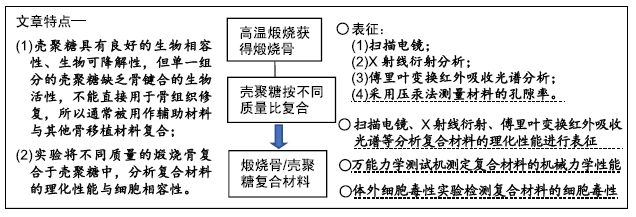
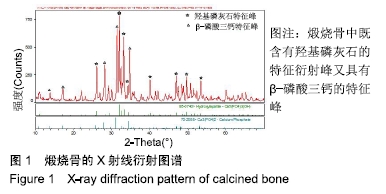
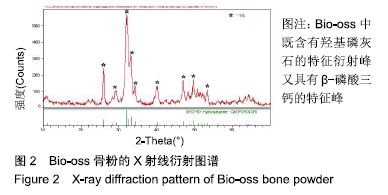
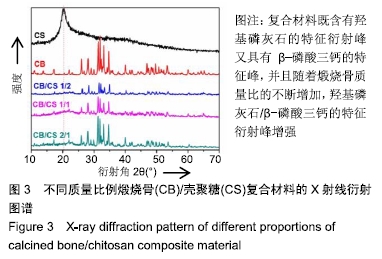
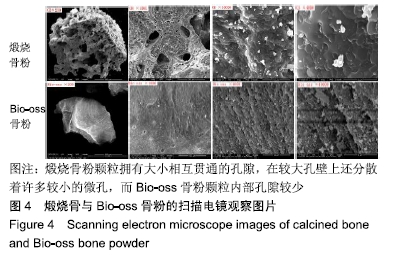
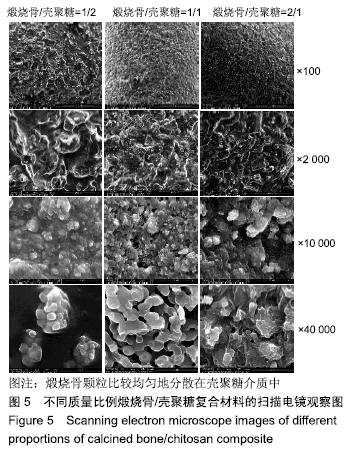
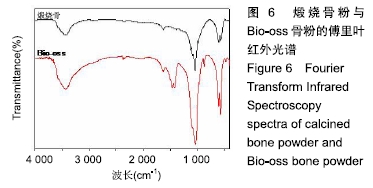
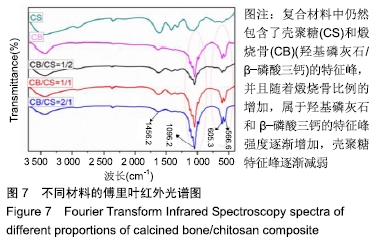
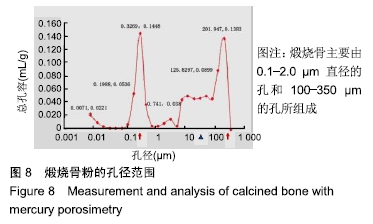
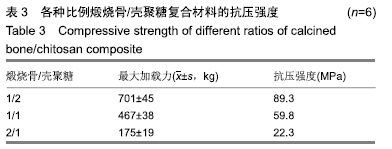
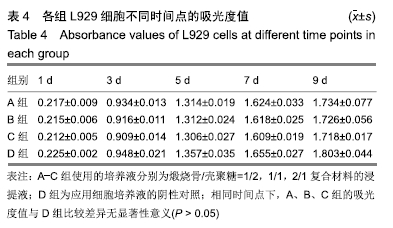
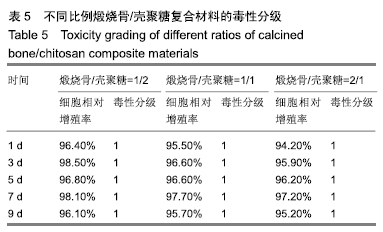
[1] TRAINI T, PIATTELLI A, CAPUTI S, et al. Regeneration of human bone using different bone substitute biomaterials.Clin Implant Dent Relat Res.2015;17(1):150-162.
[2] XI Y, MIAO X, LI Y, et al. BMP2-mimicking peptide modified with E7 coupling to calcined bovine bone enhanced bone regeneration associating with activation of the Runx2/SP7 signaling axis.J Biomed Mater Res B Appl Biomater. 2020;108(1):80-93.
[3] IIJIMA K, TSUJI Y, KURIKI I, et al. Control of cell adhesion and proliferation utilizing polysaccharide composite film scaffolds.Colloids Surf B Biointerfaces. 2017;160:228-237.
[4] GRAHAM SM, LEONIDOU A, ASLAM-PERVEZ N, et al. Biological therapy of bone defects:the immunology of bone allo-transplantation. Expert opin Biol Ther.2010;10(6):885-901.
