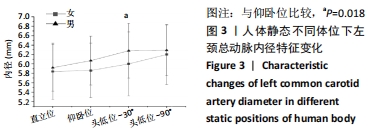
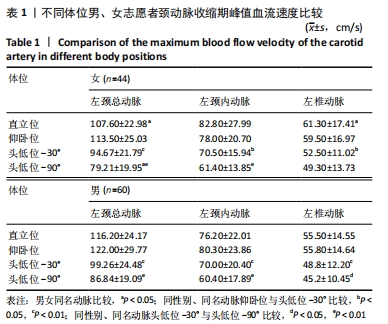
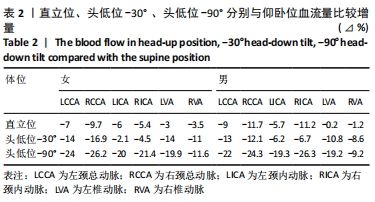
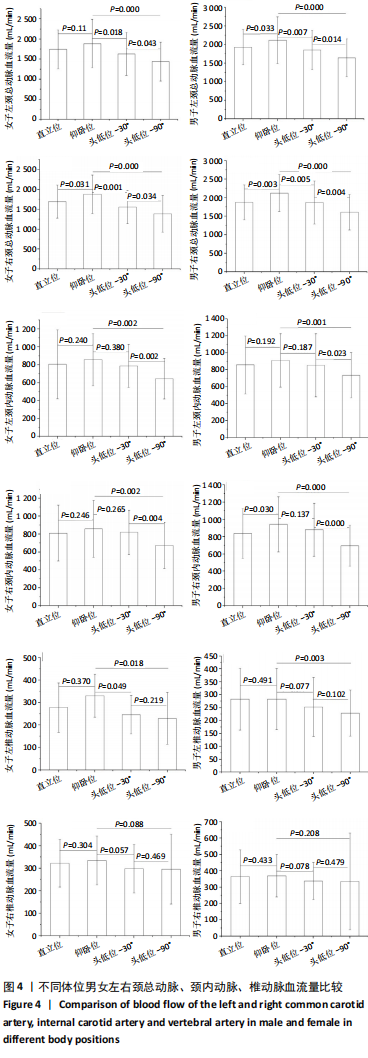
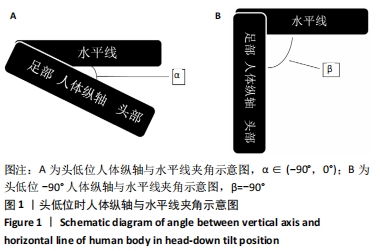
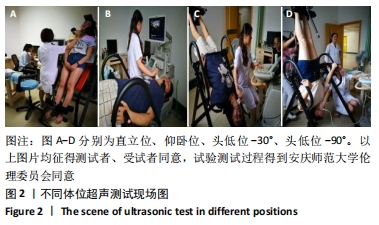
[1] 陈金鳌,张林,陈琉,等.振动训练对低龄老年人动脉血管弹性的影响[J].体育学刊,2015,22(2):120-126.
[2] 王文荣,熊开宇,何辉.中年人颈动脉WSS与FMD、IMT、心血管危险因素的相关关系[J].北京体育大学学报,2018,41(3):76-81.
[3] 赵平,李国泰,黄诚胤,等.运动调节气体信号分子系统对动脉粥样硬化的作用[J].武汉体育学院学报,2010,44(2):71-75.
[4] 林云,陈文鹤.肥胖症与动脉粥样硬化的关系研究进展[J].上海体育学院学报,2011,35(5):52-56.
[5] 林云,陈文鹤.4周有氧运动对肥胖儿童少年动脉粥样硬化致病相关因子的影响[J].中国体育科技,2012,48(4):131-136.
[6] 王祥全,王晓峰,张立伟.国外运动康复研究前沿及其热点演化分析[J].武汉体育学院学报,2018,52(3):75-82.
[7] 王帝之,张培珍.运动对动脉粥样硬化斑块逆转机制的研究进展[J].体育科学,2018,38(9):65-71.
[8] 黄浩洁,赵焕彬.筋膜自我放松效应研究进展[J].武汉体育学院学报,2018,52(4):92-100.
