1.1 设计 生物活性显影材料SrPP及骨水泥材料制备与表征实验,两组数据对比使用t检验分析,两组以上数据之间的对比采用方差分析(ANOVA)进行。
1.2 时间及地点 实验于2021年1月至2023年7月在苏州大学骨科研究所完成。
1.3 材料
1.3.1 主要试剂 多聚磷酸钠(Budenheim,德国);α-磷酸三钙(鼎安科技,中国);预糊化玉米淀粉(建杰实业,中国);二水磷酸氢钙、六水氯化锶、硫酸钡、β-甘油磷酸钠、磷酸氢二钠、地塞米松、抗坏血酸(Sigma Aldrich,美国);CCK-8试剂盒(Dojindo,日本); ATP检测试剂盒、碱性磷酸酶染色试剂盒、碱性磷酸酶检测试剂盒、BCA蛋白浓度测定试剂盒、苏木精-伊红染色试剂盒、Masson染色试剂盒(碧云天,中国);免疫组化染色试剂盒(Vector,美国)。
1.3.2 主要仪器 行星式球磨机(Machinery,中国);X射线机(GE,美国);维卡仪(雷韵,中国);万能力学试验机(衡翼,中国);电感耦合等离子体发射光谱仪(PerkinElmer,美国);X射线衍射仪(帕纳科,荷兰);多功能酶联免疫检测仪(BioRad,美国);Micro-CT(布鲁克,德国);显微镜及成像系统(Carl Zeiss,德国)。
1.3.3 实验动物 1只4周龄雄性SD大鼠,SPF级,体质量约100 g;27只10周龄雄性SD大鼠,SPF级,体质量约400 g,均购自昭衍(苏州)新药研究中心有限公司,许可证号:SCXK(苏)2018-0006,饲养在SPF级动物房。
实验方案已通过苏州大学伦理委员会批准(批准号:SUDA20220926A01),依照《GB/T35823-2018动物实验通用要求》标准条例进行。所有实验操作均全程遵循科学技术部颁发的《关于善待实验动物的指导性意见》。
1.4 方法
1.4.1 生物活性显影材料SrPP及复合CPC的制备
制备SrPP:将1 g多聚磷酸钠溶解在50 mL去离子水中,并将溶液pH值调整到10.0。将5.16 g SrCl2•6H2O溶解于50 mL乙醇(体积分数70%)中。于2 h内将多聚磷酸钠溶液滴入SrCl2•6H2O溶液中,保持反应全程pH=10.0,形成的悬液在室温下搅拌过夜。使用0.45 μm孔径滤纸进行抽滤,并使用体积分数70%乙醇清洗抽滤物,抽滤步骤重复3次。将得到的抽滤物置于60 ℃电热鼓风干燥箱中干燥12 h,研磨成粉末并通过100目筛网筛分,即可得到生物活性显影材料SrPP。
制备骨水泥:①将α-磷酸三钙与二水磷酸氢钙粉末以9∶1的质量比混合,混合粉末加入无水乙醇中使用行星式球磨仪球磨12 h,将球磨后得到的悬浊液置于60 ℃电热鼓风干燥箱中干燥6 h,然后转移至120 ℃环境下继续干燥6 h,过60目筛网得到骨水泥粉体。骨水泥液相为1 mol/L Na2HPO4溶液,液固比为0.4 mL/1 g。将粉体与液相按比例混合并搅拌均匀,得到CPC。②前期研究发现,预糊化淀粉可以提高CPC的注射性能和抗溃散能力,将预糊化淀粉和CPC粉末以1∶4的质量比混合,添加液相后搅拌至混合均匀,得到淀粉改性CPC(记为CPS)[17]。