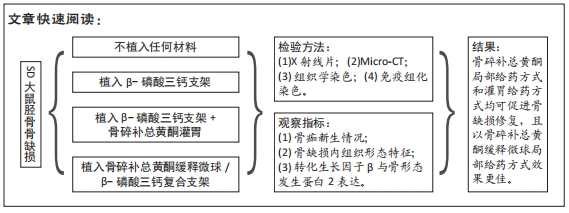
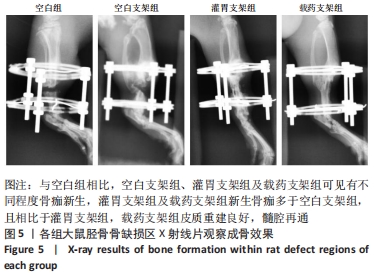
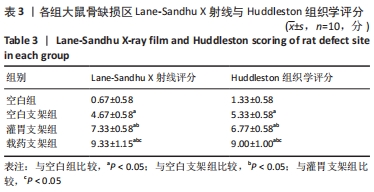
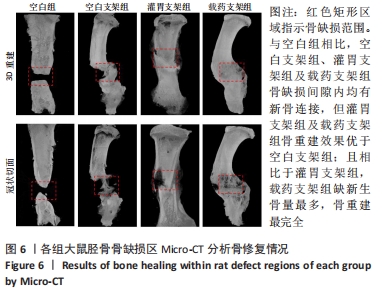
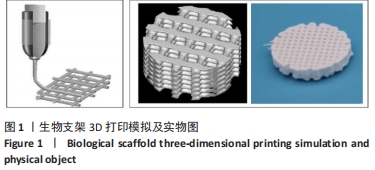
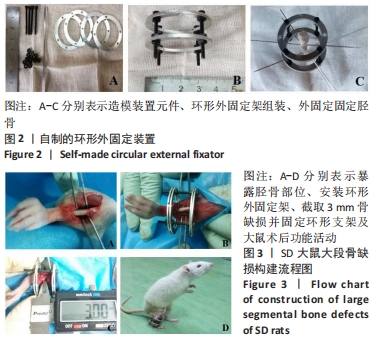
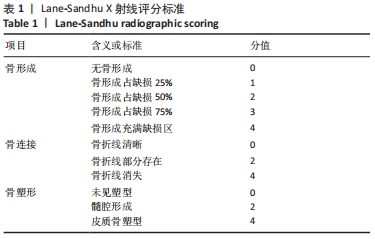
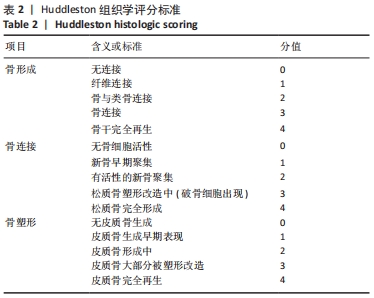
[1] MAUFFREY C, BARLOW BT, SMITH W. Management of segmental bone defects. J Am Acad Orthop Surg. 2015;23(3):143-153.
[2] ALMUBARAK S, NETHERCOTT H, FREEBERG M, et al. Tissue engineering strategies for promoting vascularized bone regeneration. Bone. 2016; 83:197-209.
[3] 马云飞.医用硫酸钙介导的Masquelet技术修复SD大鼠大段骨缺损的实验研究[D].广州:南方医科大学,2017.
[4] 戚晓阳,邱旭升,施鸿飞,等.大段骨缺损的治疗进展[J].实用骨科杂志,2017,23(8):715-719.
[5] JING X, YIN W, TIAN H, et al.Icariin doped bioactive glasses seeded with rat adipose-derived stem cells to promote bone repair via enhanced osteogenic and angiogenic activities. Life Sci. 2018;202:52-60.
[6] 谢雁鸣,秦林林,于向东,等.骨碎补、淫羊藿、菟丝子总黄酮对成骨细胞体外培养影响的比较研究[J].中国中医药信息杂志,2005, 12(7):22.
[7] 蔡群斌,李定,李悦,等.骨碎补总黄酮对 Masquelet 技术诱导膜内血管形成的影响[J].广州中医药大学学报,2017,34(6):867-871.
[8] 李定,李悦,黄枫,等.骨碎补总黄酮在诱导膜技术中对骨缺损区域血管形成和成骨质量的影响[J].中华中医药杂志,2019,34(11):5086-5089.
[9] 曾志奎,黄枫,李悦,等.骨碎补总黄酮对大鼠Masquelet诱导膜血管新生因子表达的影响[J].中华中医药学刊,2019,37(10):2345-2348+2565-2567.
[10] 姜自伟,曾景奇,黄枫,等.骨碎补总黄酮对大鼠胫骨牵张成骨效能的影响[J].中华中医药杂志,2018,33(2):661-663
[11] 姜自伟,曾景奇,李悦,等.骨碎补总黄酮对大鼠胫骨牵张末期BMP-2与Smad-1表达的影 响[J].辽宁中医杂志,2018,45(1):166-168+227.
[12] 申震,姜自伟,李定,等.基于牵张成骨技术比较两种补肾法在成血管-成骨耦联机制中的作用差异[J].中华中医药杂志,2019, 34(5):2150-2155.
[13] 韩亚力,罗奕,曾佳学.骨碎补总黄酮基于Notch信号通路改善骨质疏松的作用及机制研究[J].中国免疫学杂志,2018,34(2):261-266.
[14] 李树源,周琦石,周宏亮,等.强骨胶囊辅助诱导膜技术治疗感染性骨髓炎并骨缺损临床观察[J].山东医药,2019,59(19):73-76.
