| [1]殷亚康.钛合金表面等离子喷涂钛/羟基磷灰石复合涂层及其细胞相容性研究[D].乌鲁木齐:新疆大学,2015.[2]吴永智.等离子喷涂羟基磷灰石/纳米氧化锆梯度涂层的研究[D].北京:北京工业大学,2008.[3]郑学斌,陈益凯,梁莹,等.等离子体喷涂新型生物活性涂层研究[J].热喷涂技术,2009,1(1):59-62.[4]El-hadad AS.An approach to design new coatings for biomedical applications.Universidad Carlos III de Madrid, 2012.[5]Piccinini M.Porous calcium phosphate granules for biomedical applications.University of Trento, 2012.[6]Ibrahim MZ,Sarhan AAD,Yusuf F,et al.Biomedical materials and techniques to improve the tribological, mechanical and biomedical properties of orthopedic implants- A review article.J Alloy Compound. 2017;714:636-667.[7]Zhou H,Lee J.Nanoscale hydroxyapatite particles for bone tissue engineering.Acta Biomater. 2011;7(7):2769-2781.[8]高淑春.NiTi形状记忆合金和TA2钛合金生物材料的表面改性及生物学性能研究[D].沈阳:东北大学,2013.[9]于振涛,韩建业,麻西群,等.生物医用钛合金材料的生物及力学相容性[J].中国组织工程研究,2013, 17(25):4707-4714.[10]Geetha M,Singh AK,Sokamani RA,et al. Ti based biomaterials, the ultimate choice for orthopaedic implants-A review.Prog Mater Sci. 2009;54(3):397-425.[11]Rokosz K, Hryniewicz T, Raaen S. Development of plasma electrolytic oxidation for improved Ti6Al4V biomaterial surface properties.Int J Adv Manuf Technol.2016;85(9):1-13.[12]张文毓.生物医用钛合金的研究进展[J].化学与粘合,2014,36(5): 369-373.[13]张玉梅,王勤涛,赵铱民,等.新型医用Ti75,TiZr合金的生物腐蚀行为研究[J].稀有金属材料与工程, 2016,33(1):19-22.[14]Fomin A,Fomina M,Koshuro V,et al.Structure and mechanical properties of hydroxyapatite coatings produced on titanium using plasma spraying with induction preheating.Ceram Int. 2017;43(14): 11189-11196.[15]高亚丽,熊党生.医用镁合金等离子喷涂羟基磷灰石涂层研究[J].材料热处理学报,2011,32(1):109-113.[16]Wang Y,Liu X,Fan T,et al.In vitro evaluation of hydroxyapatite coatings with (002) crystallographic texture deposited by micro-plasma spraying. Mater Sci Eng C-Mater.2017;75:596-601.[17]冷喷涂技术在生物医学领域中的应用及展望[J].表面技术, 2016,45(9):25-31.[18]陈枭,白小波,纪岗昌,等.微米羟基磷灰石/钛复合粒子冷喷沉积行为[J].金属热处理,2018,43(11):89-95.[19]智伟,匙峰,李金雨,等.羟基磷灰石球形颗粒表面微形貌构建及其对干细胞生物学行为的调控[J].无机材料学报, 2017,32(3):319-325.[20]Asri RI,Harun WS,Hassan MA,et al.A review of hydroxyapatite-based coating techniques: Sol-gel and electrochemical depositions on biocompatible metals.J Mech Behav Biomed Mater.2016;57:95-108.[21]李素敏,张芹,赵玉涛,等.HAF/YSZ梯度复合涂层的制备及结构和性能[J].中国组织工程研究,2011, 15(47):8805-8808.[22]Jansen JA,Wolke JGC,Swann S,et al.Application of magnetron sputtering for producing ceramic coatings on implant materials.Clin Oral Implants Res.2010;4(1):28-34.[23]Boccaccini AR,Keim S,Ma R,et al.Electrophoretic deposition of biomaterials. J R Soc Interface. 2010;7 Suppl 5(51): S581-S613.[24]鞠昊.微弧氧化处理Ti6Al4V的体外生物相容性研究[D].