[9] MCALPINE CS, KISS MG, RATTIK S, et al. Sleep modulates haematopoiesis and protects against atherosclerosis. Nature. 2019; 566(7744):383-387.
[10] 屈红林,谢军,陈嘉勤,等.有氧运动通过TLR4/miR-223/NLRP3信号通路轴介导CUMS抑郁小鼠海马炎症反应[J].体育科学,2019, 39(2):39-50.
[11] 林小晶,鲁林,王晓慧.炎症因子 chemerin 在有氧运动改善动脉粥样硬化大鼠血脂和主动脉硬化中的作用[J].上海体育学院学报, 2017,41(4):49-56.
[12] KOMPANJE EJO, GENDEREN MV, INCE C. The supine head-down tilt position that was named after the German surgeon Friedrich Trendelenburg. European Surgery. 2012;44(3):168-171.
[13] DYSON J, RICHARDSON A. Treatment of supraventricular tachycardias by placement in the Trendelenburg position. Clin Auton Res. 2007; 17(6):382-384.
[14] MEDOW MS, STEWART JM, SANYAL S, et al. Pathophysiology, diagnosis, and treatment of orthostatic hypotension and vasovagal syncope. Cardiol Rev. 2008;16(1):4-20.
[15] ABRAMS BJ, SUKUMVANICH P, SEIBEL R, et al. Ultrasound for the detection of intraperitoneal fluid: the role of Trendelenburg positioning. Am J Emerg Med. 1999;17(2):117-120.
[16] MEYERS C, LOW L, KAUFMAN L, et al. Trendelenburg positioning and continuous lateral rotation improve oxygenation in hepatopulmonary syndrome after liver transplantation. Liver Transpl Surg. 1998;4(6):510-512.
[17] NISHIKAWA M, WATANABE H, KURAHASHI T. Effects of 25- and 30-degree Trendelenburg positions on intraocular pressure changes during robot-assisted radical prostatectomy. Prostate Int. 2017;5(4): 135-138.
[18] VILLAR R, HUGHSON RL. Vascular conductance and muscle blood flow during exercise are altered by inspired oxygen fraction and arterial perfusion pressure. Physiol Rep. 2017;5(5):e13144.
[19] LINDÉN C, QVARLANDER S, JÓHANNESSON G, et al. Normal-Tension Glaucoma Has Normal Intracranial Pressure: A Prospective Study of Intracranial Pressure and Intraocular Pressure in Different Body Positions. Ophthalmology. 2018;125(3):361-368.
[20] SERRADOR JM. The Cardiovascular Dizziness Connection: Role of Vestibular Autonomic Interactions in Aging and Dizziness. Dizziness and Vertigo Across the Lifespan. 2019:175-189.
[21] JURASCHEK SP, TAYLOR AA, WRIGHT JT JR, et al. Orthostatic Hypotension, Cardiovascular Outcomes, and Adverse Events: Results From SPRINT. Hypertension. 2020;75(3):660-667.
[22] MOL A, BUI HOANG PTS, SHARMIN S, et al. Orthostatic Hypotension and Falls in Older Adults: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis. J Am Med Dir Assoc. 2019;20(5):589-597.
[23] KLECZYŃSKI P, DIMITROW PP, DZIEWIERZ A, et al. Predictors of syncope in patients with severe aortic stenosis: The role of orthostatic unload test. Cardiol J. 2020;27(6):749-755.
[24] YASA E, RICCI F, MAGNUSSON M, et al. Cardiovascular risk after hospitalisation for unexplained syncope and orthostatic hypotension. Heart. 2018;104(6):487-493.
[25] KLECZYŃSKI P, PETKOW DIMITROW P, DZIEWIERZ A, et al. Decreased carotid and vertebral arterial blood-flow velocity in response to orthostatic unload in patients with severe aortic stenosis. Cardiol J. 2016;23(4):393-401.
[26] DAMANTI S, CONSONNI D, VALENTINI A, et al. Orthostatic hypotension, an often-neglected problem in community-dwelling older people: discrepancies between studies and real life. J Geriatr Cardiol. 2018; 15(10):644-646.
[27] MAGKAS N, TSIOUFIS C, THOMOPOULOS C, et al. Orthostatic hypotension: From pathophysiology to clinical applications and therapeutic considerations. J Clin Hypertens (Greenwich). 2019;21(5): 546-554.