③将SrPP在CPS的基础上以20%质量比替换CPC粉体,保持淀粉质量比不变,添加液相后搅拌至混合均匀,得到复合CPC(记为20%SrPP-CPN)。④使用星式球磨仪球磨硫酸钡粉末12 h,过200目筛网得到硫酸钡粉体。临床常见骨水泥往往选用20%BaSO4作为显影剂量,因此将BaSO4在CPS的基础上以20%质量比替换CPC粉体,保持淀粉质量比不变,添加液相后搅拌至混合均匀,制备含硫酸钡CPC(记为20%BaSO4-CPN)作为显影对照骨水泥[18]。
1.4.2 SrPP及骨水泥的显影性能 材料的显影性能检测根据ISO EN 6876:2012标准进行。随机取3只10周龄雄性SD大鼠,注射过量戊巴比妥钠处死并取出股骨,以其皮质骨作为对照。将多聚磷酸钠与SrPP制备成直径10 mm、厚度1 mm的圆片。使用医用X射线机对多聚磷酸钠与SrPP圆片和骨水泥柱体(CPC、CPS、20%SrPP-CPN、20%BaSO4-CPN)进行拍照,保持工作距离60 cm,电压70 kV,电流0.55 mA,拍照时间0.79 ms,使用Image J软件评估X射线图像灰度[19]。
1.4.3 骨水泥理化性能检测
骨水泥凝固时间:使用维卡仪分别测定骨水泥(CPC、CPS、20%SrPP-CPN)的初凝时间和终凝时间。将初凝针与骨水泥表面接触,拧紧螺丝后突然放松,初凝针垂直沉入骨水泥,当初凝针沉入骨水泥深度小于2 mm时,为骨水泥达到初凝状态。更换终凝针,将终凝针与骨水泥表面接触,拧紧螺丝后突然放松,终凝针垂直沉向骨水泥,环形附件开始不能在骨水泥上留下痕迹时为骨水泥达到终凝状态,分别记录初凝及终凝时间[5]。
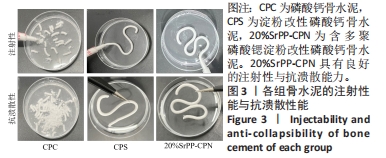
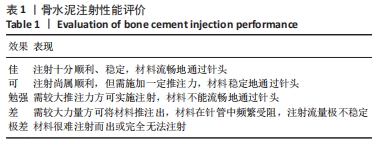
骨水泥注射性能与抗溃散性能:使用1 mL无菌注射器,去除针头、拔出活塞,将搅拌好的骨水泥(CPC、CPS、20%SrPP-CPN)匀浆转移至注射器内,插入活塞并排除注射器内空气,缓慢推动注射器将浆体注射入去离子水中,评价骨水泥的注射性能,每组材料重复3次,材料注射性能评价标准见表1。24 h后观察去离子水中的骨水泥状态[20]。
骨水泥力学性能:材料的力学性能检测根据ASTM C191-03标准进行。将混合后的骨水泥浆体装入直径6 mm、高度12 mm的圆柱状不锈钢模具中,待到骨水泥凝固后将其从模具中推出。将圆柱状骨水泥(CPC、CPS、20%SrPP-CPN)置于37 ℃饱和湿度下保存3 d,通过万能力学试验机进行单轴压缩实验,使用10 kN的测压传感器、按照0.5 mm/min的速率进行轴向压缩。在实验过程中记录应力和位移,直到试样破坏,破坏前的最大应力为峰值载荷,计算抗压强度。
ρ=4F/πD2
公式中ρ代表骨水泥样品的抗压强度,F代表峰值载荷,D代表骨水泥圆柱体的直径。
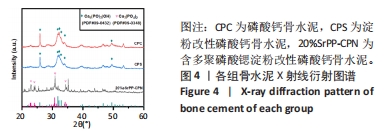
骨水泥的相成分:将固化3 d后的骨水泥(CPC、CPS、20%SrPP-CPN)研磨成粉末,通过X射线衍射仪测定骨水泥固化后的晶相组成。在10°-60°的2θ范围内,使用镍过滤铜Kα辐射(λ=0.154 0 nm)和分段扫描模式[2 (°)/min]对干燥后的骨水泥粉末进行扫描。
