| [1]Yamamoto S,Maeda K,Kouchi I,et al.Development of antiresorptive agent-related osteonecrosis of the jaw after dental implant removal:a case report. J Oral Implantol. 2018; 44(5):359-364.[2]Koga T,Minamizato T,Kawai Y,et al.Bone regeneration using dentin matrix depends on the degree of demineralization and particle size.PLoS One.2016;11(1):e0147235. [3]Garcia-Junior IR,Souza FA,Figueiredo AAS,et al.Maxillary alveolar ridge atrophy reconstructed with autogenous bone graft harvested from the proximal ulna.J Craniofac Surg. 2018;29(8):2304-2306.[4]Aksekili AME,Polat Y,Yüksel K,et al.An evaluation of the effect on lower extremity fracture healing of collagen-based fusion material containing 2 different calcium phosphate salts:an experimental rat model.Adv Clin Exp Med. 2018;27(9): 1295-1301.[5]Yeomans JD,Urist MR.Bone induction by decalcified dentine implanted into oral,osseous and muscle tissues.Arch Oral Biol. 1967;12(81):999-1008.[6]Huggins C,Wiseman S,Reddi AH.Transformation of fibroblasts by allogeneic and xenogeneic transplants of demineralized tooth and bone.J Exp Med. 1970;132: 1250-1258.[7]Bang G,Urist MR.Bone induction in excavation chambers of decalcified dentin.Arch Surg.1967;94(6):781-789.[8]Qin X,Zou F,Chen W,et al.Demineralized dentin as a semi-rigid barrier for guiding periodontal tissue regeneration.J Periodontol.2015;86(12):1370-1379. [9]Li P,Zhu H,Huang D.Autogenous DDM versus Bio-Oss granules in GBR for immediate implantation in periodontal postextraction sites:a prospective clinical study.Clin Implant Dent Relat Res.2018;20(6):923-928.[10]Shengyin Y,Ping C,Jibo B,et al.Experimental study of demineralized dentin matrix on osteoinduction and related cells identification.Hua Xi Kou Qiang Yi Xue Za Zhi. 2018; 36(1):33-38.[11]Kim YK,Lee J,Yun JY,et al.Comparison of autogenous tooth bone graft and synthetic bone graft materials used for bone resorption around implants after crestal approach sinus lifting:a retrospective study.Periodontal Implant Sci. 2014; 44(5):216-221.[12]Park M,Mah YJ,Kim DH,et al.Demineralized deciduous tooth as a source of bone graft material:its biological and physicochemical characteristics.Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol.2015;120(3):307-314.[13]Gultekin BA,Bedeloglu E,Kose TE,et al.Comparison of bone resorption rates after intraoral block bone and guided bone regeneration augmentation for the reconstruction of horizontally deficient maxillary alveolar ridges.Biomed Res Int.2016;2016:4987437.[14]Mauffrey C,Barlow BT,Smith W.Management of segmental bone defects.J Am Acad Orthop Surg.2015;23(3):143-53.[15]Eppley BL,Pietrzak WS,Blanton MW.Allograft and alloplastic bone substitutes:a review of science and technology for the craniomaxillofacial surgeon.J Craniofac Surg. 2005;16(6): 981-989.[16]Shakir M,Jolly R,Khan MS,et al.Nano- hydroxyapatite/ chitosan-starch nanocomposite as a novel bone construct: synthesis and in vitro studies.Int J Biol Macromol. 2015;80: 282-292.[17]刘鹏,周延民.自体牙骨移植材料的研究进展与临床应用[J].中国老年学杂志,2017,37(11):2858-2860.[18]Min BM.Oral biochemistry.Seoul:Daehan Narae Publishing, 2007:8-73.[19]Naso F,Gandaglia A,Iop L,et al.Alpha-Gal detectors in xenotransplantation research: a word of caution. Xenotransplantation.2012;19(4):215-220.[20]Bessho K,Tagawa T,Murata M. Purification of bone morphogenetic protein derived from bovine bone matrix.Biochem Biophys Res Commun.1989;165(2):595-601.[21]Bertassoni LE.Dentin on the nanoscale:hierarchical organization,mechanical behavior and bioinspired engineering.Dent Mater.2017;33(6):637-649.[22]Lee JY,Kim YK.Retrospective cohort study of autogenous tooth bone graft.Oral Biol Res. 2012;36:39-43.[23]靳夏莹,仲维剑,马国武.自体牙制成骨移植材料在上前牙即刻种植中的应用[J].口腔医学研究,2017,33(11):1228-1229.[24]Breschi L,Gobbi P,Lopes M,et al.Immunocytochemical analysis of dentin:a double-labeling technique. J Biomed Mater Res A.2003;67(1):11-17.[25]申丁,仲维剑.牙本质作为骨移植材料的应用研究进展[J].口腔医学研究,2016,32(6):656-658.[26]郭津源,仲维剑,柴松岭,等.牙齿煅烧颗粒结合富血小板纤维蛋白修复骨缺损的实验研究[J].口腔医学研究, 2015,31(11): 1069-1072.[27]Moharamzadeh K,Freeman C,Blackwood K.Processed bovine dentine as a bone substitute.Br J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2008;46(2):110-113.[28]崔婷婷,邱泽文,邵阳,等.异种牙本质颗粒复合骨髓浓缩物在上颌窦提升中的成骨效应[J].中国组织工程研究, 2018,22(30): 4806-4811.[29]Kim BS,Mooney DJ.Development of biocompatible synthetic extracellular matrices for tissue engineering.Trends Biotechnol. 1998;16(5):224-230.[30]Kamal M,Andersson L,Tolba R,et al.Bone regeneration using composite non-demineralized xenogenic dentin with beta-tricalcium phosphate in experimental alveolar cleft repair in a rabbit model.J Transl Med.2017;15:263.[31]Al-Asfour A,Andersson L,Kamal M,et al.New bone formation around xenogenic dentin grafts to rabbit tibia marrow.Dent Traumatol.2013;29:455-460. |
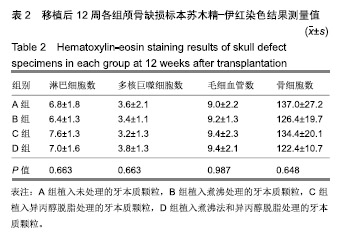
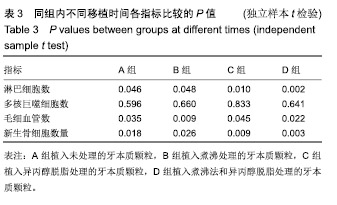
.jpg)
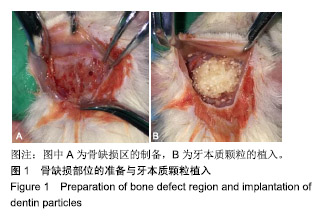
.jpg)