[1] SHI C, FLANAGAN SR, SAMADANI U. Vagus nerve stimulation to augment recovery from severe traumatic brain injury impeding consciousness: a prospective pilot clinical trial. Neurol Res. 2013;35(3):263-276.
[2] CHAUDHARY IA, SAMIULLAH R, MASOOD R, et al. Recurrent laryngeal nerve injury: an experience with 310 thyroidectomies. J Ayub Med Coll Abbottabad. 2007;19(3):46-50.
[3] MUSAT O, COLTA D, CERNAT C, et al. New perspectives in retinal imaging - angio OCT. Rom J Ophthalmol. 2016;60(2):63-67.
[4] SENDEN RJ, DE JEAN P, MCAULEY KB, et al. Polymer gel dosimeters with reduced toxicity: a preliminary investigation of the NMR and optical dose-response using different monomers. Phys Med Biol. 2006;51(14):3301-3314.
[5] CARL B, BOPP M, GJORGJEVSKI M, et al. Implementation of intraoperative computed tomography for deep brain stimulation: pitfalls and optimization of workflow, accuracy, and radiation exposure. World neurosurgery. 2018; S1878-8750(18)32902-92904.
[6] FUCHS-BUDER T, SETTEMBRE N, SCHMARTZ D. Hybrid operating theater. Der Anaesthesist. 2018;67(7):480-487.
[7] MARAVILLA K, BOWEN B. Imaging of the peripheral nervous system: evaluation of peripheral neuropathy and plexopathy. Am J Neuroradiol. 1998;19(6):1011-1023.
[8] MISGELD T, KERSCHENSTEINER M. In vivo imaging of the diseased nervous system. Nature reviews Neuroscience. 2006;7(6):449-463.
[9] CARVALHO C, SILVA-CORREIA J, OLIVEIRA J, et al. Nanotechnology in peripheral nerve repair and reconstruction. Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2019;148: 308-343.
[10] KIM SM, KIM SH, SEO DW, et al. Intraoperative neurophysiologic monitoring: basic principles and recent update. J Korean Med Sci. 2013; 28(9):1261-1269.
[11] WALZ J, BURNETT A, COSTELLO A, et al. A critical analysis of the current knowledge of surgical anatomy related to optimization of cancer control and preservation of continence and erection in candidates for radical prostatectomy. European urology. 2010;57(2):179-192.
[12] NGUYEN QT, TSIEN RY. Fluorescence-guided surgery with live molecular navigation--a new cutting edge. Nat Rev Cancer. 2013;13(9):653-662.
[13] MIEOG JSD, ACHTERBERG FB, ZLITNI A, et al. Fundamentals and developments in fluorescence-guided cancer surgery. Nat Rev Clin Oncol. 2022;19(1):9-22.
[14] CHI C, DU Y, YE J, et al. Intraoperative imaging-guided cancer surgery: from current fluorescence molecular imaging methods to future multi-modality imaging technology. Theranostics. 2014;4(11):1072-1084.
[15] HE KS, LI PF, ZHANG ZY, et al. Intraoperative near-infrared fluorescence imaging can identify pelvic nerves in patients with cervical cancer in real time during radical hysterectomy. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging. 2022;49(8): 2929-2937.
[16] BEĆ KB, GRABSKA J, HUCK CW. Near-Infrared Spectroscopy in Bio-Applications. Molecules. 2020;25(12):2948.
[17] VAN WILLIGEN DM, VAN DEN BERG NS, BUCKLE T, et al. Multispectral fluorescence guided surgery; a feasibility study in a phantom using a clinical-grade laparoscopic camera system. Am J Nucl Med Mol Imaging. 2017;7(3):138-147.
[18] REN T, WANG Z, XIANG Z, et al. A General strategy for development of activatable nir-ii fluorescent probes for in vivo high-contrast bioimaging. Angew Chem Int Ed Engl. 2021;60(2):800-805.
[19] BURGGRAAF J, KAMERLING I M, GORDON P B, et al. Detection of colorectal polyps in humans using an intravenously administered fluorescent peptide targeted against c-Met. Nat Med. 2015;21(8):955-961.
[20] VAHRMEIJER A, HUTTEMAN M, VAN DER VORST J, et al. Image-guided cancer surgery using near-infrared fluorescence. Nat Rev Clin Oncol. 2013; 10(9):507-518.
[21] DONNELLY P, FINE-GOULDEN M. How to use near-infrared spectroscopy. Arch Dis Child Educ Pract Ed. 2020;105(1):58-63.
[22] SAKUDO A. Near-infrared spectroscopy for medical applications: current status and future perspectives. Clin Chim Acta. 2016;455:181-188.
[23] BALACUMARASWAMI L, TAGGART D. Intraoperative imaging techniques to assess coronary artery bypass graft patency. Ann Thorac Surg. 2007; 83(6):2251-2257.
[24] YANG Y, YANG X, LIU C, et al. Preliminary study on the application of en bloc resection combined with near-infrared molecular imaging technique in the diagnosis and treatment of bladder cancer. World J Urol. 2020;38(12):3169-3176.
