共有7例,Ⅱ级11例,Ⅲ级仅有1例,而Ⅳ级和Ⅴ级并未观察到任何患者,这表明骨水泥 DI≤Ⅲ级时,可能会增加邻椎骨折的风险。付兆宗等[67]在骨水泥分布指数对椎体成形术后症状性邻近节段骨折影响的研究中,经过Logistic回归分析评价,结果表明骨水泥分布指数越高,椎体成形术后继发邻近椎体压缩骨折的风险越低,随着骨水泥分布指数每升高一级,邻近椎体压缩骨折发生的风险就下降80%。总之,椎体成形术后患者的骨水泥分布指数对邻椎骨折有重要影响,骨水泥分布指数越高,即分布越均匀,则邻近椎体压缩骨折发生的风险越低,并且骨水泥分布指数对OVCFs患者椎体成形术后邻近椎体压缩骨折的发生具有一定预测价值。
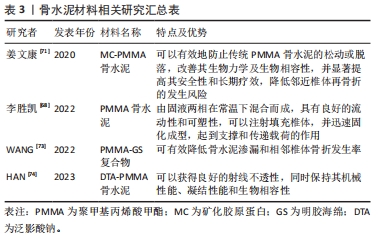
2.3.5 骨水泥材料 骨水泥材料的种类复杂多样,目前广泛应用于临床的是聚甲基丙烯酸甲酯(polymethyl methacrylate,PMMA)骨水泥。这种骨水泥通常是由固液两相在常温下混合而成,具有良好的流动性和可塑性,可以注射填充椎体,并迅速固化成型,起到支撑和传递载荷的作用[68]。PMMA骨水泥在临床应用中表现出巨大优点的同时,也存在一定的不足之处。有研究表明,具有相对高弹性模量的传统PMMA骨水泥可能会导致治疗后相邻椎体塌陷的风险增加[69]。这可能是由于PMMA骨水泥缺乏生物活性,无法与骨组织有机结合,当植入人体后与周围骨组织融合性较差,导致骨水泥松动,加之其硬度过大,极易导致邻近椎体的再骨折[70]。因此,为解决传统PMMA骨水泥的不足,有学者提出,在骨水泥中加入适当比例的矿化胶原蛋白(mineralized collagen,MC)形成新型骨水泥(MC-PMMA),可以有效地防止传统PMMA骨水泥的松动或脱落,改善其生物力学及生物相容性,并显著提高其安全性和长期疗效,降低邻近椎体压缩骨折的发生风险[71]。LUO等[72]将63例OVCFs患者随机分为MC-PMMA组和传统PMMA组,MC-PMMA组包括31例患者,传统PMMA组包括32例患者,经过14个月的随访,发现PMMA组有7例患者发生邻椎骨折,MC-PMMA组仅含有1例患者,MC-PMMA组的相邻椎体再次骨折发生率显著低于传统PMMA组(P < 0.05),具有更加良好的适应性力学性能和生物相容性。WANG等[73]发现使用聚甲基丙烯酸甲酯-明胶海绵(PMMA-GS)复合物治疗OVCFs合并上终板损伤患者可有效降低骨水泥渗漏和相邻椎体骨折发生率。HAN等[74]的研究发现在PMMA组中添加质量分数20%泛影酸钠可以获得良好的射线不透性,同时保持其机械性能、凝结性能和生物相容性。如今各种新型骨水泥材料的研发层出不穷,仍是一个热点话题,见表3。
2.3.6 骨水泥渗漏 骨水泥渗漏是椎体成形术后最常见的并发症,可占术后总并发症的70%,其中以向椎间隙渗漏最为常见,见图4。

NIEUWENHUIJSE等[4]的研究结果表明骨水泥渗漏同胸腰椎体骨质疏松骨折患者经皮椎体成形术后新发邻近椎体骨折具有显著相关性,但其导致邻近椎体压缩骨折发生的机制尚不明确。有学者指出骨水泥泄漏出椎体并进入椎间隙时,会导致受伤的椎间盘承受的应力减小,这种情况下会使得邻椎所承受的应力值增加,从而提高了再次骨折的概率[75]。也有观点认为渗漏的骨水泥会机械性的刺激相邻椎体的终板并加速椎间盘退化,进一步增加邻近椎体压缩骨折的可能性[76]。ZHONG等[77]通过队列研究发现骨水泥渗漏是OVCFs患者经皮椎体成形术后新发邻近椎体压缩骨折的独立危险因素,并采用Cox比例风险回归分析构建新发相邻椎体骨折(probability of new adjacent OVCFs,PNAV)评分系统来客观预测新发邻近椎体压缩骨折的风险,结果发现无邻近椎体压缩骨折独立危险因素患者的PNAV评分为0分,骨水泥渗漏邻近椎体压缩骨折患者的PNAV评分为4分,而预估2年内新发邻近椎体压缩骨折的绝对风险也从3.3%升高至19.9%。一项回顾性研究共纳入了286例OVCFs患者,发现随着骨水泥注射体积的增加,骨水泥渗漏的风险也会增加[78]。另外,低黏度骨水泥也是骨水泥渗漏的一个重要危险因素[79]。因此,笔者建议,在推注骨水泥过程中,使用高黏度骨水泥,进行全程透视检查,多次观察术中影像,以明确骨水泥在椎体内的分布情况,提高手术技巧和操作规范,有效减少椎体成形术中骨水泥的渗漏,从而降低继发邻近椎体压缩骨折的风险。
2.3.7 椎体高度过度恢复 童奕博等[80]认为伤椎术后越接近于正常椎体高度,则相邻椎体所受的应力越接近于正常值,邻近椎体再发骨折的风险也相应减少。韩晓东等[81]在椎体成形术后椎体高度恢复与邻近椎体压缩骨折的相关性研究中强调,椎体恢复高度对患者预后有着十分重要的意义,他们发现,骨折椎体高度恢复越高,邻近椎体压缩骨折的发生风险也随之增加。XIONG等[82]发现伤椎高度过多的恢复可能引起椎旁肌肉和韧带的张力增加,加重邻椎机械负荷并导致更多不稳定的骨折。一项研究通过对204例OVCFs 患者随访6-12个月,进行Logistic 回归分析发现椎体高度过度恢复是OVCFs术后发生再骨折的独立危险因素(OR=4.143)[39]。一项Meta分析结果显示,术后伤椎高度过度恢复的患者发生邻近椎体压缩骨折的风险是伤椎高度适宜恢复患者的2.66倍,这一结果提示了过分强调恢复伤椎高度可能反而会增加患者邻椎再骨折的风险(Z=4.80,P < 0.001)[83]。因此,在手术过程中,需要注意避免过度恢复受损椎体的高度,以减轻邻近椎体所受的压力,从而降低术后邻近椎体压缩骨折的发生风险。

| [1] WANG R, XU Y, MA X. Risk factors and strategies for recovery quality, postoperative pain, and recurrent fractures between percutaneous kyphoplasty and percutaneous vertebroplasty in elderly patients with thoracolumbar compression fractures: a retrospective comparative cohort study. Ann Transl Med. 2023;11(2):122. [2] FANG SY, DAI JL, MIN JK, et al. Analysis of risk factors related to the re-fracture of adjacent vertebral body after PKP. Eur J Med Res. 2021;26(1):127. [3] TAKAHASHI S, HOSHINO M, YASUDA H, et al. Development of a scoring system for predicting adjacent vertebral fracture after balloon kyphoplasty. Spine J. 2019;19(7):1194-1201. [4] NIEUWENHUIJSE MJ, PUTTER H, VAN ERKEL AR, et al. New vertebral fractures after percutaneous vertebroplasty for painful osteoporotic vertebral compression fractures: a clustered analysis and the relevance of intradiskal cement leakage. Radiology. 