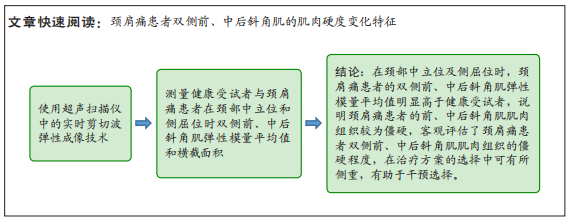
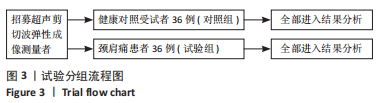
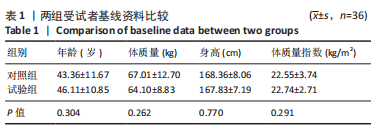
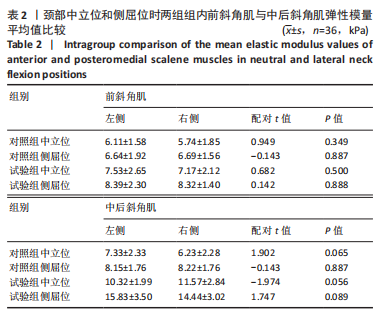
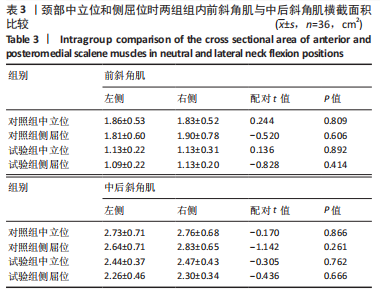
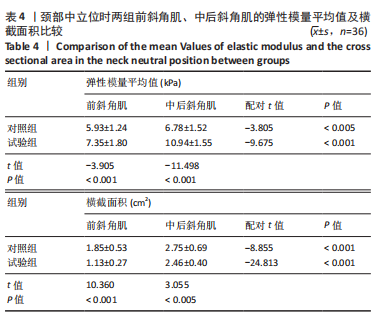
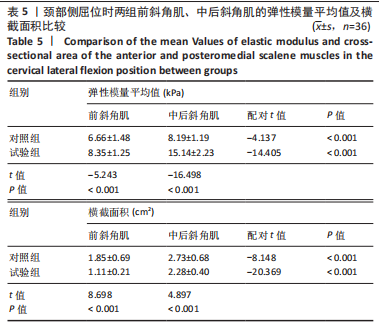
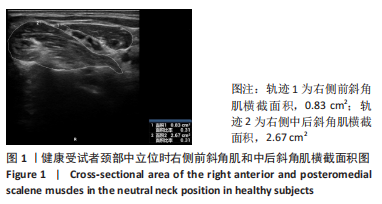
[1] GLOBAL BURDEN OF DISEASE STUDY 2013 COLLABORATORS. Global, regional, and national incidence, prevalence, and years lived with disability for 301 acute and chronic diseases and injuries in 188 countries, 1990-2013: a systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2013. Lancet. 2015;386(9995):743-800.
[2] AKAGI R, KUSAMA S. Comparison between neck and shoulder stiffness determined by shear wave ultrasound elastography and a muscle hardness meter. Ultrasound Med Biol. 2015;41(8):2266-2271.
[3] 陈德松,顾玉东.肩胛背神经卡压:不典型胸廓出口综合征[J].中华手外科杂志,1994,10(1):28-30.
[4] MACDERMID JC, WALTON DM, BOBOS P, et al. A qualitative description of chronic neck pain has implications for outcome assessment and classification. Open Orthop J. 2016;10:746.
[5] 黄萍,钱念东,齐进,等.颈肩痛患者颈肩部肌肉的表面肌电图特征[J].中国组织工程研究,2014,18(24):3855.
[6] MING Z, NäRHI M, SIIVOLA J. Neck and shoulder pain related to computer use. Pathophysiology. 2004;11(1):51-56.
[7] BRANDENBURG JE, EBY SF, SONG P, et al. Ultrasound elastography: the new frontier in direct measurement of muscle stiffness. Arch Phys Med Rehabil. 2014;95(11):2207-2219.
[8] BORDONI B, VARACALLO M. Anatomy, head and neck, scalenus muscle. 2022 Apr 16. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2022.
[9] GEORGAKOPOULOS B, LASRADO S. Anatomy, head and neck, inter-scalene triangle. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2022.
[10] TAŞ S, KORKUSUZ F, ERDEN Z. Neck muscle stiffness in participants with and without chronic neck pain: a shear-wave elastography study. J Manipulative Physiol Ther. 2018;41(7):580-588.
[11] 姚伟东,张微微,周俊合,等.基于实时剪切波弹性成像探讨针刺改善颈椎病肌肉状态的临床研究[J].中医药导报,2021,27(5): 123-126.