长春:吉林大学, 2017.[25]Yang YC.Influence of residual stress on bonding strength of the plasma-sprayed hydroxyapatite coating after the vacuum heat treatment.Surf Coat Technol. 2007;201(16-17):7187-7193. [26]Im KH,Lee SB,Kim KM,et al. Improvement of bonding strength to titanium surface by sol–gel derived hybrid coating of hydroxyapatite and titania by sol–gel process.Surf Coat Technol.2007;202(4-7):1135-1138.[27]Zheng X, Huang M, Ding C. Bond strength of plasma-sprayed hydroxyapatite/Ti composite coatings. Biomaterials. 2000;21(8): 841-849.[28]Fan X,Chen J,Zou JP,et al.Bone-like apatite formation on HA/316L stainless steel composite surface in simulated body fluid.Trans Nonferrous Met Soc China.2009;19(2):347-352.[29]Oliver WC,Pharr GM.Measurement of hardness and elastic modulus by instrumented indentation: Advances in understanding and refinements to methodology.J Mater Res. 2004;19(1):3-20.[30]Shamray VF,Sirotinkin VP,Smirnov TV.Structure of the hydroxyapatite plasma-sprayed coatings deposited on pre-heated titanium substrates. Ceram Int. 2017;43(12):9105-9109.[31]Sun L,Berndt CC,Gross KA,et al. Material fundamentals and clinical performance of plasma‐sprayed hydroxyapatite coatings: A review. J Biomed Mater Res.2010;58(5):570-592.[32]Leylavergne M,Vardelle A,Dussoubs B,et al.Comparison of plasma-sprayed coatings produced in argon or nitrogen atmosphere. J Therm Spray Technol.2018;(4):527-536.[33]Sadikov KG,Sofronitskiy AO,Dautov TG.Functional plasma sprayed coatings on magnesium ceramic substrates. JPCS. 2017:012043.[34]Sargin Y,Kiziyalli M,Telli C,et al.A new method for the solid-state synthesis of tetracalcium phosphate, a dental cement: X-ray powder diffraction and IR studies.J Eur Ceram Soc.1997;17:963-970.[35]Yang CW,Lui TS. Microstructural self-healing effect of hydrothermal crystallization on bonding strength and failure mechanism of hydroxyapatite coatings.J Eur Ceram Soc. 2008;28(11):2151-2159.[36]Yang CW,Lee TM,Lui TS,et al.A comparison of the microstructural feature and bonding strength of plasma-sprayed hydroxyapatite coatings with hydrothermal and vacuum post-heat treatment.Mater Trans. 2005;46(3):709-715.[37]Yang CY,Lee TM,Yang CW,et al.The in vitro and in vivo biological responses of plasma-sprayed hydroxyapatite coatings with post- hydrothermal treatment.J Biomed Mater Res.2007; 83A:263-271. |
.jpg)
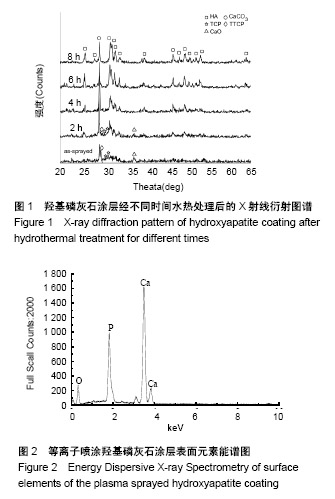
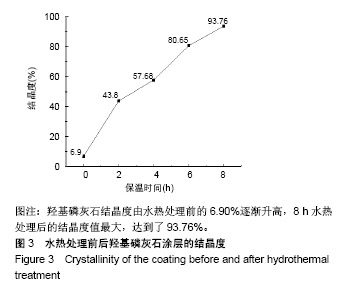
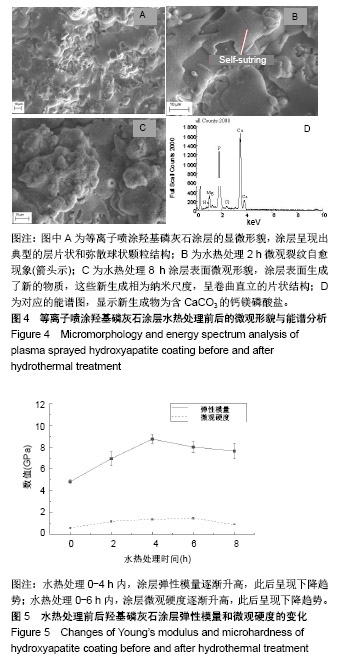
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)