2013;266(3):862-870. [5] KURUTZ M, VARGA P, JAKAB G. Prophylactic vertebroplasty versus kyphoplasty in osteoporosis: a comprehensive biomechanical matched-pair study by in vitro compressive testing. Med Eng Phys. 2019;65:46-56. [6] YUAN L, BAI J, GENG C, et al. Comparison of targeted percutaneous vertebroplasty and traditional percutaneous vertebroplasty for the treatment of osteoporotic vertebral compression fractures in the elderly. J Orthop Surg Res. 2020;15(1):359. [7] ZHANG Z, JING Q, QIAO R, et al. Risk factors analysis of adjacent fractures after percutaneous vertebroplasty for osteoporotic vertebral compression fracture. Zhongguo Xiu Fu Chong Jian Wai Ke Za Zhi. 2021;35(1):20-25. [8] PARK JS, PARK YS. Survival analysis and risk factors of new vertebral fracture after vertebroplasty for osteoporotic vertebral compression fracture. Spine J. 2021;21(8):1355-1361. [9] HU H, CAO KX, HUANG P, et al. Risk factors of adjacent vertebral refracture after percutaneous vertebroplasty for osteoporotic vertebral compression fractures in super-old patients. Zhongguo Gu Shang. 2022;35(8):710-714. [10] BIAN F, BIAN G, AN Y, et al. Establishment and validation of a nomogram for the risk of new vertebral compression fractures after percutaneous vertebroplasty in patients with osteoporotic vertebral compression fractures: a retrospective study. Geriatr Orthop Surg Rehabil. 2022;13: 21514593221098620. [11] YANG D, TAN J, LONG Y, et al. Sequential treatment of teriparatide and alendronate versus alendronate alone for elevation of bone mineral density and prevention of refracture after percutaneous vertebroplasty in osteoporosis: a prospective study. Aging Clin Exp Res. 2023;35(3):531-539. [12] 刘畅,李大同,刘元,等.急性症状性骨质疏松性胸腰椎压缩骨折椎体强化手术后疗效欠佳:与骨水泥、骨密度、邻近骨折的关系[J].中国组织工程研究,2021,25(22):3510-3516. [13] CHEN M, YANG C, CAI Z, et al. Lumbar posterior group muscle degeneration: Influencing factors of adjacent vertebral body re-fracture after percutaneous vertebroplasty. Front Med. 2023;9:1078403. [14] CHENG Y, CHENG X, WU H. Risk factors of new vertebral compression fracture after percutaneous vertebroplasty or percutaneous kyphoplasty. Front Endocrinol. 2022;13:964578. [15] LI J, XIE Y, SUN S, et al. Regional differences in bone mineral density biomechanically induce a higher risk of adjacent vertebral fracture after percutaneous vertebroplasty: a case-comparative study. Int J Surg. 2023;109(3): 352-363. [16] WARDEN SJ, CARBALLIDO-GAMIO J, AVIN KG, et al. Adaptation of the proximal humerus to physical activity: a within-subject controlled study in baseball players. Bone. 2019;121:107-115. [17] FANG XY, XU HW, CHEN H, et al. Association between poor nutritional status and increased risk for subsequent vertebral fracture in elderly people with percutaneous vertebroplasty. Clin Interv Aging. 