[5] 赵淑珍,张婷,王彦鹏,等.复合3D支架在修复颅骨缺损中的应用进展[J].中国综合临床,2019,35(2):183-186.
[6] RESMIM CM, DALPASQUALE M, VIELMO NIC, et al.Study of physico-chemical properties and in vitro antimicrobial activity of hydroxyapatites obtained from bone calcination.Prog Biomater. 2019; 8(1):1-9.
[7] GOTO T, SASAKI K. Synthesis of morphologically controlled hydroxyapatite from fish bone by urea-assisted hydrothermal treatment and its Sr2+ sorption capacity.Powder Technol. 2016;292: 314-322.
[8] TEKIYEH RM, NAJAFI M, SHAHRAKI S. Machinability of AA7075-T6/carbon nanotube surface composite fabricated by friction stir processing. Proceedings of the Institution of Mechanical Engineers, Part E: Journal of Process Mechanical Engineering. 2018;233(4): 839-848.
[9] ANWAR A, AKBAR S. Novel continuous microwave assisted flow synthesis of nanosized manganese substituted hydroxyapatite.Ceram Int.2018;44(9):10878-10882.
[10] DOMÍNGUEZ-TRUJILLO C, PEÓN E, CHICARDI E, et al. Sol-gel deposition of hydroxyapatite coatings on porous titanium for biomedical applications.Surf Coat Technol.2018;333:158-162.
[11] 赵宏霞.羟基磷灰石微结构调控的研究进展[J].功能材料, 2017,48(1): 1047-01055.
[12] RUIXIN L, CHENG X, YINGJIE L, et al. Degradation behavior and compatibility of micro, nanoHA/chitosan scaffolds with interconnected spherical macropores.Int J Biol Macromol. 2017;103: 385-394.
[13] XU AT, QI WT, LIN MN, et al. The optimization of sintering treatment on bovine-derived bone grafts for bone regeneration: in vitro and in vivo evaluation.J Biomed Mater Res B Appl Biomater. 2020;108(1): 272-281.
[14] HEIDARI F, RAZAVI M, GHAEDI M, et al. Investigation of mechanical properties of natural hydroxyapatite samples prepared by cold isostatic pressing method.J Alloys Compd. 2017;693: 1150-1156.
[15] TONSUAADU K, GROSS KA, PLUDUMA L, et al. A review on the thermal stability of calcium apatites. J Therm Anal Calorim. 2012; 110(2):647-659.
[16] AHMAD FARA ANK, ABDULLAH HZ. Influence of Calcination Temperature on the Microstructure and Crystallographic Properties of Hydroxyapatite from Black Tilapia Fish Scale. Mater Sci Forum. 2016; 840:151-155.
[17] 徐子昂,刘晨,肖良,等.髓核组织工程支架的构建及其生物相容性[J].中国矫形外科杂志,2019,35(13):1211-1216.
[18] 赵献峰.壳聚糖负载TiO2抗菌材料的研究[J].山西化工, 2018,38(3): 17-18,32.
[19] XIA YJ, WEI W, XIA H, et al. Effect of recombinant human bone morphogenetic protein delivered by chitosan microspheres on ectopic osteogenesis in rats.Exp Ther Med. 2019;17(5):3891-3898.
[20] YUAN H, CHEN N, LU XY, et al. Experimental study of natural hydroxyapatite-chitosan composite on reconstructing bone defect. Stomatology.2005;25(2):65-67.
[21] TENG SH, LEE EJ, YOON BH, et al. Chitosan/nanohydroxyapatite composite membranes via dynamic filtration for guided bone regeneration.J Biomed Mater Res A.2009;88(3):569-580.
[22] GE Z, BAGUENARD S, LIM LY, et al. Hydroxyapatite–chitin materials as potential tissue engineered bone substitutes. Biomaterials. 2004; 25(6):1049-1058.
[23] ITOH S, YAMAGUCHI I, SUZUKI M, et al. Hydroxyapatite-coated tendon chitosan tubes with adsorbed laminin peptides facilitate nerve regeneration in vivo.Brain Res.2003;993(1-2):111-123.
[24] LÜ X, ZHENG B, TANG X, et al. In vitro biomechanical and biocompatible evaluation of natural hydroxyapatite/chitosan composite for bone repair.J Appl Biomater Biomech. 2011;9(1):11-18.
[25] MARUYAMA M, ITO M. In vitro properties of a chitosan-bonded self-hardening paste with hydroxyapatite granules.J Biomed Mater Res.1996;32(4):527-532.
[26] 司徒镇强,吴军正.细胞培养[M].2版.西安:世界图书出版社公司, 2003: 186-187.
[27] JIANG SD, JIANG LS, DAI LY. Surgical treatment of calcaneal fractures with use of beta-tricalcium phosphate ceramic grafting.Foot Ankle Int.2008;29(10):1015-1019.
[28] 王诗美.类骨质羟基磷灰石植入兔股骨缺损的实验研究[D].成都:四川大学, 2005.
