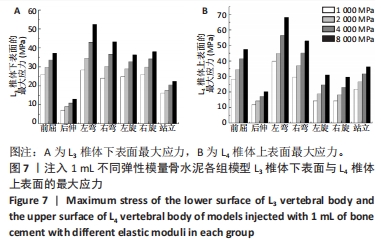
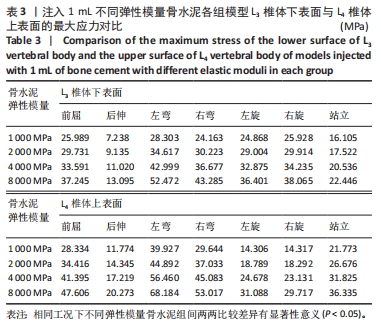
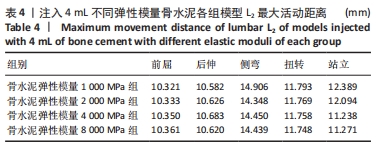
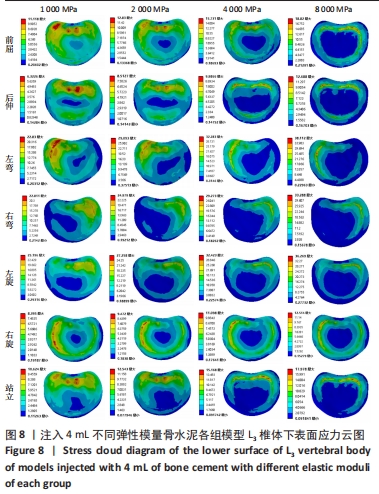
[1] MAHER C, UNDERWOOD M, BUCHBINDER R. Non- specific low backpain. Lancet. 2017;389(10070):736-747.
[2] VARGA PP, JAKAB G, BORS IB, et al. Experiences with PMMA cement as a stand-alone intervertebral spacer: Percutaneous cement discoplasty in the case of vacuum phenomenon within lumbar intervertebral discs. Orthopade. 2015;44 Suppl 1:S1-7.
[3] KISS L, VARGA PP, SZOVERFI Z, et al. Indirectforaminal decompression and improvement in the lumbar alignment after percutaneous cement discoplasty. Eur Spine J. 2019;28(6):1441-1447.
[4] 向刚刚,童猛,曹鹏,等.新型骨水泥研究进展[J].中国中医骨伤科杂志,2023,31(6):83-88.
[5] SZCZĘSNY G, KOPEC M, POLITIS DJ, et al. A Review on Biomaterials for Orthopaedic Surgery and Traumatology: From Past to Present. Materials (Basel). 2022;15(10):3622.
[6] GINEBRA MP, CANAL C, ESPANOL M, et al. Calcium phosphate cements as drug delivery materials. Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2012;64(12):1090-1110.
[7] XU H, ZHU L, TIAN F, et al. In vitro and in vivo evaluation of injectable strontium-modified calcium phosphatecement for bone defect repair in rats. Int J Mol Sci. 2022;24(1):568.
[8] WELCH-PHILLIPS A, GIBBONS D, AHERN DP, et al. What Is Finite Element Analysis? Clin Spine Surg. 2020;33(8):323-324.
[9] CAI XY, SANG D, YUCHI CX, et al. Using finite element analysis to determine effects of the motion loading method on facet joint forces after cervical disc degeneration. Comput Biol Med. 2020;116:103519.
[10] BELYTSCHKO T, KULAK RF, SCHULTZ AB, et al. Finite element stress analysis of an intervertebral disc. J Biomech. 1974;7(3):277-285.
[11] 方新果,赵改平,王晨曦,等.基于CT图像腰椎L4~L5节段有限元模型建立与分析[J].中国生物医学工程学报,2014,33(4):487-492.
[12] 秦大平,张晓刚,聂文忠,等.不同运动状态下模拟人体腰椎结构特征变化的有限元分析[J].医用生物力学,2017,32(4):355-362.
[13] 张敏,彭婧,张强,等.有限元法分析老年骨质疏松患者L_(3/4)椎板减压椎间融合的力学性能[J].中国组织工程研究,2024,28(6): 847-851.
[14] 李嘉睿,燕杨,武晓刚,等.单边双通道内镜下腰椎椎间融合的生物力学分析[J].中国组织工程研究,2023,27(34):5523-5529.
[15] 王智.基于CT数据L4-5有限元模型的构建以及L5的应力分析[D].太原:山西医科大学,2011
[16] 张涵.基于Abaqus椎体成形术生物力学有限元分析[D].遵义:遵义医学院,2018.
[17] 李银倩,吕杰,丁立军,等.韧带损伤影响腰椎稳定性的生物力学特征[J].中国组织工程研究,2024,28(21):3286-3292.
[18] MARKOLF KL. Deformation of the thoracolumbar intervertebral joints in response to external loads a biomechanical study using autopsy material.J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1972;54(3):511-533.
[19] SCHULTZ AB, WARWICH DN, BERKSON MH, et al. Mechanical properties of human lumbar spine motion segments part 1:responses in flexion,extension,lateral bending,and torsion. J Biomech Eng. 1979;101: 46-52.
