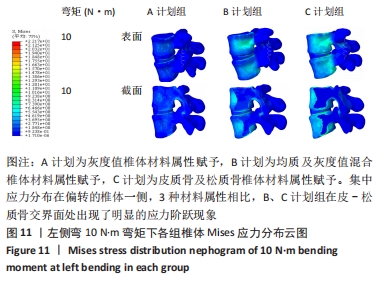
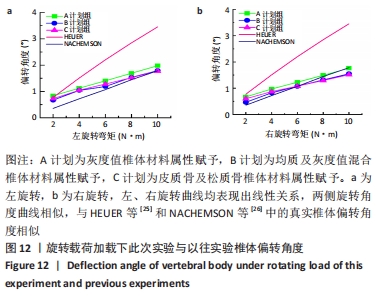
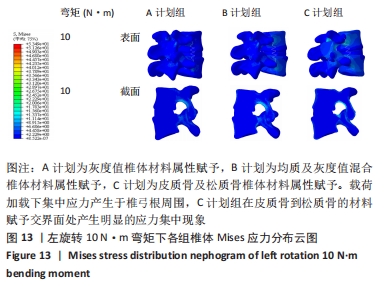
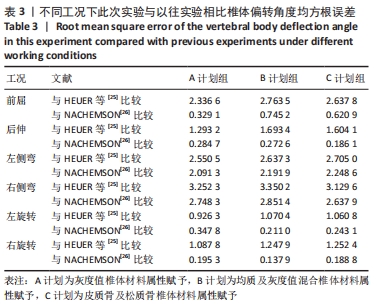
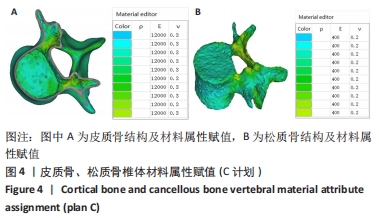
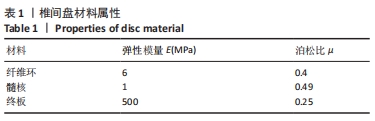
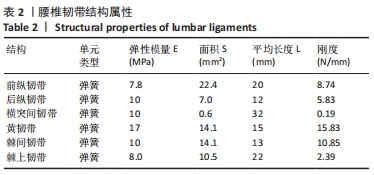
[1] 孙枫原,李宗远,何希,等.有限元分析在脊柱侧凸生物力学研究中的应用及进展[J].中国组织工程研究,2019,23(32):5221-5226.
[2] LIANG L, LIU ML, MARTIN C, et al. A deep learning approach to estimate stress distribution: a fast and accurate surrogate of finite-element analysis. J R Soc Interface. 2018;15(138):20170844.
[3] 赵鹏飞,陈玲,门玉涛.有限元分析肌肉力对腰椎内固定系统的影响[J].中国组织工程研究,2018,22(23):3654-3658.
[4] 刘慧,沈国权,张喜林,等.肌肉加载下腰椎间盘突出的有限元研究[J].医用生物力学,2019,34(5):493-499.
[5] CHOI HW, KIM YE. Effect of lumbar fasciae on the stability of the lower lumbar spine. Comput Method Biomec. 2017;20(13):1431-1437.
[6] ANDERSSON G, SCHULTZ AB. Effects of fluid injection on mechanical properties of intervertebral discs. J Biomech. 1979;12(6):453-458.
[7] TENCER AF. Some static mechanical properties of the lumbar intervertebral joint, intact and injured. J Biomech Eng. 1982;104(3):193-201.
[8] 文毅,苏峰,刘肃,等.L4-5椎体有限元模型建立及退变椎间盘力学分析[J].中国组织工程研究,2019,23(8):1222-1227.
[9] 薛志鹏,李泰贤,李龚,等.基于CT灰度值赋值的股骨头坏死有限元模型对比[J].中国组织工程研究,2020,24(3):395-400.
[10] 罗林聪,马立敏,林泽,等.基于AnyBody骨骼肌肉多体动力学分析的有限元仿真[J].医用生物力学,2019,34(3):237-242+250.
[11] 张聪,赵岩,杜小宇,等.青少年特发性脊柱侧凸腰主弯患者腰椎-骨盆的生物力学分析[J].中国组织工程研究,2020,24(8):1155-1161.
[12] 成博,赵文,罗伟,等.基于CT三维重建模型在数字化骨科的应用研究[J].武汉理工大学学报,2017,39(2):89-94.
[13] RASMUSSEN J, TRHOLM S, ZEE MD. Computational analysis of the influence of seat pan inclination and friction on muscle activity and spinal joint forces. Nt J Ind Ergonom. 2009;39(1):52-57.
[14] 李丹.基于腰椎多层螺旋CT扫描三维形态学分析的腰椎材料、形态及结构属性变化与骨折相关性的FEA研究[D].长春:吉林大学,2011.
[15] MORGAN EF, BAYRAKTAR HH, KEAVENY TM. Trabecular bone modulus-density relationships depend on anatomic site. J Biomech. 2003;36(7):897-904.
[16] RHO JY, KUHN-SPEARING L, ZIOUPOS P. Mechanical properties and the hierarchical structure of bone. Med Eng Phys. 1998;20(2):92-102.
[17] 聂文忠.脊柱胸腰部的生物力学建模与应用研究[D].上海:上海交通大学, 2009.
[18] 苏晋.腰椎有限元模型的建立与生物力学分析[D].大连:大连医科大学,2010.
[19] 贾少薇,张顺心,范顺成,等.脊柱侧凸腰骶椎结构的有限元分析及其变形趋势[J].医用生物力学,2017,32(3):235-241.
[20] GOEL VK, KONG W, HAN JS, et al. A Combined Finite Element and Optimization Investigation of Lumbar Spine Mechanics With and Without Muscles. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 1993;18(11):1531-1541.
[21] ROHLMANN A, BOUSTANI HN, BERGMANN G, et al. Effect of a pedicle-screw-based motion preservation system on lumbar spine biomechanics: A probabilistic finite element study with subsequent sensitivity analysis. J Biomech. 2010;43(15): 2963-2969.
[22] 国家技术监督局.成年人人体质心.中华人民共和国国家标准GB/T 17245-1998.1998.
[23] YAMAMOTO I, PANJABI MM, CRISCO T, et al. Three-dimensional movements of the whole lumbar spine and lumbosacral joint. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 1989; 14(11):1256-1260.
[24] BROWN T, HANSEN RJ, YORRA AJ. Some mechanical tests on the lumbosacral spine with particular reference to the intervertebral discs;a preliminary report. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1957;39(5):1135-1164.
[25] HEUER F, SCHMIDT H, KLEZL Z, et al. Stepwise reduction of functional spinal structures increase range of motion and change lordosis angle. J Biomech. 2007; 40(2):271-280.
[26] NACHEMSON AL, SCHULTZ AB, BERKSON MH. Mechanical properties of human lumbar spine motion segments. Influence of age, sex, disc level, and degeneration. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 1979;4(1):1-8.
[27] CHEN YC, TU YK, ZHUANG JY, et al. Evaluation of the parameters affecting bone temperature during drilling using a three-dimensional dynamic elastoplastic finite element model. Med Biol Eng Comput. 2017;55(11):1949-1957.
[28] 朱康平,祝建雯,曲恒磊.国外生物医用钛合金的发展现状[J].稀有金属材料与工程,2012,41(11):2058-2063.
|