2022;17:1503-1512. [18] LI H, YANG DL, MA L, et al. Risk factors associated with adjacent vertebral compression fracture following percutaneous vertebroplasty after menopause: a retrospective study. Med Sci Monit. 2017;23:5271-5276. [19] MA X, XIA H, WANG J, et al. Re-fracture and correlated risk factors in patients with osteoporotic vertebral fractures. J Bone Miner Metab. 2019;37(4):722-728. [20] INOSE H, KATO T, ICHIMURA S, et al. Risk factors for subsequent vertebral fracture after acute osteoporotic vertebral fractures. Eur Spine J. 2021;30(9):2698-2707. [21] CHENG X, LONG HQ, XU JH, et al. Comparison of unilateral versus bilateral percutaneous kyphoplasty for the treatment of patients with osteoporosis vertebral compression fracture (OVCF): a systematic review and meta-analysis. Eur Spine J. 2016;25(11):3439-3449. [22] REN HL, JIANG JM, CHEN JT, et al. Risk factors of new symptomatic vertebral compression fractures in osteoporotic patients undergone percutaneous vertebroplasty. Eur Spine J. 2015;24(4):750-758. [23] 李春涛,李文毅,高尚聚,等.中国人群椎体成形术后发生邻近椎体压缩性骨折危险因素Meta分析[J].中华骨质疏松和骨矿盐疾病杂志,2021,14(6): 638-646. [24] LI W, WANG H, DONG S, et al. Establishment and validation of a nomogram and web calculator for the risk of new vertebral compression fractures and cement leakage after percutaneous vertebroplasty in patients with osteoporotic vertebral compression fractures. Eur Spine J. 2022;31(5):1108-1121. [25] 刘进,唐静,陈果,等.夹心椎与普通邻椎再骨折风险比较及危险因素分析[J].中国修复重建外科杂志,2021,35(9):1161-1166. [26] CHIU PY, KAO FC, HSIEH MK, et al. A retrospective analysis in 1347 patients undergoing cement augmentation for osteoporotic vertebral compression fracture: is the sandwich vertebra at a higher risk of further fracture? Neurosurgery. 2021;88(2):342-348. [27] GUO X, ZHU N, ZHANG H, et al. Vertebral refracture after percutaneous vertebroplasty for osteoporotic vertebral compression fractures with and without brace wearing: a retrospective study of 300 patients. Front Surg. 2023; 9:1056729. [28] 姜天淇,葛泽峰,田新月,等.骨质疏松性椎体压缩性骨折经皮椎体成形术后继发椎体再骨折的相关因素分析[J].脊柱外科杂志,2023,21(1):21-25. [29] ZHANG ZL, YANG JS, HAO DJ, et al. Risk factors for new vertebral fracture after percutaneous vertebroplasty for osteoporotic vertebral compression fractures. Clin Interv Aging. 2021;16:1193-1200. [30] JI C, RONG Y, WANG J, et al. Risk factors for refracture following primary osteoporotic vertebral compression fractures. Pain Physician. 2021;24(3):E335-E340. [31] HEINI PF, ORLER R. Vertebroplastik bei hochgradiger osteoporose. Technik und Erfahrung mit plurisegmentalen Injektionen [Vertebroplasty in severe osteoporosis. Technique and experience with multi-segment injection]. Orthopade. 2004;33(1):22-30. [32] NAKAMURA T, FUKUNAGA M, NAKANO T, et al. Efficacy and safety of once-yearly zoledronic acid in Japanese patients with primary osteoporosis: two-year results from a randomized placebo-controlled double-blind study (ZOledroNate treatment in Efficacy to osteoporosis; ZONE study). Osteoporos Int. 2017;28(1):389-398. [33] HUANG Y, WU D. Clinical application of zoledronic acid combined with vitamin K2 in percutaneous vertebroplasty for multi-segment osteoporotic vertebral compression fractures. Zhongguo Gu Shang. 