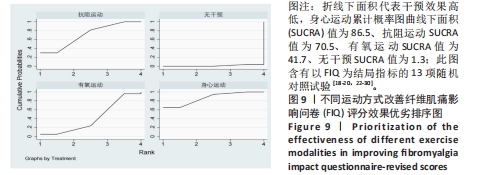
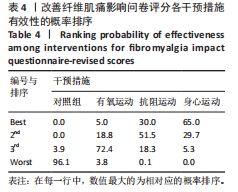
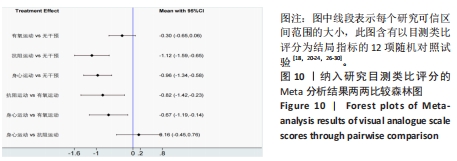
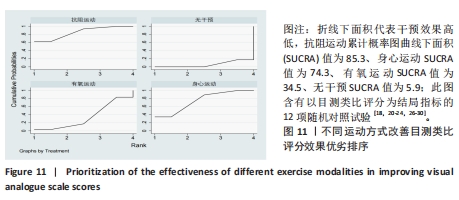
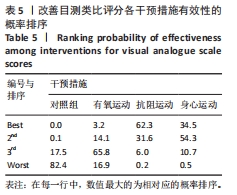
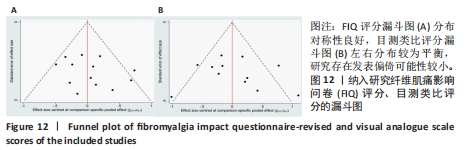
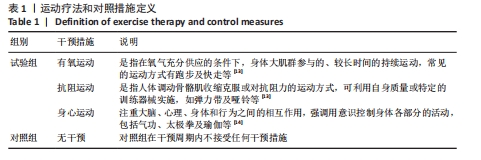
[1] ARNOLD LM, BENNETT RM, CROFFORD LJ, et al. AAPT diagnostic criteria for fibromyalgia. J Pain. 2019;20(6):611-628.
[2] 朱谦.纤维肌痛临床诊疗中国专家共识[J].中国疼痛医学杂志,2021,27(10):721-727.
[3] HAUSER W, ABLIN J, FITZCHARLES MA, et al. Fibromyalgia. Nat Rev Dis Primers. 2015;1: 15022.
[4] WHITE LA, ROBINSON RL, YU AP, et al. Comparison of health care use and costs in newly diagnosed and established patients with fibromyalgia. J Pain. 2009;10(9):976-983.
[5] JI RR, NACKLEY A, HUH Y, et al. Neuroinflammation and central sensitization in chronic and widespread pain. Anesthesiology. 2018;129(2):343-366.
[6] SARZI-PUTTINI P, GIORGI V, MAROTTO D, et al. Fibromyalgia: an update on clinical characteristics, aetiopathogenesis and treatment. Nat Rev Rheumatol. 2020;16(11): 645-660.
[7] CLAUW DJ. Fibromyalgia: a clinical review. JAMA. 2014;311(15):1547-1555.
[8] 梁东风,杨春花,张洁,等.度洛西汀和普瑞巴林治疗纤维肌痛的疗效和安全性对照研究[J].中国疼痛医学杂志,2023,29(3):194-200.
[9] BIDONDE J, BUSCH AJ, SCHACHTER CL, et al. Aerobic exercise training for adults with fibromyalgia. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017;6(6):CD012700.
[10] MAESTRE-CASCALES C, CASTILLO-PAREDES A, ROMERO-PARRA N, et al. Gradual strength training improves sleep quality, physical function and pain in women with fibromyalgia. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2022;19(23):15662.
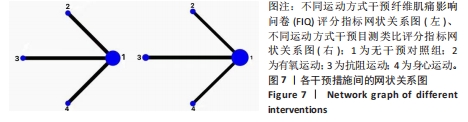
[11] ZHANG KD, WANG LY, ZHANG ZH, et al. Effect of exercise interventions on health-related quality of life in patients with fibromyalgia syndrome: a systematic review and network meta-analysis. J Pain Res. 2022;15:3639-3656.