[20] TENCER AF, AHMED AM, BURKE DL. Some static mechanical properties of the lumbar intervertebral joint: intact and injured. Biomech Eng. 1982;104(3):193-201.
[21] WHITE AA, KRAG M, PANJABI MM, et al. Effect of preload on load displacement curves of the lumbar spine. Orthop Clin North AM. 1977;8(1):181-192.
[22] 赵文韬,秦大平,张晓刚,等.功能复位椎体强化治疗骨质疏松性椎体压缩骨折的有限元分析[J].世界科学技术-中医药现代化, 2018,20(3):439-445.
[23] 包拥政,祝周兴,冯云升,等.低弹性模量骨水泥对骨质疏松压缩性骨折椎体及邻近椎体应力的影响:三维有限元分析[J].中国组织工程研究,2016,20(16):2285-2293.
[24] 刘鹤飞,田庆华,易飞,等.经皮骨水泥椎间融合术在椎体转移瘤治疗中的应用[J].介入放射学杂志,2019,28(5):459-464.
[25] 王莹莹,杨寅,王义清,等.经皮骨水泥椎间盘成形术治疗顽固性腰痛1例[J].颈腰痛杂志,2020,41(2):256.
[26] 田庆华,王涛,何煜,等.经皮骨水泥椎间融合术与骨水泥椎间盘成形术治疗老年腰椎间盘突出症的疗效比较[J].介入放射学杂志, 2021,30(3):264-269.
[27] TECHENS C, PALANCA M, ELIES PE, et al. Testing the impact of discoplasty on the biomechanics of the intervertebral disc with simulatedde generation:Aninvitro study. Med Enphys. 2020;84:51-59.
[28] 李爽,徐宝山,马信龙.经皮椎间盘骨水泥成形术的研究进展[J].中国矫形外科杂志,2021,29(21):1961-1964.
[29] CAMINO WILLHUBER G, BENDERSKY M, DE CICCO FL, et al. Development of a New Therapy-OrientedClassification of Intervertebral Vacuum Phenomenon With Evaluation of Intra- andInterobserver Reliabilities. Global Spine J. 2021;11(4):480-487.
[30] TECHENS C, PALANCA M, ÉLTES PE, et al. Testing the impact of discoplasty on the biomechanics of the intervertebral disc with simulated degeneration: An in vitro study. Med Eng Phys. 2020;84:51-59.
[31] LAZARY A. Expert’s Comment concerning Grand Rounds Case entitled”Percutaneous cement discoplasty for the treatment of advanced degenerative disk disease in elderly patients” : (C. Sola, et al., Eur Spine J; 2018: DOI 10.107/s00586-018-5547-7). Eur Spine J. 2021;30(8):2209-2210.
[32] KARAHALILOGLU Z, KILICAY E. In vitro evaluationof bone cements impregnated with selenium nanoparticlesstabilized by phosphatidylcholine (PC) for application inbone. J Biomater Appl. 2020;35(3):385-404.
[33] SLANE J, VIVANCO J, ROSE W, et al. Mechanical, material,and antimicrobial properties of acrylic bone cementimpregnated with silver nanoparticles. Mater Sci Eng C Mater Biol Appl. 2015;48:188-196.
[34] LI X, LI G, ZHANG K, et al. Cu-loaded brushite bone cements with good antibacterial activity and operability. J Biomed Mater Res B Appl Biomater. 2021;109(6):877-889.
[35] PHAKATKAR AH, SHIRDAR MR, QI ML, et al.Novel PMMA bone cement nanocomposites containing magnesium phosphate nanosheets and hydroxyapatite nanofibers. Mater Sci Eng C Mater Biol Appl. 2020; 109:110497.
[36] XUE YD, ZHANG ZC, DAI WX. Investigation of preoperative traction followed by percutaneous kyphoplasty combined with percutaneous cement discoplasty for the treatment of severe thoracolumbar osteoporotic vertebral compression fractures. Int J Gen Med. 2021;14: 6563-6571.
[37] ZHANG Q, CHON T, ZHANG Y, et al. Finite element analysis of the lumbar spine in adolescent idiopathic scoliosis subjected to different loads. Comput Biol Med. 2021;136:104745.
[38] TIAN QH, LU YY, SUN XQ, et al. Feasibility of percutaneous lumbar discectomy combined with percutaneous cementoplasty for symptomatic lumbar disc herniation with modic type I endplate changes. Pain Physician. 2017;20(4):E481-E488.
[39] CAMINO-WILLHUBER G, KIDO G, PEREIRA-DUARTE M, et al. Percutane-ous cement discoplasty for the treatment of advanced degenerativedisc conditions: a case series analysis. Global Spine J. 2020;10(6):729-734.
[40] SOLA C, CAMINO WILLHUBER G, KIDO G, et al. Percutaneous cement discoplasty for the treatment of advanced degenerative disk disease in elderly patients. Eur Spine J. 2021;30(8):2200-2208.
[41] 关凯,赵伟东,关福强,等.经皮骨水泥椎间盘成型术治疗腰椎退行性侧凸1例[J].中国微侵袭神经外科杂志,2021,26(7):341-342.
[42] 杨光远,况娟,李文革.经皮骨水泥椎间盘成形术在老年性椎间盘突出症中的应用[J].中国中西医结合影像学杂志,2022,20(6):581-585,593. |