2020;33(9):820-826. [34] SU CH, TU PH, YANG TC, et al. Comparison of the therapeutic effect of teriparatide with that of combined vertebroplasty with antiresorptive agents for the treatment of new-onset adjacent vertebral compression fracture after percutaneous vertebroplasty. J Spinal Disord Tech. 2013;26(4):200-206. [35] MILLS ES, HAH RJ, FRESQUEZ Z, et al. Secondary fracture rate after vertebral osteoporotic compression fracture is decreased by anti-osteoporotic medication but not increased by cement augmentation. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2022;104(24):2178-2185. [36] GAO W, CHEN Y, WANG X, et al. Establishment and verification of a predictive nomogram for new vertebral compression fracture occurring after bone cement injection in middle-aged and elderly patients with vertebral compression fracture. Orthop Surg. 2023;15(4):961-972. [37] CORTET B, LUCAS S, LEGROUX-GEROT I, et al. Bone disorders associated with diabetes mellitus and its treatments. Joint Bone Spine. 2019;86(3):315-320. [38] MAZZANTINI M, FIGLIOMENI A, BOTTAI V, et al. High rate of vertebral refracture after vertebroplasty in patients taking glucocorticoids: a prospective two-year study. Clin Exp Rheumatol. 2020;38(4):649-653. [39] 刘军,张陆,刘志昂,等.经皮椎体增强术后邻近椎体再骨折的相关因素[J].中国矫形外科杂志,2020,28(4):319-322. [40] COSTA-RODRIGUES J, ROCHA I, FERNANDES MH. Complex osteoclastogenic inductive effects of nicotine over hydroxyapatite. J Cell Physiol. 2018;233(2):1029-1040. [41] KIYOTA Y, MURAMATSU H, SATO Y, et al. Smoking cessation increases levels of osteocalcin and uncarboxylated osteocalcin in human sera. Sci Rep. 2020; 10(1):16845. [42] LUO Z, LIU Y, LIU Y, et al. Cellular and molecular mechanisms of alcohol-induced osteopenia. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2017;74(24):4443-4453. [43] CHEN Z, CHEN Z, WU Y, et al. Risk factors of secondary vertebral compression fracture after percutaneous vertebroplasty or kyphoplasty: a retrospective study of 650 patients. Med Sci Monit. 2019;25:9255-9261. [44] CUI L, CHEN L, XIA W, et al. Vertebral fracture in postmenopausal Chinese women: a population-based study. Osteoporos Int. 2017;28(9):2583-2590. [45] DENG D, LIAN Z, CUI W, et al. Function of low back muscle exercise: preventive effect of refracture analysis of postoperative vertebral fractures. Orthopade. 2019;48(4):337-342. [46] BUCHBINDER R, OSBORNE RH, EBELING PR, Et al. A randomized trial of vertebroplasty for painful osteoporotic vertebral fractures. N Engl J Med. 2009; 361(6):557-568. [47] HE B, ZHAO J, ZHANG M, et al. Effect of surgical timing on the refracture rate after percutaneous vertebroplasty: a retrospective analysis of at least 4-year follow-up. Biomed Res Int. 2021;2021:5503022. [48] YANG CC, CHIEN JT, TSAI TY, et al. Earlier vertebroplasty for osteoporotic thoracolumbar compression fracture may minimize the subsequent development of adjacent fractures: a retrospective study. Pain Physician. 