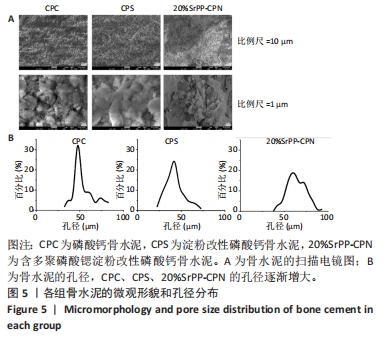
骨水泥的微观结构:将圆柱状骨水泥(CPC、CPS、20%SrPP-CPN)置于37 ℃饱和湿度恒温恒湿箱中3 d,然后截断暴漏出横截面,用导电胶将样品固定于样品台上,横断面表面于离子溅射仪中喷金,使其镀上一层导电薄膜,将喷金后的样品放入扫描电镜舱内,抽真空后在15 kV电压下进行微观结构观察并拍照记录,并分析骨水泥的孔径分布[21]。
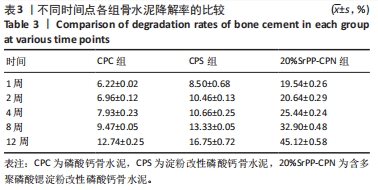
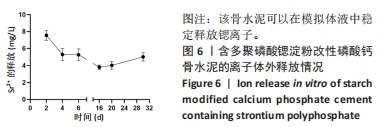
骨水泥的降解性能与锶离子释放:称量圆柱状骨水泥(CPC、CPS、20%SrPP-CPN)质量后,在37 ℃恒温环境下浸入0.05 mol/L Tris-HCl溶液中(pH=7.3),浸提比例为0.2 g/1 mL。Tris-HCl溶液每2 d更换一次。在第2,4,6,16,20,30天时测试浸提液中释放的Sr2+浓度。换液过程每7 d为一个周期,将浸泡的骨水泥取出并加热干燥,称量干燥后骨水泥样品质量,记录第1,2,4,8,12周的样品质量。浸提前后样品的质量之差与原样品的质量之比即为骨水泥材料降解率。
1.4.4 骨水泥的生物相容性
骨髓间充质干细胞的分离培养:采用全骨髓贴壁法分离培养大鼠骨髓间充质干细胞[22]。取4周龄雄性SD大鼠,注射过量戊巴比妥钠处死,于超净工作台中取出胫骨和股骨,置于无菌培养皿中并用无菌PBS清洗2次,使用无菌手术器械剪去长骨干骺端暴露骨髓腔,用注射器将无血清α-MEM培养基从骨髓腔一端注入,将骨髓腔内容物冲洗至50 mL无菌离心管中,直至骨髓腔呈白色停止冲洗。将离心管1 200×g离心5 min,弃上清,向沉淀中加入红细胞裂解液并充分混合,于37 ℃恒温培养箱中静置5 min,加入足量无菌PBS终止反应;1 200×g离心5 min,弃上清,加入无菌PBS冲洗沉淀,再次离心去上清,得到骨髓间充质干细胞。向无菌α-MEM培养基中加入体积分数10%胎牛血清得到α-MEM完全培养基。向细胞中加入10 mL α-MEM完全培养基,置于37 ℃、体积分数5%CO2细胞培养箱中培养细胞,每3 d更换一次培养基并去除非贴壁细胞。于细胞增殖至培养皿90%左右面积时进行传代,传至第3代进行相关实验。取第3代贴壁生长细胞进行表面标志物(CD29、CD90、CD34、CD45)流式检测[23],鉴定为骨髓间充质干细胞。
骨水泥浸提培养基的配置:脱模后的骨水泥(CPC、CPS、20%SrPP-CPN)固化3 d,称质量并使用强紫外照射灭菌10 min,参照《GB/T16886.5-2016医疗器械生物学评价第5部分体外细胞毒性试验》标准,制备骨水泥浸提液。将骨水泥浸泡于无血清α-MEM培养基中,材料/培养基=0.2 g/1 mL,置于37 ℃环境中24 h后离心取上清液,使用0.22 μm过滤器过滤,加入体积分数10%胎牛血清配制成浸提培养基。向浸提培养基中加入10 mmol/L的β-甘油磷酸钠、10 nmol/L的地塞米松和50 μg/mL的抗坏血酸得到成骨诱导条件培养基。