[12] MACFARLANE GJ, KRONISH C, DEAN LE, et al. EULAR revised recommendations for the management of fibromyalgia. Ann Rheum Dis. 2017;76(2):318-328.
[13] 《运动处方中国专家共识(2023)》专家组.运动处方中国专家共识(2023)[J].中国运动医学杂志,2023,42(1):3-13.
[14] 陈爱国,梁洪英,颜军,等.留守儿童执行功能的发育特征及身心运动干预研究[J].中国特殊教育,2016(11):69-74.
[15] 刘鸣.系统评价、Meta-分析设计与实施方法[M].北京:人民卫生出版社,2011:68-71.
[16] 张天嵩.高级Meta分析方法 : 基于Stata实现[M].上海:复旦大学出版社,2015:326-360.
[17] SALANTI G, ADES AE, LOANNIDIS JP. Graphical methods and numerical summaries for presenting results from multiple-treatment meta-analysis: an overview and tutorial. J Clin Epidemiol. 2011;64(2):163-171.
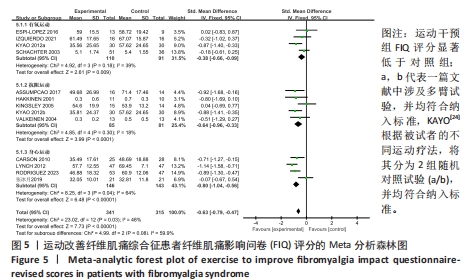
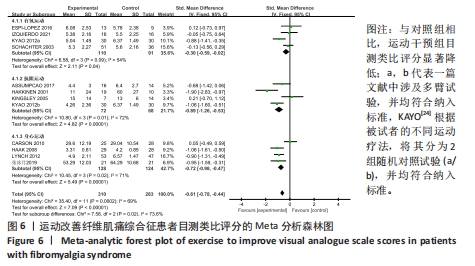
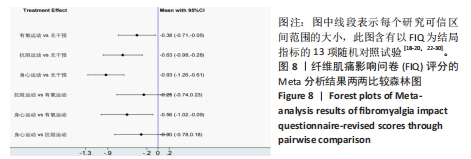
[18] ASSUMPCAO A, MATSUTANI LA, YUAN SL, et al. Muscle stretching exercises and resistance training in fibromyalgia: which is better? A three-arm randomized controlled trial. Eur J Phys Rehabil Med. 2018;54(5):663-670.
[19] CARSON JW, CARSON KM, JONES KD, et al. A pilot randomized controlled trial of the Yoga of Awareness program in the management of fibromyalgia. Pain. 2010;151(2):530-539.
[20] ESPI-LOPEZ GV, INGLES M, RUESCAS-NICOLAU MA, et al. Effect of low-impact aerobic exercise combined with music therapy on patients with fibromyalgia. A pilot study. Complement Ther Med. 2016;28:1-7.
[21] HAAK T, SCOTT B. The effect of Qigong on fibromyalgia (FMS): a controlled randomized study. Disabil Rehabil. 2008;30(8):625-633.
[22] KAYO AH, PECCIN MS, SANCHES CM, et al. Effectiveness of physical activity in reducing pain in patients with fibromyalgia: a blinded randomized clinical trial. Rheumatol Int. 2012; 32(8):2285-2292.
[23] KINGSLEY JD, PANTON LB, TOOLE T, et al. The effects of a 12-week strength-training program on strength and functionality in women with fibromyalgia. Arch Phys Med Rehabil. 2005; 86(9):1713-1721.
[24] LYNCH M, SAWYNOK J, HIWE C, et al. A randomized controlled trial of qigong for fibromyalgia. Arthritis Res Ther. 2012;14(4): R178.