2018; 21(5):E483-E491. [49] MA YH, TIAN ZS, LIU HC, et al. Predictive risk factors for recollapse of cemented vertebrae after percutaneous vertebroplasty: a meta-analysis. World J Clin Cases. 2021;9(12):2778-2790. [50] BU D, HE X. Comparison of different approaches of percutaneous vertebroplasty in the treatment of osteoporotic spinal compression fractures and analysis of influencing factors of re-fracture. Pak J Med Sci. 2023;39(1):144-149. [51] WANG M, LI B, WANG Y, et al. The effects of bone cement volume in percutaneous vertebroplasty for thoracolumbar junction vertebral compression fractures: a clinical comparative study. Mediators Inflamm. 2022;2022:4230065. [52] LI Q, LONG X, WANG Y, et al. Development and validation of a nomogram for predicting the probability of new vertebral compression fractures after vertebral augmentation of osteoporotic vertebral compression fractures. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2021;22(1):957. [53] SUN HB, JING XS, LIU YZ, et al. The optimal volume fraction in percutaneous vertebroplasty evaluated by pain relief, cement dispersion, and cement leakage: a prospective cohort study of 130 patients with painful osteoporotic vertebral compression fracture in the thoracolumbar vertebra. World Neurosurg. 2018; 114:e677-e688. [54] ZHOU C, HUANG S, LIAO Y, et al. Correlation analysis of larger side bone cement volume/vertebral body volume ratio with adjacent vertebral compression fractures during vertebroplasty. Front Endocrinol. 2023;14:1072087. [55] LEE HJ, PARK J, LEE IW, et al. Clinical, radiographic, and morphometric risk factors for adjacent and remote vertebral compression fractures over a minimum follow-up of 4 years after percutaneous vertebroplasty for osteoporotic vertebral compression fractures: novel three-dimensional voxel-based morphometric analysis. World Neurosurg. 2019;125:e146-e157. [56] 陈昌礼.骨水泥分布情况对PVP术后邻椎骨折的影响探讨[J].颈腰痛杂志, 2018,39(5):675-676. [57] GU C, HUANG A, WANG Y, et al. Biomechanics of the unilateral posterosuperior, unipedicular, and bipedicular approaches for treatment by percutaneous vertebroplasty: a comparative study. Am J Transl Res. 2022;14(5):3448-3455. [58] DAI H, LIU Y, HAN Q, et al. Biomechanical comparison between unilateral and bilateral percutaneous vertebroplasty for osteoporotic vertebral compression fractures: a finite element analysis. Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2022;10:978917. [59] MO L, WU Z, LIANG D, et al. Influence of bone cement distribution on outcomes following percutaneous vertebroplasty: a retrospective matched-cohort study. J Int Med Res. 2021;49(7):3000605211022287. [60] CHEN Y, ZHANG H, CHEN H, et al. Comparison of the effectiveness and safety of unilateral and bilateral percutaneous vertebroplasty for osteoporotic vertebral compression fractures: a protocol for systematic review and meta-analysis. Medicine. 