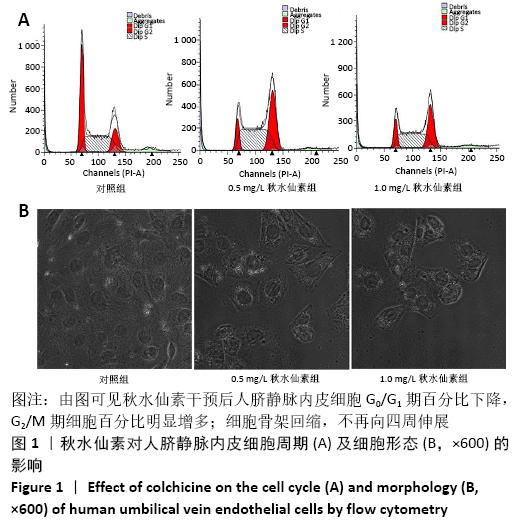
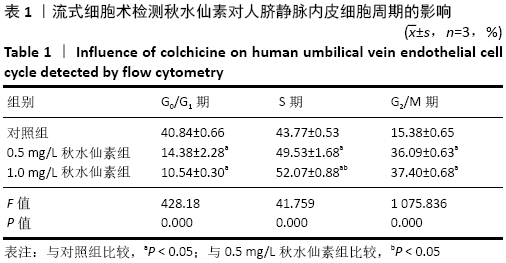
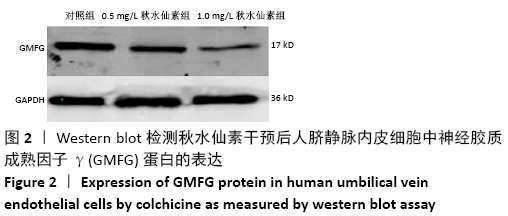
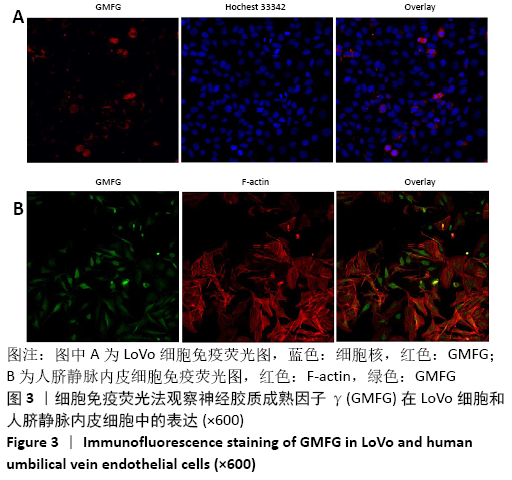
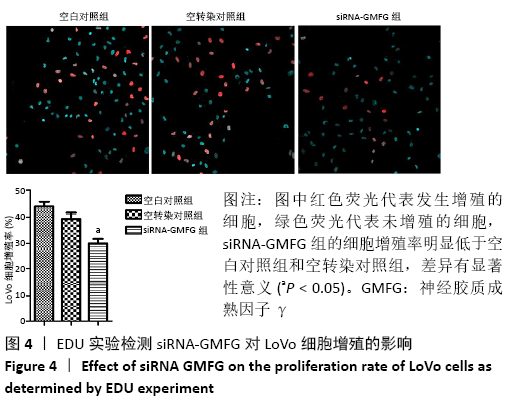
[1] CHEN W, SUN K, ZHENG R, et al. Cancer incidence and mortality in China, 2014. Chin J Cancer Res. 2018;30(1):1-12.
[2] LIU S, ZHENG R, ZHANG M, et al. Incidence and mortality of colorectal cancer in China, 2011. Chin J Cancer Res. 2015;27(1):22-28.
[3] BRAY F, FERLAY J, SOERJOMATARAM I, et al. Global cancer statistics 2018: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J Clin. 2018;68(6):394-424.
[4] MALVEZZI M, CARIOLI G, BERTUCCIO P, et al. European cancer mortality predictions for the year 2018 with focus on colorectal cancer. Ann Oncol. 2018;29(4):1016-1022.
[5] ZHANG Z, WANG Y, ZHANG J, et al. COL1A1 promotes metastasis in colorectal cancer by regulating the WNT/PCP pathway. Mol Med Rep. 2018;17(4):5037-5042.
[6] ZHANG X, HU F, LI G, et al. Human colorectal cancer-derived mesenchymal stem cells promote colorectal cancer progression through IL-6/JAK2/STAT3 signaling. Cell Death Dis. 2018;9(2):25.
[7] ZHANG S, WANG Q, ZHOU C, et al. Colorectal cancer, radiotherapy and gut microbiota. Chin J Cancer Res. 2019;31(1):212-222.
[8] MILLER SA, POLICASTRO RA, SAVANT SS, et al. Lysine-Specific Demethylase 1 Mediates AKT Activity and Promotes Epithelial-to-Mesenchymal Transition in PIK3CA-Mutant Colorectal Cancer. Mol Cancer Res. 2020;18(2):264-277.