[29] JIN HH, KIM DH, KIM TW, et al. In vivo evaluation of porous hydroxyapatite/chitosan-alginate composite scaffolds for bone tissue engineering.Int J Biol Macromol. 2012;51(5):1079-1085.
[30] WANG J, QU L, MENG X, et al. Preparation and biological properties of PLLA/beta-TCP composites reinforced by chitosan fibers.Biomed Mater.2008;3(2):025004.
[31] 马东洋,薛振恂,刘兰忠,等.天然珊瑚和同种异体脱钙骨基质作为骨组织工程支架的组织相容性研究[J].西北国防医学杂志, 2003,24(4):259-260.
[32] HOLLINGER JO, BATTISTONE GC. Biodegradable bone repair materials. Synthetic polymers and ceramics.Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1986;(207):290-305.
[33] LU JX, FLAUTRE B, ANSELME K, et al. Role of interconnections in porous bioceramics on bone recolonization in vitro and in vivo.J Mater Sci Mater Med.1999;10(2):111-120.
[34] PEÑA J, ROMÁN J, VICTORIA CABAÑAS M, et al. An alternative technique to shape scaffolds with hierarchical porosity at physiological temperature.Acta Biomater. 2010;6(4):1288-1296.
[35] VENKATESAN J, QIAN ZJ, RYU B, et al. A comparative study of thermal calcination and an alkaline hydrolysis method in the isolation of hydroxyapatite from Thunnus obesus bone.Biomed Mater. 2011; 6(3):035003.
[36] VENKATESAN J, KIM SK. Effect of Temperature on Isolation and Characterization of Hydroxyapatite from Tuna (Thunnus obesus) Bone. Materials (Basel).2010;3(10):4761-4772.
[37] ZHANG J, NIE J, ZHANG Q, et al. Preparation and characterization of bionic bone structure chitosan/hydroxyapatite scaffold for bone tissue engineering.J Biomater Sci Polym Ed.2014;25(1):61-74.
[38] ROGINA A, IVANKOVIĆ M, IVANKOVIĆ H. Preparation and characterization of nano-hydroxyapatite within chitosan matrix. Mater Sci Eng C Mater Biol Appl.2013;33(8):4539-4544.
[39] PU XM, WEI K, ZHANG QQ. In situ forming chitosan/hydroxyapatite rods reinforced via genipin crosslinking.Mater Lett.2013;94:169-171.
[40] LIU H, PENG H, WU Y, et al. The promotion of bone regeneration by nanofibrous hydroxyapatite/chitosan scaffolds by effects on integrin-BMP/Smad signaling pathway in BMSCs. Biomaterials. 2013; 34(18):4404-4417.
[41] VENKATESAN J, PALLELA R, BHATNAGAR I, et al. Chitosan-amylopectin/hydroxyapatite and chitosan-chondroitin sulphate/hydroxyapatite composite scaffolds for bone tissue engineering.Int J Biol Macromol. 2012;51(5):1033-1042.
[42] VENKATESAN J, RYU B, SUDHA PN, et al. Preparation and characterization of chitosan-carbon nanotube scaffolds for bone tissue engineering.Int J Biol Macromol. 2012;50(2):393-402.
[43] LIMA PA, RESENDE CX, SOARES GD, et al. Preparation, characterization and biological test of 3D-scaffolds based on chitosan, fibroin and hydroxyapatite for bone tissue engineering.Mater Sci Eng C Mater Biol Appl. 2013;33(6):3389-3395.
[44] SUN F, LIM BK, RYU SC, et al. Preparation of multi-layered film of hydroxyapatite and chitosan. Mater Sci Eng C. 2010;30(6):789-794.
[45] KIM H, KIM HM, JANG JE, et al. Osteogenic Differentiation of Bone Marrow Stem Cell in Poly(Lactic-co-Glycolic Acid) Scaffold Loaded Various Ratio of Hydroxyapatite.Int J Stem Cells. 2013;6(1):67-74.
[46] MOHAMED KR, EL-RASHIDY ZM, SALAMA AA. In vitro properties of nano-hydroxyapatite/chitosan biocomposites. Ceram Int. 2011;37(8): 3265-3271.
[47] 张霁文.煅烧骨/羧甲基壳聚糖复合材料修复家兔下颌骨缺损实验研究[D].贵阳:贵州医科大学,2016.
[48] COSTA-PINTO AR, CORRELO VM, SOL PC, et al. Chitosan-poly(butylene succinate) scaffolds and human bone marrow stromal cells induce bone repair in a mouse calvaria model.J Tissue Eng Regen Med.2012;6(1):21-28.
[49] SHAMELI K, AHMAD MB, YUNUS WM, et al. Green synthesis of silver/montmorillonite/chitosan bionanocomposites using the UV irradiation method and evaluation of antibacterial activity.Int J Nanomedicine. 2010;5:875-887.
[50] SHAMELI K, AHMAD MB, YUNUS WM, et al. Silver/poly (lactic acid) nanocomposites: preparation, characterization, and antibacterial activity. Int J Nanomedicine.2010;5:573-579.
|