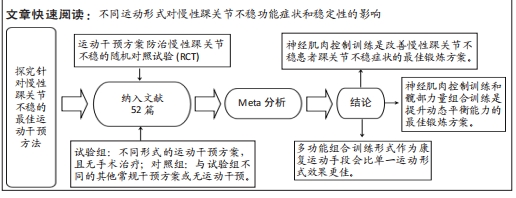
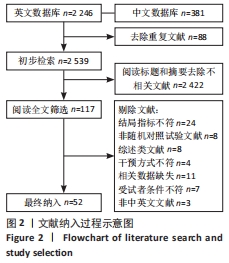
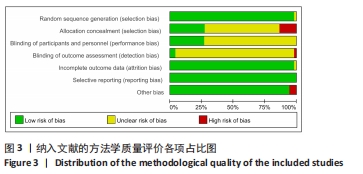
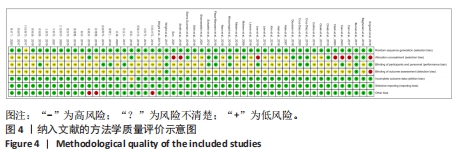
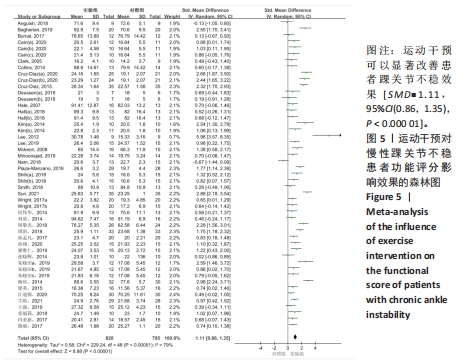
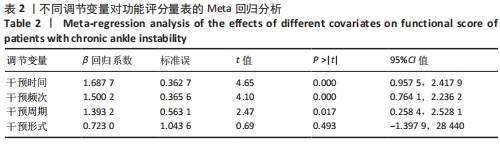
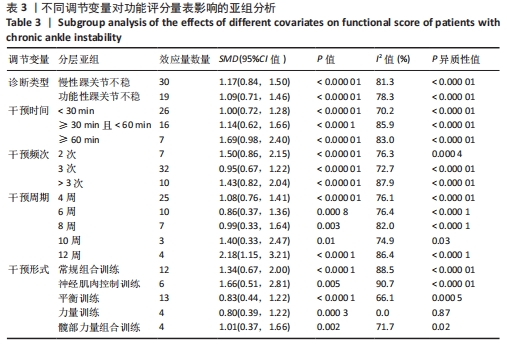
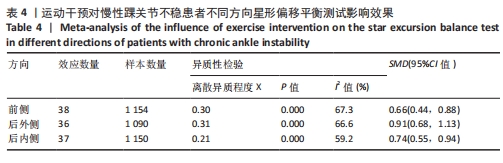
[1] SOBOROFF SH, PAPPIUS EM, KOMAROFF AL. Benefits, risks, and costs of alternative approaches to the evaluation and treatment of severe ankle sprain. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1984;183:160-168.
[2] HUPPERETS MD, VERHAGEN EA, VAN MW. The 2BFit study: is unsupervised balance board training programme given in addition to usual care, effective in preventing ankle sprain recurrences? Design of a randomized controlled trial. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2008;20(9):71.
[3] YEUNG M, CHAN KM, SO C, et al. An epidemiological survey on ankle sprain. Br J Sports Med. 1994;28(2):112-116.
[4] VALDERRABANO V, LEUMANN A, PAGENSTERT G, et al. Chronic ankle instability in sports -- a review for sports physicians. Sportverletz Sportschaden. 2006;20(4):177-183.
[5] 施晓剑,韩甲,刘宇,等.慢性踝关节不稳的病例机制和评估诊断研究进展[J].中国运动医学杂志,2019,38(9):816-824.
[6] 章丽莉,杨玉珊,郑洁姣.慢性踝关节不稳姿势稳定性的研究进展[J].中国康复理论与实践,2019,25(8):908-912.
[7] DE VRIES JS, KRIPS R, SIEREVELT IN, et al. Interventions for treating chronic ankle instability. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2011; 10(8):CD004124.
[8] 刘鸣.系统评价、Meta-分析设计与实施方法[M].北京:人民卫生出版社,2011:158-164.
[9] 江迪锦,廖志平.本体感觉训练对慢性踝关节不稳者运动功能的影响[J].医学信息, 2020,33(17):98-100.
[10] 孙孟凡.PNF技术联合核心稳定性训练对功能性踝关节不稳康复的影响[D].武汉:武汉体育学院,2017.