2021;100(51):e28453. [61] 肖庆华,林晓生,张震,等.椎体强化术后骨水泥弥散分布评价的研究进展[J].中国骨质疏松杂志,2021,27(3):440-445. [62] 吴登将,陈为坚,张远华,等.椎体增强术后骨水泥分布指数对手术椎体及邻边椎体再发骨折的影响[J].中国老年学杂志,2022,42(6):1392-1395. [63] 余俊喜,吴少坚,刘燕群,等.骨水泥分布状况与骨质疏松性椎体压缩骨折术后再发邻近骨折的关系[J].中国临床医生杂志,2020,48(4):466-468. [64] 刘进,夏宾,蔡鹏,等.定量CT有限元分析椎体强化对不同位置非强化椎生物力学参数的影响[J].中国组织工程研究,2023,27(34):5436-5440. [65] ZHOU C, LIAO Y, HUANG S, et al. Effect of cement distribution type on clinical outcome after percutaneous vertebroplasty for osteoporotic vertebral compression fractures in the aging population. Front Surg. 2022;9:975832. [66] 蒋学国.骨水泥分布情况对PVP术后邻椎骨折影响的影响探讨[J].颈腰痛杂志,2019,40(2):204-207. [67] 付兆宗,陈忠羡,秦英,等.骨水泥分布指数对椎体成形术后症状性邻近节段骨折的影响[J].南方医科大学学报,2017,37(7):947-951. [68] 李胜凯,李涛,魏超,等.磷酸钙/聚甲基丙烯酸甲酯复合骨水泥与聚甲基丙烯酸甲酯骨水泥生物力学性能的对照[J].中国组织工程研究,2022, 26(16):2461-2466. [69] PENG Y, DU X, HUANG L, et al. Optimizing bone cement stiffness for vertebroplasty through biomechanical effects analysis based on patient-specific three-dimensional finite element modeling. Med Biol Eng Comput. 2018;56(11): 2137-2150. [70] WANG X, KOU JM, YUE Y, et al. Clinical outcome comparison of polymethylmethacrylate bone cement with and without mineralized collagen modification for osteoporotic vertebral compression fractures. Medicine. 2018; 97(37):e12204. [71] 姜文康,耿伟,许莹莹,等.矿化胶原改性骨水泥在骨质疏松性椎体压缩骨折中的应用[J].中国组织工程研究,2020,24(15):2381-2386. [72] LUO K, JIANG G, ZHU J, et al. Poly (methyl methacrylate) bone cement composited with mineralized collagen for osteoporotic vertebral compression fractures in extremely old patients. Regen Biomater. 2020;7(1):29-34. [73] WANG YQ, QIAO L, WANG B, et al. Percutaneous vertebroplasty with the polymethyl methacrylate - gelatin sponge complex in the treatment of patients with osteoporotic vertebral compression fractures accompanied by superior endplate injuries. Turk Neurosurg. 2024;34(1):74-80. [74] HAN J, ZHENG X, LIU J, et al. Modification and evaluation of diatrizoate sodium containing polymethyl methacrylate bone cement. J Biomater Appl. 2023; 37(7):1300-1314. [75] MAO W, DONG F, HUANG G, et al. Risk factors for secondary fractures to percutaneous vertebroplasty for osteoporotic vertebral compression fractures: a systematic review. J Orthop Surg Res. 2021;16(1):644. [76] YIN H, HE X, YI H, et al. Analysis of the causes on poor clinical efficacy of kyphoplasty performed in unilateral transpedicular puncture for the treatment of senile osteoporotic vertebral compression fractures. Sci Rep. 2019;9(1):1498. [77] ZHONG BY, HE SC, ZHU HD, et al. Risk prediction of new adjacent vertebral fractures after PVP for patients with vertebral compression fractures: development of a prediction model. Cardiovasc Intervent Radiol. 2017;40(2):277-284. [78] REN H, FENG T, CAO J, et al. A retrospective study to evaluate the effect of dynamic fracture mobility on cement leakage in percutaneous vertebroplasty and percutaneous kyphoplasty in 286 patients with osteoporotic vertebral compression fractures. Med Sci Monit. 