[12] 张芷绮.斜角肌拨法推拿结合针刺治疗神经根型颈椎病的临床研究[D].成都:成都中医药大学,2017.
[13] 贾学恕,王安利,邹志康,等.6周颈部离心训练对大学生颈部功能的影响[J].中国学校卫生,2022,43(8):1170-1173.
[14] 徐海东,张耘硕,王青波,等.基于“动静平衡”原则探析脊髓型颈椎病诊断及正脊治疗[J].山东中医杂志,2022,41(12):1321-1325.
[15] 罗鹏飞,李宁,谢兴文,等.基于 “筋骨平衡” 理论探讨旋转手法治疗颈椎病的生物力学机制研究进展[J].中医正骨,2020,32(9): 46-49.
[16] 于栋,刘侃,时宗庭,等.动力失衡模型兔颈椎间盘病理改变及终板软骨细胞的迁移凋亡规律[J].中国组织工程研究,2022,26(11): 1675.
[17] 孙钰,杨利学.杨利学教授 “三位一体” 外治疗法治疗神经根型颈椎病的临证经验[J].中国中医急症,2021,30(10):1832-1834,1862.
[18] MOORE N, DUONG M, GULMEZ SE, et al. Pharmacoepidemiology of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs. Therapies. 2019;74(2):271-277.
[19] 黄丽珍,康亚宁.实时剪切波弹性成像对颈肩部肌筋膜疼痛综合征阿是穴针刺疗效评估[J].临床超声医学杂志,2019,21(9):681-684.
[20] SCHLEIP R, NAYLOR IL, URSU D, et al. Passive muscle stiffness may be influenced by active contractility of intramuscular connective tissue. Med Hypotheses. 2006;66(1):66-71.
[21] DE BRUIN M, SMEULDERS MJ, KREULEN M, et al. Intramuscular connective tissue differences in spastic and control muscle: a mechanical and histological study. PloS One. 2014;9(6):e101038.
[22] 周述强,张敏霞.颈椎相关肌肉慢性损伤与颈椎病[J].安徽中医临床杂志,2003,15(3):247-248.
[23] CREZE M, NORDEZ A, SOUBEYRAND M, et al. Shear wave sonoelastography of skeletal muscle: basic principles, biomechanical concepts, clinical applications, and future perspectives. Skeletal Radiol. 2018;47:457-471.
[24] IJMKER S, HUYSMANS M, BLATTER BM, et al. Should office workers spend fewer hours at their computer? A systematic review of the literature. Occup Environ Med. 2007;64(4):211-222.
[25] LIU C, FENG Y, ZHANG H, et al. Assessing the viscoelastic properties of upper trapezius muscle: Intra-and inter-tester reliability and the effect of shoulder elevation. J Electromyogr Kinesiol. 2018;43:226-229.
[26] 郑保奇,董常峰,赵宁波.声触诊弹性成像在丙肝肝硬化评估中的应用价值[J].影像技术,2022,34(6):56-60.
[27] 巴桃桃,吕晓民,高沿航.酒精性肝病现有共识及尚未解决的问题[J].肝脏,2020,25(1):13.
[28] TALJANOVIC MS, GIMBER LH, BECKER GW, et al. Shear-wave elastography: basic physics and musculoskeletal applications. Radiographics. 2017;37(3):855-870.
[29] GOO M, JOHNSTON LM, HUG F, et al. Systematic review of instrumented measures of skeletal muscle mechanical properties: Evidence for the application of shear wave elastography with children. Ultrasound Med Biol. 2020;46(8):1831-1840.
[30] PHAN A, LEE J, GAO J. Ultrasound shear wave elastography in assessment of skeletal muscle stiffness in senior volunteers. Clin Imaging. 2019;58:22-26.
[31] RYU J, JEONG WK. Current status of musculoskeletal application of shear wave elastography. Ultrasonography. 2017;36(3):185.
[32] WINN N, LALAM R, CASSAR-PULLICINO V. Sonoelastography in the musculoskeletal system: current role and future directions. World J Radiol. 2016;8(11):868.
[33] DAVIS LC, BAUMER TG, BEY MJ, et al. Clinical utilization of shear wave elastography in the musculoskeletal system. Ultrasonography. 2019;38(1):2-12.
[34] PALUCH Ł, NAWROCKA-LASKUS E, WIECZOREK J, et al. Use of ultrasound elastography in the assessment of the musculoskeletal system. Pol J Radiol. 2016;81:240-246.
[35] HOBSON-WEBB LD. Emerging technologies in neuromuscular ultrasound. Muscle Nerve. 2020;61(6):719-725.