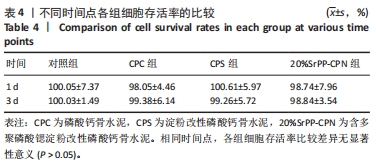
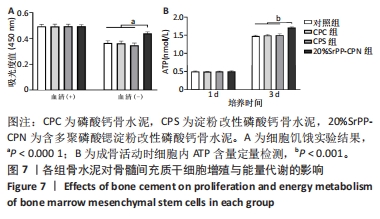
CCK-8实验:将第3代骨髓间充质干细胞以5 000个/孔的密度接种于96孔板内,分4组培养,分别加入100 μL的α-MEM完全培养基、CPC浸提培养基、CPS浸提培养基、20%SrPP-CPN浸提培养基。培养1,3 d时吸除培养基,各孔内加入110 μL CCK-8工作液(VCCK-8原液∶VPBS=1∶10),置于37 ℃、体积分数5%CO2细胞培养箱中避光孵育2 h,通过酶联免疫检测仪在450 nm波长处测试吸光度值[24]。
细胞内能量代谢:将第3代骨髓间充质干细胞以3×104/孔的密度种植于6孔板中,加入2 mL α-MEM完全培养基培养3 d,更换为成骨诱导条件培养基继续培养1,3 d(对照组加入不含骨水泥浸提液的成骨诱导培养基),每孔加入200 μL ATP检测裂解液,4 ℃下15 000×g离心5 min,取上清加入不透光96孔板内,每孔加入ATP检测工作液(VATP检测试剂∶VATP检测试剂稀释液=1∶4)100 μL室温放置5 min,每孔加入20 μL待测样品及各梯度浓度标准溶液,充分混匀,使用化学发光仪检测相对光单位(RLU)值,计算ATP浓度。
细胞饥饿实验:将第3代骨髓间充质干细胞以5 000个/孔的密度接种于96孔板内,分2种环境(含胎牛血清与不含胎牛血清的培养基培养),每种环境均分为4组培养,分别加入100 μL的α-MEM培养基(对照组)、CPC浸提培养基、CPS浸提培养基、20%SrPP-CPN浸提培养基。培养48 h后进行CCK-8实验[25]。
1.4.5 骨水泥体外促成骨能力
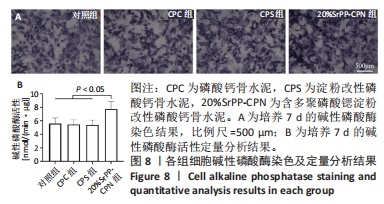
碱性磷酸酶染色:将第3代骨髓间充质干细胞以2×104/孔的密度接种于24孔板中,分4组培养,分别加入1 mL的不含骨水泥浸提液的成骨诱导培养基、CPC成骨诱导条件培养基、CPS成骨诱导条件培养基、20%SrPP-CPN成骨诱导条件培养基。培养7 d后,向每孔内加入200 μL碱性磷酸酶染色液(V缓冲液∶VBCIP液∶VNBT=300∶1∶2),放入培养箱内避光孵育30 min,观察到细胞变色后吸除染料,置于倒置显微镜下观察。
碱性磷酸酶活性检测:按碱性磷酸酶染色分组培养7 d后,加入RIPA裂解液于冰上裂解细胞30 min,4 ℃下15 000×g离心30 min,取上清。利用 BCA法检测各组上清中蛋白浓度。将各组上清样品及不同浓度标准工作液加入96孔板中,每孔加入50 μL现配显色底物,放入培养箱内避光孵育5 min,每孔加入100 μL反应终止液,使用酶标仪测定405 nm波长处吸光度值,计算碱性磷酸酶活性。
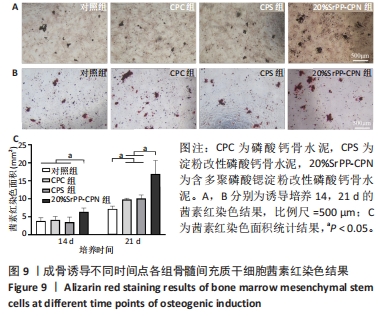
