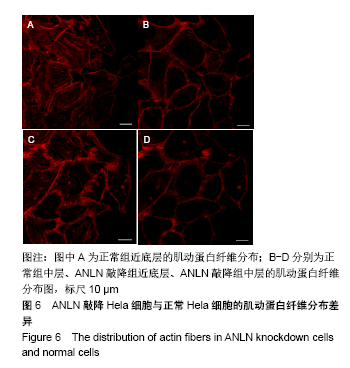
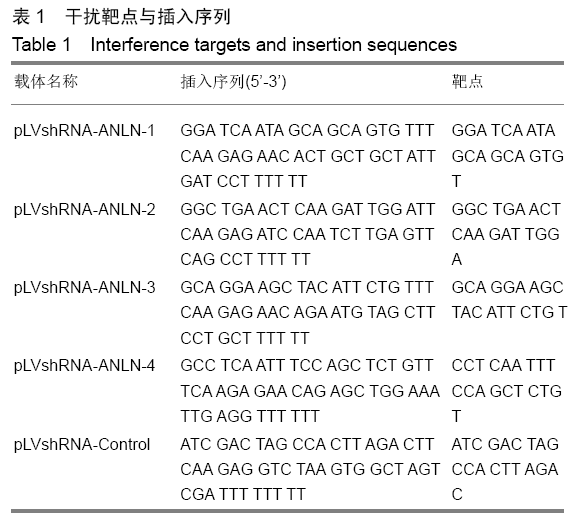
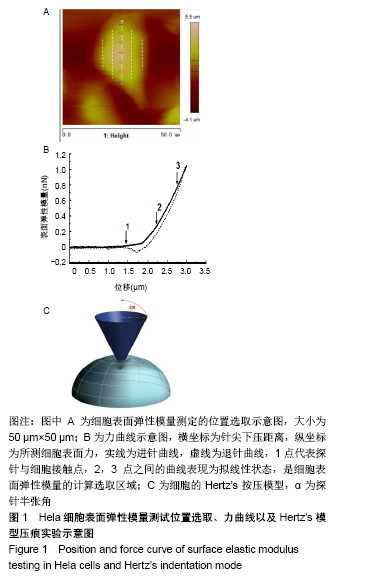
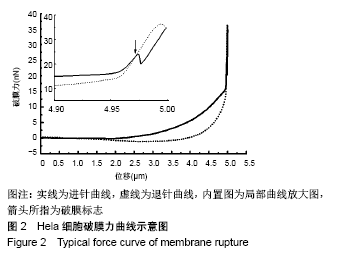
[1] LIU J, FAIRN GD, CECCARELLI DF, et al. Cleavage furrow organization requires PIP(2)-mediated recruitment of anillin. Curr Biol. 2012;22(1):64-69.
[2] FIELD CM, ALBERTS BM. Anillin, a contractile ring protein that cycles from the nucleus to the cell cortex. J Cell Biol. 1995;131(1):165-178.
[3] STRAIGHT AF, FIELD CM, MITCHISON TJ. Anillin binds nonmuscle myosin II and regulates the contractile ring. Mol Biol Cell. 2005;16(1):193-201.
[4] OEGEMA K, SAVOIAN MS, MITCHISON TJ,et al. Functional analysis of a human homologue of the Drosophila actin binding protein anillin suggests a role in cytokinesis. J Cell Biol. 2000;150(3):539-552.
[5] D'AVINO PP, TAKEDA T, CAPALBO L, et al. Interaction between Anillin and RacGAP50C connects the actomyosin contractile ring with spindle microtubules at the cell division site. J Cell Sci. 2008;121(Pt 8):1151-1158.
[6] GREGORY SL, EBRAHIMI S, MILVERTON J, et al. Cell division requires a direct link between microtubule-bound RacGAP and Anillin in the contractile ring. Curr Biol. 2008; 18(1):25-29.
[7] PIEKNY AJ, GLOTZER M. Anillin is a scaffold protein that links RhoA, actin, and myosin during cytokinesis. Curr Biol. 2008;18(1):30-36.
[8] TRACHE A, MEININGER GA. Atomic force microscopy (AFM). Curr Protoc Microbiol. 2008;Chapter 2:Unit 2C.2.
[9] REYES CC, JIN M, BREZNAU EB, et al. Anillin regulates cell-cell junction integrity by organizing junctional accumulation of Rho-GTP and actomyosin. Curr Biol. 2014; 24(11):1263-1270.
[10] WANG D, CHADHA GK, FEYGIN A, et al. F-actin binding protein, anillin, regulates integrity of intercellular junctions in human epithelial cells. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2015;72(16): 3185-3200.