[11] 廖维仁.PNF训练对体育专业大学生功能性踝关节不稳的干预作用[D].桂林:广西师范大学,2019.
[12] 张晓辉,刘书芳,廖八根.不同训练方法对运动员功能性踝关节不稳康复的影响[J].中国运动医学杂志,2014,33(6):514-518.
[13] 梁英,高敏,王萍芝,等.动静态平衡训练治疗慢性踝关节不稳的疗效研究[J].中华老年骨科与康复电子杂志,2015,1(2):23-28.
[14] 杨珍.功能锻炼对慢性躁关节不稳的临床疗效研究[D].武汉:华中师范大学,2014.
[15] 周敬杰,张明,张秀芳,等.本体感觉训练联合Kaltenborn关节松动术治疗慢性踝关节不稳的疗效观察[J].中华物理医学与康复杂志,2018,40(2):151-153.
[16] 梁珊珊.不同干预方式对功能性踝关节不稳者姿势稳定性的影响研究[D].天津:天津体育学院,2019.
[17] 闫亚新,杨建全.功能性力量训练对大学生慢性踝关节不稳的康复研究[J].中国临床研究,2017,30(2):245-247.
[18] 郭雨涵.核心训练对普通人群功能性踝关节不稳的影响[D].北京:北京体育大学,2019.
[19] 徐珊珊.机械振动结合短时间小强度康复训练对功能性踝关节不稳的影响[D].武汉:武汉体育学院,2018.
[20] 何伟华,李珂,独建库,等.肌肉功能锻炼对慢性外踝关节不稳的治疗效果[J].实用医学杂志,2014,30(9):1514-1515.
[21] 刘欣,张云鹏,王磊,等.康复指导在功能性踝关节不稳康复中的意义[J].中国康复理论与实践,2014,20(5):467-469.
[22] 周阳.髋、膝相关肌肉强化对功能性踝关节不稳康复的影响[D].杭州:浙江中西药大学, 2018.
[23] 鲁君兰.髋部力量训练对慢性踝关节不稳患者平衡能力的影响[D].上海:上海体育学院, 2020.
[24] 孙翔.髋外展肌训练对大学生功能性踝关节不稳姿势稳定性的影响[D].沈阳:沈阳体育学院,2020.
[25] 骆丽,孙武东,赵祥虎,等.强化髋周肌群力量训练对功能性踝关节不稳的效果[J].中国康复理论与实践,2017,23(10):1195-1199.
[26] 章丽莉.三维和二维动态平衡训练对功能性踝关节不稳者姿势控制的影响[D].上海:上海体育学院,2019.
[27] 王强,李洋.神经肌肉控制训练对功能性踝关节不稳的本体感觉疗效[J].四川医学, 2019,40(12):1250-1253.
[28] 牛皓,姜斌,张杰,等.下肢整体康复训练治疗功能性踝关节不稳的疗效观察[J].中国康复,2021,36(1):12-16.
[29] 朱晓田.太极拳结合康复训练对功能性踝关节不稳的干预效果研究[D].西安:西安体育学院,2019.
[30] ANGUISH B, SANDREY MA. Two 4-week balance-training programs for chronic ankle instability. J Athl Train. 2018;53(7):662-671.
[31] WRIGHT CJ, LINENS SW, CAIN MS. A randomized controlled trial comparing rehabilitation efficacy in chronic ankle instability. J Sport Rehabil. 2017;26(4):238-249.
[32] LEE E, CHO J, LEE S. Short-foot exercise promotes quantitative somatosensory function in ankle instability: a randomized controlled trial. Med Sci Monit. 2019;7(25):618-626.
[33] CLOAK R, NEVILL AM, CLARKE F, et al. Vibration training improves balance in unstable ankles. Int J Sports Med. 2010;12(12):894-900.
[34] BURCAL CJ, TRIER AY, WIKSTROM EA. Balance training versus balance training with STARS in patients with chronic ankle instability: a randomized controlled trial. J Sport Rehabil. 2017;26(5):347-357.
[35] BAGHERIAN S, RAHNAMA N, WIKSTROM EA. Corrective exercises improve movement efficiency and sensorimotor function but not fatigue sensitivity in chronic ankle instability patients: a randomized controlled trial. Clin J Sport Med. 2019;29(3):193-202.
[36] CRUZ-DIAZ D, HITA-CONTRERAS F, MARTINEZ-AMAT A, et al. Ankle-joint self-mobilization and CrossFit training in patients with chronic ankle instability: a randomized controlled trial. J Athl Train. 2020;55(2):159-168.