[25] YAN P, CHEN D, YAN X, et al. Ex vivo near-infrared molecular imaging of human upper urinary tract urothelial carcinoma with a CD47-based targeted tracer. Front Oncol. 2022;12:825476.
[26] NTZIACHRISTOS V, BREMER C, WEISSLEDER R. Fluorescence imaging with near-infrared light: new technological advances that enable in vivo molecular imaging. Eur Radiol. 2003;13(1):195-208.
[27] JATHOUL A, GROUNDS H, ANDERSON J, et al. A dual-color far-red to near-infrared firefly luciferin analogue designed for multiparametric bioluminescence imaging. Angew Chem Int Ed Engl. 2014;53(48):13059-13063.
[28] WANG S, ZHAO Y, XU Y. Recent advances in applications of multimodal ultrasound-guided photoacoustic imaging technology. Vis Comput Ind Biomed Art. 2020;3(1):24.
[29] CHOI J, TAAL A, MENG W, et al. Fully integrated time-gated 3D fluorescence imager for deep neural imaging. IEEE Trans Biomed Circuits Syst. 2020; 14(4):636-645.
[30] HAO H, WANG X, QIN Y, et al. Ex vivo near-infrared targeted imaging of human bladder carcinoma by ICG-anti-CD47. Front Oncol. 2023;13:1083553.
[31] OU C, LUO Y, HE L, et al. Application of fluorescence endoscopy with methylene blue dye and indocyanine green dual-tracer method in sentinel lymph node biopsy for women with breast cancer. Gland surgery. 2023; 12(6):780-790.
[32] 胡跃东,张梦梦,张俊文,等.荧光素酶标记胶质瘤细胞模型的构建及其在溶瘤病毒治疗中的应用[J].中华神经外科杂志,2022,38(8):843-848.
[33] MARAGKOS G, SCHüPPER A, LAKOMKIN N, et al. Fluorescence-guided high-grade glioma surgery more than four hours after 5-aminolevulinic acid administration. Front Neurol. 2021;12:644804.
[34] DU Y, LIU X, ZHU S. Near-infrared-II cyanine/polymethine dyes, current state and perspective. Front Chem. 2021;9:718709.
[35] GIRAUDEAU C, MOUSSARON A, STALLIVIERI A, et al. Indocyanine green: photosensitizer or chromophore? Still a debate. Curr Med Chem. 2014. doi:10.2174/0929867321666131218095802.
[36] 王晓颖.吲哚菁绿荧光成像技术在肝脏外科应用中国专家共识(2023版)[J].中国实用外科杂志,2023,43(4):371-383.
[37] REINHART M, HUNTINGTON C, BLAIR L, et al. Indocyanine green:historical context, current applications, and future considerations. Surg Innov. 2016; 23(2):166-175.
[38] CHEN Y, ZHANG H, LEI Z, et al. Recent advances in intraoperative nerve bioimaging: fluorescence‐guided surgery for nerve preservation. Small Struct. 2020. doi:10.1002/sstr.202000036.
[39] MANGANO MS, DE GOBBI A, BENIAMIN F, et al. Robot-assisted nerve-sparing radical prostatectomy using near-infrared fluorescence technology and indocyanine green:initial experience. Urologia. 2018;85(1):29-31.
[40] JIANG JX, KEATING JJ, JESUS EM, et al. Optimization of the enhanced permeability and retention effect for near-infrared imaging of solid tumors with indocyanine green. Am J Nucl Med Mol Imaging. 2015;5(4):390-400.
[41] GRAGNANIELLO C, KAMEL M, AL-MEFTY O. Utilization of fluorescein for identification and preservation of the facial nerve and semicircular canals for safe mastoidectomy: a proof of concept laboratory cadaveric study. Neurosurgery. 2010;66(1):204-207.
[42] CHEN SC, WANG MC, WANG WH, et al. Fluorescence-assisted visualization of facial nerve during mastoidectomy: a novel technique for preventing iatrogenic facial paralysis. Auris Nasus Larynx. 2015;42(2):113-118.
[43] WENG W, LIU Y, ZHOU J, et al. Thoracoscopic indocyanine green near-infrared fluorescence for thoracic sympathetic ganglions. Ann Thorac Surg. 2016;101(6):2394.
[44] HE KS, ZHOU J, YANG F, et al. Near-infrared intraoperative imaging of thoracic sympathetic nerves: from preclinical study to clinical trial. Theranostics. 2018;8(2):304-313.
[45] JIN H, ZHENG L, LU L, et al. Near-infrared intraoperative imaging of pelvic autonomic nerves: a pilot study. Surg Endosc. 2022;36(4):2349-2356.
[46] KANNO K, AIKO K, YANAI S, et al. Clinical use of indocyanine green during nerve-sparing surgery for deep endometriosis. Fertil Steril. 2021;116(1): 269-271.
[47] HANDGRAAF HJ, VERBEEK FP, TUMMERS QR, et al. Real-time near-infrared fluorescence guided surgery in gynecologic oncology: a review of the current state of the art. Gynecol Oncol. 2014;135(3):606-613.