[11] FRENETTE P, HAINES E, LOLOYAN M, et al. An anillin-Ect2 complex stabilizes central spindle microtubules at the cortex during cytokinesis. PLoS One. 2012;7(4):e34888.
[12] MCKENZIE AJ, HICKS SR, SVEC KV, et al. The mechanical microenvironment regulates ovarian cancer cell morphology, migration, and spheroid disaggregation. Sci Rep. 2018;8(1): 7228.
[13] SCHIFFHAUER ES, ROBINSON DN. Mechanochemical Signaling Directs Cell-Shape Change. Biophys J. 2017;112(2): 207-214.
[14] PILLET F, CHOPINET L, FORMOSA C, et al. Atomic Force Microscopy and pharmacology: from microbiology to cancerology. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2014;1840(3): 1028-1050.
[15] JINSCHEK JR, HELVEG S. Image resolution and sensitivity in an environmental transmission electron microscope. Micron. 2012;43(11):1156-1168.
[16] GUO Q, XIA Y, SANDIG M, et al. Characterization of cell elasticity correlated with cell morphology by atomic force microscope. J Biomech. 2012;45(2):304-309.
[17] LEKKA M, GIL D, POGODA K, et al. Cancer cell detection in tissue sections using AFM. Arch Biochem Biophys. 2012; 518(2):151-156.
[18] ZEMŁA J, DANILKIEWICZ J, ORZECHOWSKA B, et al. Atomic force microscopy as a tool for assessing the cellular elasticity and adhesiveness to identify cancer cells and tissues. Semin Cell Dev Biol. 2018;73:115-124.
[19] NI Y, QIN Y, FANG Z, et al. ROCK Inhibitor Y-27632 Promotes Human Retinal Pigment Epithelium Survival by Altering Cellular Biomechanical Properties. Curr Mol Med. 2017;17(9): 637-646.
[20] CASCIONE M, DE MATTEIS V, RINALDI R, et al. Atomic force microscopy combined with optical microscopy for cells investigation. Microsc Res Tech. 2017;80(1):109-123.
[21] SMITH JR, TSIBOUKLIS J, NEVELL TG, et al. AFM friction and adhesion mapping of the substructures of human hair cuticles. Applied Surface Science. 2013; 285(Part B): 638-644.
[22] MILLER KG, ALBERTS BM. F-actin affinity chromatography: technique for isolating previously unidentified actin-binding proteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A.1989;86(13):4808-4812.
[23] CAPPELLA B , DIETLER G. Force-distance curves by atomic force microscopy. Surf Sci Rep.1999;34(1-3):1-3,5-104.
[24] SIRGHI L, BRETAGNOL F, MORNET S, et al. Atomic force microscopy characterization of the chemical contrast of nanoscale patterns fabricated by electron beam lithography on polyethylene glycol oxide thin films. Ultramicroscopy. 2009;109(3):222-229.
[25] LI QS, LEE GY, ONG CN, et al. AFM indentation study of breast cancer cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun.2008; 374(4):609-613.
[26] CROSS SE, JIN YS, RAO J, et al. Nanomechanical analysis of cells from cancer patients. Nat Nanotechnol.2007;2(12): 780-783.
[27] ZHOU W, WANG Z, SHEN N, et al. Knockdown of ANLN by lentivirus inhibits cell growth and migration in human breast cancer. Mol Cell Biochem.2015;398(1-2):11-19.
[28] FIELD CM, COUGHLIN M, DOBERSTEIN S, et al. Characterization of anillin mutants reveals essential roles in septin localization and plasma membrane integrity. Development. 2005;132(12):2849-2860.
[29] ATILLA-GOKCUMEN GE, MURO E, RELAT-GOBERNA J, et al. Dividing cells regulate their lipid composition and localization. Cell. 2014;156(3):428-439.
[30] YOKOKAWA M, TAKEYASU K, YOSHIMURA SH. Mechanical properties of plasma membrane and nuclear envelope measured by scanning probe microscope. J Microsc. 2008; 232(1):82-90.
[31] 李海涛,梁婷,邵毅杰,等.针刺与异常机械应力对大鼠椎间盘纤维环纳米级生物力学特性影响的对比[J].中国组织工程研究,2018, 22(34):5510-5517.
[32] TOMAR S, PLOTNIK JP, HALEY J, et al. ETS1 induction by the microenvironment promotes ovarian cancer metastasis through focal adhesion kinase. Cancer Lett. 2018;414: 190-204.
|