[36] 李春歌,王博冉,乔春梅,等.多模态超声在痛风性关节炎中的诊断价值[J].内蒙古医科大学学报,2021,43(3):324-327.
[37] 吕景,张娜,邸海燕,等.剪切波弹性成像联合超微血管显像对乳腺病灶良恶性的鉴别诊断价值[J]. 肿瘤影像学,2020,29(5):448-452.
[38] 李娅,汤四新,张恒.超声BI-RADS分级结合SWE技术在诊断乳腺良恶性病变中的价值[J].肿瘤影像学,2020,29(4):393-396.
[39] 张永东.按摩斜角肌治疗神经根型颈椎病的临床观察[J].特别健康, 2021(30):127.
[40] 薛炳鹤,张永旺,左广,等.斜角肌柔性手法联合神经松动术治疗神经根型颈椎病的临床研究[J].河北中医药学报,2022,37(3):11-14.
[41] BEDEWI MA, ALHARIQI BA, ALDOSSARY NM, et al. Shear wave elastography of the scalene muscles in healthy adults: a preliminary study. Medicine (Baltimore). 2021;100(32):e26891.
[42] KUO WH, JIAN DW, WANG TG, et al. Neck muscle stiffness quantified by sonoelastography is correlated with body mass index and chronic neck pain symptoms. Ultrasound Med Biol. 2013;39(8):1356-1361.
[43] CALVO-LOBO C, DIEZ-VEGA I, MARTíNEZ-PASCUAL B, et al. Tensiomyography, sonoelastography, and mechanosensitivity differences between active, latent, and control low back myofascial trigger points: a cross-sectional study. Medicine (Baltimore). 2017; 96(10):e6287.
[44] 徐亮.青少年静坐行为与颈肩症状的关联研究[D]. 合肥:安徽医科大学,2017.
[45] 杨世斌.颈肌与颈型颈椎病的关系[J].颈腰痛杂志,2008,9(1):77-79.
[46] CROMBIE IK, CROFT PR, LINTON SJ, et al. Epidemiology of pain:a report of the Task Force on Epidemiology of the International Association for the Study of Pain. Seattle:IASP Press, 1999:235-256.
[47] 李佩芳,陈佳丽,宁宁,等.后疫时代下颈肩痛防治策略[J].华西医学,2020,35(10):1153-1157.
[48] MARTíNEZ-MERINERO P, TARANCÓN FA, MONTAÑEZ-AGUILERA J, et al. Interaction between Pain, Disability, Mechanosensitivity and Cranio-Cervical Angle in Subjects with Cervicogenic Headache: A Cross-Sectional Study. J Clin Med. 2021;10(1):159.
[49] FALLA D, RAINOLDI A, MERLETTI R, et al. Myoelectric manifestations of sternocleidomastoid and anterior scalene muscle fatigue in chronic neck pain patients. Clin Neurophysiol. 2003;114(3):488-495.
[50] KARIMI N, REZASOLTANI A, RAHNAMA L, et al. Ultrasonographic analysis of dorsal neck muscles thickness changes induced by isometric contraction of shoulder muscles: A comparison between patients with chronic neck pain and healthy controls. Man Ther. 2016;22:174-178.
[51] MARTINEZ-MERINERO P, NUñEZ-NAGY S, ACHALANDABASO-OCHOA A, et al. Relationship between forward head posture and tissue mechanosensitivity: a cross-sectional study. J Clin Med. 2020;9(3):634.
[52] DIETERICH AV, ANDRADE RJ, LE SANT G, et al. Shear wave elastography reveals different degrees of passive and active stiffness of the neck extensor muscles. Eur J Appl Physiol. 2017;117(1):171-178.
[53] DIETERICH AV, YAVUZ UŞ, PETZKE F, et al. Neck muscle stiffness measured with shear wave elastography in women with chronic nonspecific neck pain. J Orthop Sports Phys Ther. 2020;50(4):179-188.
[54] PASKALI F, SIMANTZIK J, DIETERICH A, et al. Specification of neck muscle dysfunction through digital image analysis using machine learning. Diagnostics (Basel). 2022;13(1):7.
[55] YAVUZ A, BORA A, BULUT MD, et al. Acoustic Radiation Force Impulse (ARFI) elastography quantification of muscle stiffness over a course of gradual isometric contractions: a preliminary study. Med Ultrason. 2015;17(1):49-57.
[56] FALLA D, JULL G, HODGES P. Feedforward activity of the cervical flexor muscles during voluntary arm movements is delayed in chronic neck pain. Exp Brain Res. 2004;157(1):43-48.
[57] HVEDSTRUP J, KOLDING LT, ASHINA M, et al. Increased neck muscle stiffness in migraine patients with ictal neck pain: a shear wave elastography study. Cephalalgia. 2020;40(6):565-574. |