[15] 陈丽辉.骨碎补总黄酮(强骨胶囊)治疗老年骨质疏松症的效果及对骨密度的影响[J].临床合理用药杂志,2018,11(11):60-61.
[16] 章轶立,魏戌,谢雁鸣,等.骨碎补总黄酮(强骨胶囊)治疗绝经后骨质疏松症大鼠实验的系统评价[J].中国骨质疏松杂志,2019, 25(12):1700-1706.
[17] 王清滢,章轶立,谢雁鸣,等.骨碎补总黄酮治疗绝经后骨质疏松症的Meta分析[J].中国骨质疏松志,2019,25(4):465-471.
[18] ZHANG Y, JIANG J, SHEN H, et al. Total flavonoids from RhizomaDrynariae (Gusuibu)fortreating osteoporotic fractures:implication in clinical practice. Drug Des Devel Ther. 2017;11:1881-1890.
[19] 李晋玉.骨碎补总黄酮联合纳米骨材料对成骨细胞增殖分化及血管新生的影响[D].北京:北京中医药大学,2018.
[20] 李少刚.生物硅-微球支架材料结合AFDR修复大鼠颅骨缺损的实验研究[D].北京:北京中医药大学,2016.
[21] 金合.可注射骨修复材料结合骨碎补总黄酮修复鼠骨缺损[D].北京:北京中医药大学,2010.
[22] 陈虹舟.骨碎补总黄酮/聚乳酸-羟基乙酸微囊复合自固化磷酸钙治疗家兔股骨缺损模型的实验研究[D].扬州:扬州大学,2016.
[23] 薛鹏,杜斌,王礼宁,等.可控释淫羊藿苷-β-磷酸三钙复合支架的制备[J].中国组织工程研究,2018,22(6):865-870.
[24] 潘朝晖,栾兆新,高朋.两种交联剂对β-磷酸三钙明胶复合骨支架理化及生物学性能影响的比较[J].中国组织工程研究,2018,22(6): 833-839.
[25] 申震,姜自伟,李定,等.基于Masquelet诱导膜技术比较不同固定方式构建的胫骨大段骨缺损模型[J].中国实验动物学报,2018, 26(6):673-680.
[26] 关德强,于波.大段骨缺损修复的研究进展[J].世界最新医学信息文摘,2017,17(52):70-71+76.
[27] CYPHER TJ. Biological principles of bone graft healing. J Foot Ankle Surg. 1996;35(5):413-417.
[28] FALDINI C, MISCIONE MT, ACRI F, et al. Single level cervical fusion by an anterior approach using autologous bone graft influences the adjacent levels degenerative changes: clinical and radiographic results at 10-year minimum follow-up. Eur Spine J. 2012;21 Suppl(1):S90-S93.
[29] SADHASIVAM S, YEN-HSIN F, SAVITHA S, et al. Hydroxyapatite-calcium sulfate-hyaluronic acid composite encapsulated with collagenase as bone substitute for alveolar bone regeneration. Biomaterials. 2016;74: 99-108.
[30] LANGER R. Tissue engineering. Science. 1993;260:920-926.
[31] ROSETI L, PARISI V, PETRETTA M, et al. Scaffolds for Bone Tissue Engineering: State of the art and new perspectives. Mater Sci Eng C Mater Biol Appl. 2017;78:1246-1262.
[32] 国家药典委员会.中华人民共和国药典(一部)[M].北京:中国医药科技出版社,2010:121.
[33] 钱茜.骨碎补化学成分和药理作用研究进展[J].中国生化药物杂志, 2015,39(3):186-188.
[34] 李绪松.骨碎补总黄酮局部填充修复家兔膝关节软骨全层缺损的实验研究[D].成都:成都中医药大学,2014.
[35] SWEET L, KANG Y, CZISCH C, et al. Geometrical versus Random β-TCP Scaffolds: Exploring the Effects on Schwann Cell Growth and Behavior. PLoS One. 2015;10(10):e0139820.
[36] 常再平,杨海龙,张明宇.葛根素促进成骨细胞复合β-磷酸三钙的成骨[J].中国组织工程研究,2018,22(28):4447-4451.
[37] SIQUEIRA L, PASSADOR FR, COSTA MM, et al. Influence of the addition of β-TCP on the morphology, thermal properties and cell viability of poly (lactic acid) fibers obtained by electrospinning. Mater Sci Eng C Mater Biol Appl. 2015;52:135-143.
[38] YOMODA M, SOBAJIMA S, KASUYA A, et al. Calcium phosphate cement-gelatin powder composite testing in canine models: Clinical implications for treatment of bone defects. J Biomater Appl. 2015;29(10):1385-1393.
[39] CRANE JL, XIAN L, CAO X. Role of TGF-beta signaling in coupling bone remodeling. Methods Mol Biol. 2016;1344:287-300.
[40] ABE E. Function of BMPs and BMP antagonists in adult bone. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2006;1068(1):41-53.
[41] 杨丽,朱晓峰,王攀攀,等.骨碎补水提液对大鼠MSCs骨向分化的影响及机制研究[J].中药材,2013,36(8):1287-1292.
[42] 高怡加,黄培镇,李悦,等.骨碎补总黄酮对牵张成骨过程中骨形态发生蛋白-2和转化生长因子-β1表达的影响[J].广州中医药大学学报,2016,33(5):679-683.
[43] 李晋玉,赵学千,孙旗,等.骨碎补总黄酮的实验及临床研究概况[J].中国骨质疏松杂志,2018,24(10):1357-1364.
|