2022;28:e935080. [79] LI K, FENG H, LUO D, et al. Efficacy and safety of high-viscosity cement in percutaneous vertebroplasty for treatment of osteoporotic vertebral compression fractures: a retrospective cohort study. Medicine. 2020;99(23):e20515. [80] 童奕博,李明辉.骨质疏松性椎体骨折患者椎体成形后邻近椎体再发骨折的影响因素[J].中国组织工程研究,2024,28(8):1241-1246. [81] 韩晓东,孟纯阳.PVP术后椎体前缘高度恢复率与邻近椎体骨折的相关性研究[J].中国矫形外科杂志,2019,27(10):885-889. [82] XIONG YC, GUO W, XU F, et al. Refracture of the cemented vertebrae after percutaneous vertebroplasty: risk factors and imaging findings. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2021;22(1):459. [83] 汤亮,轩安武,朱振标.经皮椎体成形术/经皮椎体后凸成形术后邻椎再骨折危险因素的Meta分析[J].局解手术学杂志,2021,30(10):881-890. |
| [1] | 席金涛, 鲁齐林, 汪 洋, 王小娟, 吕 鹏, 陈 龙, 石 震, 谢 维, 竺义亮, 李绪贵. 经椎间孔腰椎椎间融合后融合器后移的危险因素分析[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2024, 28(9): 1394-1398. |
| [2] | 牛河钢, 杨 昆, 张晶晶, 闫怡竹, 张银顺. 新型成人后路寰椎骨折钉板复位内固定系统的设计[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2024, 28(9): 1399-1402. |
| [3] | 王梦晗, 齐 涵, 张 元, 陈言智. 3种3D打印模型辅助治疗Robinson ⅡB2型锁骨骨折[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2024, 28(9): 1403-1408. |
| [4] | 杨策凯, 蔡卓延, 陈 明, 刘 昊, 翁 汭, 崔健超, 张顺聪, 姚珍松. 绝经后女性椎旁肌退化与经皮穿刺椎体成形后再骨折的相关性[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2024, 28(9): 1414-1419. |
| [5] | 霞黑达·依拉尔江, 尼加提·吐尔逊, 热依拉·库尔班, 白布加甫·叶力思, 陈 欣. 三维有限元分析不同特征骨组织中应力的分布规律[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2024, 28(8): 1277-1282. |
| [6] | 章晓云, 刘 桦, 柴 源, 陈 锋, 曾 浩, 高振罡, 黄有荣. 益肾固疏方干预老年性骨质疏松症患者骨代谢标志物的变化及临床疗效[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2024, 28(8): 1155-1160. |
| [7] | 代越星, 郑利钦, 吴敏辉, 李志鸿, 李少彬, 郑德声, 林梓凌. 血管数量对小血管网计算流体力学的影响[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2024, 28(8): 1206-1210. |
| [8] | 韩 冰, 刘宏滨, 王和洪, 赵汉青, 赵日光, 孙燚炎, 张 玉. 青年男性下肢力线和髌股疼痛综合征危险因素的相关性[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2024, 28(8): 1211-1216. |
| [9] | 童奕博 , 李明辉. 骨质疏松性椎体骨折患者椎体成形后邻近椎体再发骨折的影响因素[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2024, 28(8): 1241-1246. |
| [10] | 薛晓峰, 魏永康, 乔晓红, 杜玉勇, 牛建军, 任立新, 杨慧峰, 张治民, 郭 媛, 陈维毅. 股骨颈骨折空心钉内固定后股骨近端骨质疏松的有限元分析[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2024, 28(6): 862-867. |
| [11] | 黄培镇, 董 航, 蔡群斌, 林梓凌, 黄 枫. 顺行和逆行髓内钉治疗不同部位股骨干骨折的有限元分析[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2024, 28(6): 868-872. |
| [12] | 谭能贤, 吴文正, 郑楚荣, 罗列良, 古 鹏, 欧阳崇志, 郑晓辉. 不同空心加压螺钉固定方式对股骨颈垂直型骨折的有限元分析[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2024, 28(6): 873-878. |
| [13] | 王明明, 张 中, 孙建华, 赵 刚, 宋 华, 颜华东, 吕 彬. 胫骨远端骨折伴软组织损伤3种不同微创固定方式的有限元分析[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2024, 28(6): 879-885. |
| [14] | 王体惠, 王 旭, 吴锦清, 陈继良, 王晓露, 缪 娟. 股骨远端三维模拟截骨在膝关节置换中的应用[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2024, 28(6): 905-910. |
| [15] | 吴钟汉, 王景坤, 李 涛, 许新忠, 余水生, 程 里, 田大胜, 汤 健, 荆珏华. 股骨近端防旋髓内钉治疗外侧壁完整型和外侧壁危险型股骨转子间骨折[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2024, 28(6): 911-916. |
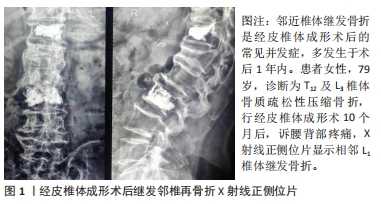