茜素红染色:按碱性磷酸酶染色分组培养14,21 d后,吸除培养基,每孔加入200 μL预冷40 g/L多聚甲醛固定30 min,加入500 μL茜素红S染液室温孵育30 min,吸除染液后置于倒置显微镜观察,使用Image J软件统计茜素红染色面积。
1.4.6 骨水泥体内促成骨能力
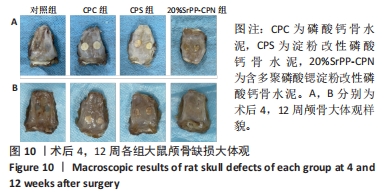
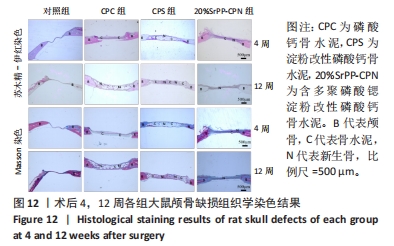
大鼠颅骨缺损模型的构建及分组干预:取24只10周龄雄性SD大鼠,术前12 h禁食、4 h禁水,腹腔注射1%戊巴比妥钠(40 mg/kg)麻醉,对大鼠颅顶处皮肤备皮并使用安尔碘消毒,维持俯卧位,取颅顶近端正中切口(切口长约2 cm),划开皮肤并逐层剥离颅顶软组织及骨膜,暴露颅骨(图1),使用环钻于大鼠颅中缝两侧各造一个直径5 mm的缺损[26-27],采用随机数字表法分4组干预,每组6只,对照组不植入任何材料,其余3组缺损处分别植入CPC、CPS与20%SrPP-CPN,骨水泥均为直径5 mm、厚度2 mm的预塑形圆片。无菌生理盐水冲洗后缝合皮肤,术后3 d每日肌注80×104 U青霉素预防感染。饲养全程关注实验动物状态。术后4,12周,每组随机取3只大鼠进行安乐死,取整个颅骨置于体积分数10%甲醛中固定,拍照记录。

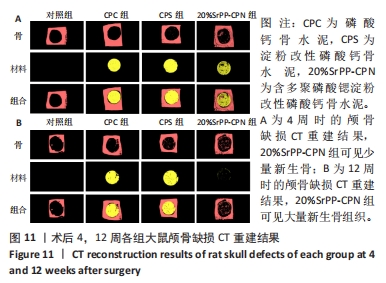
Micro-CT扫描及重建:所有标本采用Skyscan Micro-CT设备进行扫描,参数设置:电压65 kV、电流385 μA、1.0 mm铝过滤器和18 μm分辨率。使用CTAn和Mimics软件进行三维重建,选定5 mm直径的感兴趣区域,选择横断面积最大的层面作为中心层面,上下各选取50层图层。
组织学染色:Micro-CT扫描结束后,所有标本置于10%乙二胺四乙酸盐溶液中脱钙,隔天更换一次。脱钙8周后修剪样品,确保原缺损周围保留至少约2 mm自体骨,依次使用梯度乙醇和正丁醇脱水,然后包埋,使用石蜡切片机以6 μm厚度进行切片,分别进行苏木精-伊红、Masson与免疫组化染色。
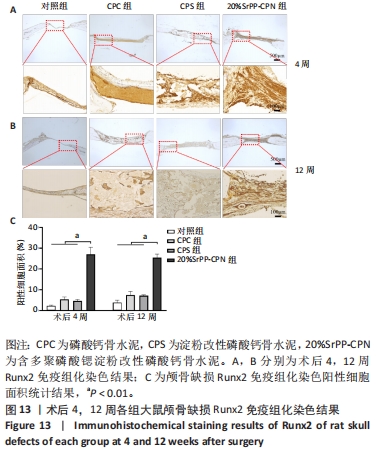
免疫组化染色方法:切片脱蜡水化后,加入体积分数3%过氧化氢+甲醇溶液浸泡10 min;使用胰酶浸泡1 h,置于37 ℃环境中进行抗原修复;马血清抗原封闭30 min,吸除血清,每个样品滴加Runx2抗体(1∶100稀释比)10 μL,4 ℃冰箱过夜;PBS冲洗载玻片,每个样品滴加二抗10 μL,室温下孵育30 min;用PBS冲洗去二抗,二氨基联苯胺显色剂显色2 min,苏木精复染5 min,梯度乙醇脱水,二甲苯透明处理,中性树脂封固,晾干后置于正置显微镜下观察。
1.5 主要观察指标 各组骨水泥的显影能力、生物相容性及体内外促成骨能力。
1.6 统计学分析 数据均记录为x±s,使用GraphPad Prism 8软件进行统计学检验。两组数据比较使用t检验分析,两组以上数据之间的对比采用方差分析(ANOVA)。P < 0.05认为差异有显著性意义。文章统计学方法已经苏州大学生物统计学专家审核。