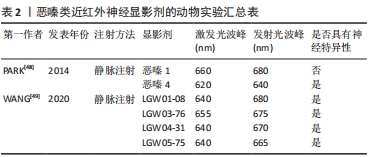
[48] PARK MH, HYUN H, ASHITATE Y, et al. Prototype nerve-specific near-infrared fluorophores. Theranostics. 2014;4(8):823-833.
[49] WANG LG, BARTH CW, KITTS CH, et al. Near-infrared nerve-binding fluorophores for buried nerve tissue imaging. Sci Transl Med. 2020;12(542): eaay0712.
[50] BARTH CW, GIBBS SL. Visualizing Oxazine 4 nerve-specific fluorescence ex vivo in frozen tissue sections. Proc SPIE Int Soc Opt Eng. 2016;9696:96960R.
[51] BARTH CW, GIBBS SL. Direct administration of nerve-specific contrast to improve nerve sparing radical prostatectomy. Theranostics. 2017;7(3):573-593.
[52] WANG LG, BARTH CW, COMBS JR, et al. Investigation of oxazine and rhodamine derivatives as peripheral nerve tissue targeting contrast agent for in vivo fluorescence imaging. Proc SPIE Int Soc Opt Eng. 2019; 10862:108620H.
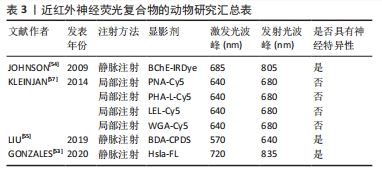
[53] GONZALES J, PIROVANO G, CHOW CY, et al. Fluorescence labeling of a NaV1.7-targeted peptide for near-infrared nerve visualization. EJNMMI Res. 2020;10(1):49.
[54] JOHNSON N D, DUYSEN EG, LOCKRIDGEO. Intrathecal delivery of fluorescent labeled butyrylcholinesterase to the brains of butyrylcholinesterase knock-out mice: visualization and quantification of enzyme distribution in the brain. Neurotoxicology. 2009;30(3):386-392.
[55] LIU Y, LIU J, ZHANG J, et al. A brand-new generation of fluorescent nano-neural tracers: biotinylated dextran amine conjugated carbonized polymer dots. Biomater Sci. 2019;7(4):1574-1583.
[56] DYCK SM, KARIMI-ABDOLREZAEE S. Chondroitin sulfate proteoglycans: key modulators in the developing and pathologic central nervous system. Exp Neurol. 2015;269:169-187.
[57] KLEINJAN GH, BUCKLE T, VAN WILLIGEN DM, et al. Fluorescent lectins for local in vivo visualization of peripheral nerves. Molecules. 2014;19(7):9876-9892.
[58] LI B, ZHAO M, LIN J, et al. Management of fluorescent organic/inorganic nanohybrids for biomedical applications in the NIR-II region. Chem Soc Rev. 2022;51(18):7692-7714.
[59] ZHAO M, WANG J, LEI Z, et al. NIR-II pH sensor with a FRET adjustable transition point for in situ dynamic tumor microenvironment visualization. Angew Chem Int Ed Engl. 2021;60(10):5091-5095.
[60] LI B, LIU H, HE Y, et al. A “Self-Checking” pH/Viscosity-activatable NIR-II molecule for real-time evaluation of photothermal therapy efficacy. Angew Chem Int Ed Engl. 2022;61(16):e202200025.
[61] CAO Z, FENG L, ZHANG G, et al. Semiconducting polymer-based nanoparticles with strong absorbance in NIR-II window for in vivo photothermal therapy and photoacoustic imaging. Biomaterials. 2018; 155:103-111.
[62] FENG L, WU L, QU X. New horizons for diagnostics and therapeutic applications of graphene and graphene oxide. Adv Mater. 2013;25(2):168-186.
[63] PAJOUHESH H, LENZ GR. Medicinal chemical properties of successful central nervous system drugs. NeuroRx. 2005;2(4):541-553.
[64] FAGERHOLM U. The highly permeable blood-brain barrier: an evaluation of current opinions about brain uptake capacity. Drug Discov Today. 2007; 12(23-24):1076-1082.
[65] WALSH EM, COLE D, TIPIRNENI KE, et al. Fluorescence imaging of nerves during surgery. Ann Surg. 2019;270(1):69-76.
[66] WATERHOUSE RN. Determination of lipophilicity and its use as a predictor of blood-brain barrier penetration of molecular imaging agents. Mol Imaging Biol. 2003;5(6):376-389.
[67] SAJI H. In vivo molecular imaging. Biol Pharm Bull. 2017;40(10):1605-1615.
[68] GIBBS-STRAUSS SL, NASR KA, FISH KM, et al. Nerve-highlighting fluorescent contrast agents for image-guided surgery. Molecular Imaging. 2011;10(2): 91-101.
[69] GIBBS SL, XIE Y, GOODWILL HL, et al. Structure-activity relationship of nerve-highlighting fluorophores. PLoS One. 2013;8(9):e73493.
|