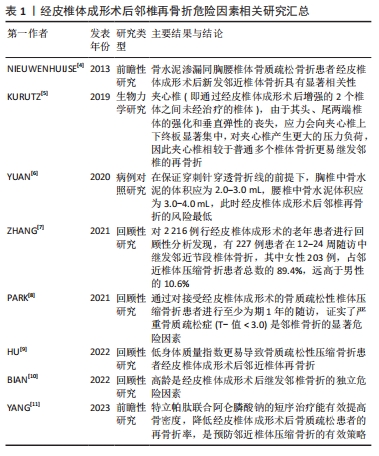 文章通过回顾国内外相关文献,对经皮椎体成形术后邻近椎体继发性压缩骨折相关危险因素的研究进展作一全面综述,为进一步减少经皮椎体成形术后邻近椎体压缩骨折的发生以及制定相应治疗方案提供一定的参考。
中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:人工关节;骨植入物;脊柱;骨折;内固定;数字化骨科;组织工程
文章通过回顾国内外相关文献,对经皮椎体成形术后邻近椎体继发性压缩骨折相关危险因素的研究进展作一全面综述,为进一步减少经皮椎体成形术后邻近椎体压缩骨折的发生以及制定相应治疗方案提供一定的参考。
中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:人工关节;骨植入物;脊柱;骨折;内固定;数字化骨科;组织工程
1.1.1 检索人及检索时间 第一作者在2023年9月进行检索。
1.1.2 检索文献时限 查阅2018年1月至2023年9月期间收录的经皮椎体成形术后邻近椎体压缩骨折危险因素的研究进展相关文章,同时纳入少数经典远期文献。
1.1.3 检索数据库 应用计算机检索中国知网、万方医学网、维普、PubMed、Springer、ScienceDirect及Elsevier数据库收录的相关文献。
1.1.4 检索词 “骨质疏松症,骨折,经皮椎体成形术,邻近椎体压缩骨折,危险因素”为中文检索词,以“osteoporosis,fractures,percutaneous vertebroplasty,adjacent vertebral compression fractures,risk factors”为英文检索词,分别进行文献检索。
1.1.5 检索文献类型 文献为综述、研究综述、基础研究、荟萃分析及临床研究。
1.1.6 手工检索情况 无。
1.1.7 检索策略 以PubMed数据库检索策略为例:“((((osteoporosis) AND (fractures)) OR (percutaneous vertebroplasty)) AND (adjacent vertebral compression fractures)) AND (risk factors)”。
1.1.8 检索文献量 初检3 052篇文献,其中中文1 340篇,英文1 712篇,包括中国知网数据库856篇,万方数据库322篇,维普数据库162篇,PubMed 数据库1 123篇,Springer数据库371篇,ScienceDirect数据库55篇,Elsevier数据库163篇。
1.2 入组标准
1.2.1 纳入标准 ①有关经皮椎体成形术后邻近椎体压缩骨折危险因素的相关研究;②同一领域中论点、论据可靠的文献。
1.2.2 排除标准 ①重复性研究且研究目的无相关性的文献; ②资料无法提取的部分文献。
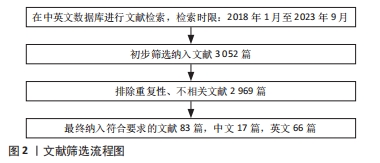
1.3 数据的提取与质量评估 计算机检索初检得到3 052篇文献,研究内容由作者独立提取并通过研究筛选,重点记录侧重于经皮椎体成形术后邻近椎体压缩骨折危险因素方面的研究。通过阅读文题和摘要进行初步筛选,排除与文章主题不相关的文献,根据纳入标准和排除标准最后纳入83篇文献进行综述分析,其中中文17篇,英文66篇,包括中国知网数据库10篇,万方数据库7篇,PubMed 数据库44篇,Springer数据库15篇,Elsevier数据库7篇,见图2。
3.2 作者综述区别于他人他篇的特点 该综述主要着眼于总结和归纳高龄、性别、骨密度、身体质量指数、初始骨折椎体数量及部位、手术时机、手术方式、骨水泥的材料、注射量、弥散分布、伤椎恢复高度、骨水泥渗漏、抗骨质疏松治疗、术后佩戴支具及其他因素等15个方面对于经皮椎体成形术后邻近椎体压缩骨折的影响,仔细分析了危险因素引起邻椎骨折的具体机制,为减少邻近椎体继发骨折发生风险以及制定相应治疗方案提供一定的参考。
3.3 综述的局限性 虽然大多数文献支持这些危险因素会增加术后邻近椎体压缩骨折的发生率,但仍有部分研究持反对意见,导致最后的结果有待进一步探讨。除此之外,涉及经皮椎体成形术后邻近椎体压缩骨折危险因素方面的文献及相关研究数据的数量还不够多,邻近椎体压缩骨折是经皮椎体成形术术后的常见并发症,虽然区别于椎体成形术后继发普通椎体骨折,但邻椎骨折与其仍具有很多的共同点。由于手术时机及术后佩戴支具在邻椎骨折影响落后于普通椎体继发骨折,在论据不足时,文章选取继发普通椎体骨折的相关文献作为旁证,具有一定的局限性。
3.4 综述的重要意义 文章认为高龄、性别、骨密度、身体质量指数、初始骨折椎体数量、手术时机、手术方式、骨水泥的材料、注射量、弥散分布、伤椎恢复高度、骨水泥渗漏、抗骨质疏松治疗、术后佩戴支具及其他因素等是经皮椎体成形术后邻近椎体压缩骨折的相关危险因素。寻找合适的手术时机,早期手术,改善患者疼痛症状;研发新型骨水泥材料,改善其生物力学及生物相容性,并显著提高其安全性和长期疗效;改进手术方式,提高手术操作技能;确定最佳骨水泥的用量和分布,避免伤椎高度过度恢复和骨水泥的渗漏,恢复脊柱正常生物力学特点,降低邻近椎体应力,减缓相邻椎间盘退变;并且术后规律抗骨质疏松治疗,提高骨密度;坚持佩戴支具,尽早恢复脊柱稳定性;培养良好生活习惯,进行户外活动及腰背肌的锻炼,保持适宜体质量,防治内科疾病;对于高龄女性及多发椎体骨折患者,应缩短复查间期,延长复查时间,这将有望进一步减少经皮椎体成形术后邻近椎体压缩骨折的发生。 中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:人工关节;骨植入物;脊柱;骨折;内固定;数字化骨科;组织工程
 #br#
#br#
文题释义:
经皮椎体成形术:是指在X射线透视下,使用穿刺针经皮肤穿刺,通过椎弓根建立工作通道,向伤椎内注入骨水泥以达到增强椎体强度和稳定性、防治椎体塌陷、有效恢复椎体高度目的的治疗骨质疏松压缩性椎体骨折的一种脊柱外科微创技术,具有简单易施行、开放创伤小、镇痛速度快及手术疗效好的优点。邻近椎体压缩骨折:是指骨质疏松性椎体压缩骨折患者在接受经皮椎体成形术治疗后,由于存在某些危险因素,导致手术椎体相邻节段椎体的再次骨折,引起患者腰背部疼痛,降低生活质量,是经皮椎体成形术的常见并发症之一。
近年来,随着中国人口老龄化的加剧,骨质疏松的发病率不断升高。资料显示,中国约有8 800万人患有不同程度的骨质疏松症。预计到2050年,中国骨质疏松症的总人数将达到2.12亿。骨质疏松性椎体压缩骨折(osteoporotic vertebral compression fractures,OVCFs)是骨质疏松的常见并发症之一,好发于胸腰椎。患者椎体发生压缩骨折后,腰背部可产生剧烈疼痛,影响日常活动,经皮椎体成形术(percutaneous vertebroplasty,PVP)是临床上治疗OVCFs的有效手术方式,因其理想的治疗效果和较高的安全性为广大患者和医护人员所接受。
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||