[37] SHIH YF, YU HT, CHEN WY, et al. The effect of additional joint mobilization on neuromuscular performance in individuals with functional ankle instability. Phys Ther Sport. 2018;30(3):22-28.
[38] HALE SA, HERTEL J, OLMSTED-KRAMER LC. The effect of a 4-week comprehensive rehabilitation program on postural control and lower extremity function in individuals with chronic ankle instability. J Orthop Sports Phys Ther. 2007;37(6):303-311.
[39] MCKEON PO, INGERSOLL CD, KERRIGAN DC, et al. Balance training improves function and postural control in those with chronic ankle instability. Med Sci Sports Exerc. 2008;40(10): 1810-1819.
[40] MINOONEJAD H, KARIMIZADEH AM, RAJABI R, et al. Hop stabilization training improves neuromuscular control in college basketball players with chronic ankle instability: a randomized controlled trial. J Sport Rehabil. 2019;28(6):576-583.
[41] LEE KY, LEE HJ, KIM SE, et al. Short term rehabilitation and ankle instability. Int J Sports Med. 2012;33(6):485-496.
[42] CAIN MS, GARCEAU SW, LINENS SW. Effects of a four week biomechanical ankle platform system protocol on balance in high school athletes with chronic ankle instability. J Sport Rehabil. 2017;26(1):1-7.
[43] SMITH BI, CURTIS D, DOCHERTY CL. Effects of hip strengthening on neuromuscular control, hip strength, and self-reported functional deficits in individuals with chronic ankle instability. J Sport Rehabil. 2018;27(4):364-370.
[44] SIERRA-GUZMAN R, JIMENEZ-DIAZ F, RAMIREZ C, et al. Whole-body-vibration training and balance in recreational athletes with chronic ankle instability. J Athl Train. 2018;53(4):355-363.
[45] WRIGHT CJ, LINENS SW, CAIN MS. Establishing the minimal clinical important difference and minimal detectable change for the cumberland ankle instability tool. Arch Phys Med Rehabil. 2017;98(9):1806-1811.
[46] CRUZ-DIAZ D, LOMAS-VEGA R, OSUNA-PEREZ MC, et al. Effects of 6 weeks of balance training on chronic ankle instability in athletes: a randomized controlled trial. Int J Sports Med. 2015;36(9):754-760.
[47] NAM SM, KIM K, LEE DY. Effects of visual feedback balance training on the balance and ankle instability in adult men with functional ankle instability. J Phys Ther Sci. 2018;30(1): 113-115.
[48] PLAZA-MANZANO G, VERGARA-VILA M, VAL-OTERO S, et al. Manual therapy in joint and nerve structures combined with exercises in the treatment of recurrent ankle sprains: A randomized, controlled trial. Man Ther. 2016;26(12):141-149.
[49] CLOAK R, NEVILL A, DAY S, et al. Six-week combined vibration and wobble board training on balance and stability in footballers with functional ankle instability. Clin J Sport Med. 2013;23(5):384-391.
[50] SHAMSEDDINI SF, HADADI M, REZAEI I, et al. The effect of the combination of whole body vibration and shoe with an unstable surface in chronic ankle instability treatment: a randomized clinical trial. BMC Sports Sci Med Rehabil. 2021;13(1):28.
[51] KIM KJ, KIM YE, JUN HJ, et al. Which treatment is more effective for functional ankle instability: strengthening or combined muscle strengthening and proprioceptive exercises? J Phys Ther Sci. 2014;26(3):385-388.
[52] DEUSSEN S, ALFUTH M. The influence of sensorimotor training modalities on balance, strength, joint function, amd plantar foot sensitivity in recreational athletes with a history of ankle sprain: a randomized controlled pilot study. Int J Sports Phys Ther. 2018;13(6):993-1007.
[53] HALL EA, CHOMISTEK AK, KINGMA JJ, et al. Balance-and strength-training protocols to improve chronic ankle instability deficits, part II: assessing patient-reported outcome measures. J Athl Train. 2018;53(6):578-583.
[54] CAIN MS, BAN RJ, CHEN YP, et al. Four-week ankle-rehabilitation programs in adolescent athletes with chronic ankle instability. J Athl Train. 2020;55(8):801-810.
[55] MELAM GR, ALHUSAINI AA, PERUMAL V, et al. Effect of weight-bearing overload using elastic tubing on balance and functional performance in athletes with chronic ankle instability. Sci Sports. 2018;33(5):229-236.
[56] SUN Y. Effects of different rehabilitation training methods under color doppler flow imaging on functional ankle instability. J Med Imag Health Inform. 2020;9(10):2112-2117.