[9] GANDHI M, SMITH BA, BOVELLAN M, et al. GMF is a cofilin homolog that binds Arp2/3 complex to stimulate filament debranching and inhibit actin nucleation. Curr Biol. 2010;20(9):861-867.
[10] NAKANO K, KUWAYAMA H, KAWASAKI M, et al. GMF is an evolutionarily developed Adf/cofilin-super family protein involved in the Arp2/3 complex-mediated organization of the actin cytoskeleton. Cytoskeleton (Hoboken). 2010;67(6):373-382.
[11] HARDEMAN EC, BRYCE NS, GUNNING PW. Impact of the actin cytoskeleton on cell development and function mediated via tropomyosin isoforms. Semin Cell Dev Biol. 2020;102:122-131.
[12] 李璐,黄红武. 肌动蛋白细胞骨架重构调节免疫细胞功能的研究进展[J].免疫学杂志,2019,35(8):727-731.
[13] IKEDA K, KUNDU RK, IKEDA S, et al. Glia maturation factor-gamma is preferentially expressed in microvascular endothelial and inflammatory cells and modulates actin cytoskeleton reorganization. Circ Res. 2006; 99(4):424-433.
[14] AERBAJINAI W, GHOSH MC, LIU J, et al. Glia maturation factor-γ regulates murine macrophage iron metabolism and M2 polarization through mitochondrial ROS. Blood Adv. 2019;3(8):1211-1225.
[15] AERBAJINAI W, LIU J, KUMKHAEK C, et al. Glia maturation factor-gamma modulates M2 activation of macrophage via suppression of mitochondria function. Blood. 2017;130(Supplement 1):998.
[16] ZUO P, FU Z, TAO T, et al. The expression of glia maturation factors and the effect of glia maturation factor-γ on angiogenic sprouting in zebrafish. Exp Cell Res. 2013;319(5):707-717.
[17] AERBAJINAI W, LIU L, ZHU J, et al. Glia Maturation Factor-γ Regulates Monocyte Migration through Modulation of β1-Integrin. J Biol Chem. 2016;291(16):8549-8564.
[18] AERBAJINAI W, LIU L, KUMKHAEK C, et al. Glia maturation factor-gamma mediates human monocytes migration through regulating β1/β2-integrin recycling. Blood. 2013; 122(21):1027.
[19] SAADIYA Z, NUDRAT B, RAMLA S. Glia maturation factor gamma, is a novel diagnostic marker of leukemia, has TAL1 binding sites in its promoter. Journal of King Saud University – Science. 2020; 32:511-517.
[20] 魏星,冀静,赵永林.GMFG蛋白在宫颈癌中的表达及其与EMT的相关性[J].山西医科大学学报,2018,49(11):1306-1310.
[21] ZUO P, MA Y, HUANG Y, et al. High GMFG expression correlates with poor prognosis and promotes cell migration and invasion in epithelial ovarian cancer. Gynecol Oncol. 2014;132(3):745-751.
[22] 左鹏.神经胶质成熟因子γ在斑马鱼血管芽细胞迁移和卵巢癌侵袭转移中的作用及机制研究[D].杭州:浙江大学,2014.
[23] YAMAGUCHI H, CONDEELIS J. Regulation of the actin cytoskeleton in cancer cell migration and invasion. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2007; 1773(5):642-652.
[24] LI X, WANG J. Mechanical tumor microenvironment and transduction: cytoskeleton mediates cancer cell invasion and metastasis. Int J Biol Sci. 2020;16(12):2014-2028.
[25] JEONG YJ, HWANG SK, MAGAE J, et al. Ascofuranone suppresses invasion and F-actin cytoskeleton organization in cancer cells by inhibiting the mTOR complex 1 signaling pathway. Cell Oncol (Dordr). 2020. doi: 10.1007/s13402-020-00520-w. Online ahead of print.
[26] WANG H, CHEN Z, CHANG H, et al. Expression of glia maturation factor γ is associated with colorectal cancer metastasis and its downregulation suppresses colorectal cancer cell migration and invasion in vitro. Oncol Rep. 2017;37(2):929-936.
[27] INAGAKI M, AOYAMA M, SOBUE K, et al. Sensitive immunoassays for human and rat GMFB and GMFG, tissue distribution and age-related changes. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2004;1670(3):208-216.
[28] SHI Y, CHEN L, LIOTTA LA, et al. Glia maturation factor gamma (GMFG): a cytokine-responsive protein during hematopoietic lineage development and its functional genomics analysis. Genomics Proteomics Bioinformatics. 2006;4(3):145-155.
[29] 林文韬,王武炼,肖莉莉,等.基于GEO数据库发现骨肉瘤关键基因GMFG及其生物学功能[J].福建医药杂志, 2020,42(2):112-115.
|