[28] 郭强,徐芳,陈道芳,等.彩色多普勒血流成像技术评价缺血性脑卒中患者颈动脉和椎动脉血流动力学及脑血流灌注量的变化[J].中华医学超声杂志(电子版),2016,13(9):670-676.
[29] 陈金鳌,张林,李亚峰,等.长期抗阻运动对中老年人颈动脉顺应性的影响[J].体育科学,2014,34(2):60-67.
[30] 丁宝维,夏玉光,唐维平,等.随年龄变化的成人颈动脉和椎动脉颅外段的超声特征[J].中国老年学杂志,2014,34(24):6935-6937.
[31] 孙佳艺,赵冬,刘静,等.中国缺血性脑卒中住院患者颈动脉粥样硬化病变性别差异的分析[J].心肺血管病杂志,2016,35(2):81-86.
[32] 赵国璇,胡志红,杨静生,等.头低位(-30°)卧床条件下不同耐力者的头颈部血流变化的特点[J].航天医学与医学工程,1998,11(5): 324-328.
[33] 吴斌,吴萍,薛月英,等.反复体位改变训练可提高人体头低位耐力[J].中国应用生理学杂志,2008,24(1):116-120.
[34] 范少光,汤浩. 人体生理学(第三版)[M].北京:北京大学医学出版社,2006.
[35] 鲁力立,吴斌,吴萍,等.不同职业健康女性与男性对-30°头低位的反应[J].航天医学与医学工程,2007,20(2):87-91.
[36] 张雪梅,赵欣,赵颖,等.正常成人椎动脉内径及多普勒血流量参考值范围的研究[J].临床超声医学杂志,2017,19(1):22-25.
[37] 苏全生,黄志强,孙力行.体位变化对心动时相和心泵功能的影响[J].成都体育学院学报,1989(2): 88-96.
[38] 黄志强,苏全生,孙力行.不同体位对血流动力学指标和心泵功能的影响[J].四川体育科学,1989(1):15-20.
[39] ADE CJ, BROXTERMAN RM, BARSTOW TJ. Effects of body posture and exercise training on cardiorespiratory responses to exercise. Respir Physiol Neurobiol. 2013;188(1):39-48.
[40] ZHANG R, LEVINE BD. Autonomic ganglionic blockade does not prevent reduction in cerebral blood flow velocity during orthostasis in humans. Stroke. 2007;38(4):1238-1244.
[41] IMMINK RV, SECHER NH, ROOS CM, et al. The postural reduction in middle cerebral artery blood velocity is not explained by PaCO2. Eur J Appl Physiol. 2006;96(5):609-614.
[42] VILLAR R, HUGHSON RL. Lower limb vascular conductance and resting popliteal blood flow during head-up and head-down postural challenges. Clin Physiol Funct Imaging. 2013;33(3):186-191.
[43] 沈羡云. 14 天头低位倾斜对鼠肾功能、血管和细胞外液的影响[J].航天医学与医学工程,1992,5(3):211.
[44] 薛莲,孙飙.头低位倾斜对血液循环及呼吸系统的影响[J].南京体育学院学报(自然科学版),2005, 4(2): 13-17.
[45] 潘毅.倒立在跳水基础训练中的应用[J].体育科技,2007,28(2):43-56.
[46] 王霆,李建英,石岩,等.优秀射箭运动员倒立训练后脑电非线性参数及脑功能变化特征的研究[J].体育科学,2014,34(2): 48-53.
[47] 姜丽,王霆.倒立训练对射击射箭运动员脑电图影响的研究[J].搏击•体育论坛,2014,6(7):78-81.
[48] VIJAYALAKSHMI P, MADANMOHAN. Acute effect of 30 degrees, 60 degrees and 80 degrees head-down tilt on blood pressure in young healthy human subjects. Indian J Physiol Pharmacol. 2006;50(1):28-32.
[49] 李志宏,刘瑛,张桂青.手倒立与中老年知识分子高血压脑溢血的预防研究[J].体育与科学,2002,23(6): 59-60.
[50] LÜ J, SUN M, LIANG L, et al. Effects of momentum-based dumbbell training on cognitive function in older adults with mild cognitive impairment: a pilot randomized controlled trial. Clin Interv Aging. 2015;11:9-16.
|