[57] LINENS SW, ROSS SE, ARNOLD BL. Wobble board rehabilitation for improving balance in ankles with chronic instability. Clin J Sport Med. 2016;26(1):76-82.
[58] CLARK VM, BURDEN AM. A 4-week wobble board exercise programme improved muscle onset latency and perceived stability in individuals with a functionally unstable ankle. Phy Ther Sport. 2005;6(4):181-187.
[59] COLLINS CK, MASARACCHIO M, CLELAND JA. The effectiveness of strain counterstrain in the treatment of patients with chronic ankle instability: A randomized clinical trial. J Man Manip Ther. 2014;22(3):119-228.
[60] SCHAEFER JL, SANDREY M. Effects of a 4-week dynamic-balance-training program supplemented with graston instrument-assisted soft-tissue mobilization for chronic ankle instability. J Sport Rehabil. 2012;21(4):313-326.
[61] 尹彦,罗冬梅,刘卉,等.功能性踝关节不稳的机制与自评量表的研究进展[J].中国康复理论与实践,2018,24(6):671-677.
[62] 施晓剑,韩甲,刘宇,等.慢性踝关节不稳的病理机制和评估诊断研究进展[J].中国运动医学杂志,2019,38(9):816-824.
[63] 刘宝林,张阳.运动干预对功能性踝关节不稳者康复治疗的研究进展[J].中国康复医学杂志,2020,35(6):758-763.
[64] THOMPSON C, SCHABRUN S, ROMERO R, et al. Factors contributing to chronic ankle instability: a systematic review and meta analysis of systematic reviews. Sports Med. 2018;48(1):189-205.
[65] FITZGERALD D, TRAKARNRATANAKUL N, SMYTH B, et al. Effects of a wobble board-based therapeutic exergaming system for balance training on dynamic postural stability and intrinsic motivation levels. J Orthop Sports Phys Ther. 2010;40(1):11-19.
[66] LUAN L, ADAMS R, WITCHALLS J, et al. Does strength training for chronic ankle instability improve balance and patient-reported outcomes and by clinically detectable amounts? A systematic review and meta-analysis. Phys Ther. 2021;101(7):pzab046.
[67] LEE S, POWERS CM. Individuals with diminished hip abductor muscle strength exhibit altered ankle biomechanics and neuromuscular activation during unipedal balance tasks. Gait Posture. 2014;39(3):933-938.
[68] RIOS JL, GORGES AL, DOS SANTOS MJ. Individuals with chronic ankle instability compensate for their ankle deficits using proximal musculature to maintain reduced postural sway while kicking a ball. Hum Mov Sci. 2015;43:33-44.
[69] PINTSAAR A, BRYNHILDSEN J, TROPP U. Postural corrections after standardised perturbations of single limb stance: effect of training and orthotic devices in patients with ankle instability. Br J Sports Med. 1996;30(2): 151-155.
[70] 任艺,王蕊,章耀华.本体感觉神经肌肉促进技术联合神经肌肉电刺激对慢性踝关节不稳的效果[J]. 中国康复理论与实践, 2023,29(7):750-755.
[71] 王悦同,彭亮,苏玉莹,等.平衡训练对慢性踝关节不稳影响效果的 Meta 分析[J].中国组织工程研究,2024,28(24):3930-3936.
[72] 苏玉莹,彭亮,李卫,等.整合性神经肌肉训练对慢性踝关节不稳康复与预防的研究进展[J].中国体育科技,2023,59(7):47-52.
[73] 王斌,朱飞龙,张明,等.功能性踝关节不稳患者的等速肌力测试、平衡及步态特征分析[J].中国康复医学杂志,2023,38(7): 960-965.
[74] 吴一晗,魏乔叶,刘中强.慢性踝关节不稳的模型进化与病理机制研究进展[J].中国康复医学杂志,2023,38(7):1017-1023.
[75] 于歌,王璐,陈亚平.全身振动训练对慢性踝关节不稳姿势稳定性影响的Meta分析[J].中国康复理论与实践,2023,29(4):423-432.
[76] 章丽莉,张兴来,张杰,等.视觉反馈对慢性踝关节不稳者落地过程中生物力学的影响[J].中国组织工程研究,2023,28(6):900-904.
[77] 施晓剑,荣积峰,蔡斌,等.物理治疗技术改善慢性踝关节不稳神经肌肉控制障碍的系统综述[J].中国康复理论与实践,2022, 28(2):132-143.
[78] 曹祚,王璐,王翔,等.动态平衡训练对慢性踝关节不稳患者疗效的Meta分析[J].中华灾害救援医学,2021,9(12):1385-1394. |