[25] RODRIGUEZ-MANSILLA J, MEJIAS-GIL A, GARRIDO-ARDILA EM, et al. Effects of an exercise for well-being and physical training programme on muscle strength, range of movement, respiratory capacity and quality of life in women with fibromyalgia: a randomized controlled trial. J Clin Med. 2023;12(3):774.
[26] SCHACHTER CL, BUSCH AJ, PELOSO PM, et al. Effects of short versus long bouts of aerobic exercise in sedentary women with fibromyalgia: a randomized controlled trial. Phys Ther. 2003;83(4):340-358.
[27] HAKKINEN A, HAKKINEN K, HANNONEN P, et al. Strength training induced adaptations in neuromuscular function of premenopausal women with fibromyalgia: comparison with healthy women. Ann Rheum Dis. 2001;60(1): 21-26.
[28] IZQUIERDO-ALVENTOSA R, INGLES M, CORTES-AMADOR S, et al. Effectiveness of high-frequency transcranial magnetic stimulation and physical exercise in women with fibromyalgia: a randomized controlled trial. Phys Ther. 2021;101(10):pzab159.
[29] VALKEINEN H, ALEN M, HANNONEN P, et al. Changes in knee extension and flexion force, EMG and functional capacity during strength training in older females with fibromyalgia and healthy controls. Rheumatology (Oxford). 2004;43(2):225-228.
[30] 张冰月,夏晶,黄怡然,等.五禽戏干预纤维肌痛综合征的疗效分析[J].中国医药导刊, 2019,21(4):217-221.
[31] 许瀚,尹毅,赵燕.运动干预对成人代谢综合征患者心血管危险因素影响的Meta分析[J].中国体育科技,2020,56(5):59-70.
[32] LI YT, JIANG Q, JIA Y, et al. A Chinese version of the revised Fibromyalgia Impact Questionnaire: a validation study. Int J Rheum Dis. 2023;26(2):242-249.
[33] 万丽,赵晴,陈军,等.疼痛评估量表应用的中国专家共识(2020版)[J].中华疼痛学杂志,2020,16(3):11.
[34] BIDARI A, CHAVIDEL-PARSA B, RAJABI S, et al. The acute effect of maximal exercise on plasma beta-endorphin levels in fibromyalgia patients. Korean J Pain. 2016;29(4):249-254.
[35] BOBINSKI F, FERREIRA TAA, CORDOVA MM, et al. Role of brainstem serotonin in analgesia produced by low-intensity exercise on neuropathic pain after sciatic nerve injury in mice. Pain. 2015;156(12):2595-2606.
[36] LIMA LV, ABNER TSS, SLUKA KA. Does exercise increase or decrease pain? Central mechanisms underlying these two phenomena. J Physiol. 2017;595(13):4141-4150.
[37] Neelapala YVR, Mercuri D, Macedo L, et al. Mechanisms hypothesized for
pain-relieving effects of exercise in fibromyalgia: a scoping review. Ther Adv Musculoskelet Dis. 2023. doi:10.1177/ 1759720X231182894
[38] 臧铭,蒋佳慧,郭玮.不同运动锻炼方式延缓认知老化的研究进展[J].中国老年学杂志, 2021,41(24):5778-5782.
[39] ADLER-NEAL AL, ZEIDAN F. Mindfulness meditation for fibromyalgia: mechanistic and clinical considerations. Curr Rheumatol Rep. 2017;19(9):59.
[40] WANG C, SCHMID GH, FIELDING RA, et al. Effect of tai chi versus aerobic exercise for fibromyalgia: comparative effectiveness randomized controlled trial. BMJ. 2018;360: k851.
[41] JONES KD. Recommendations for resistance training in patients with fibromyalgia. Arthritis Res Ther. 2015;17(1):258.
[42] Nelson NL. Muscle strengthening activities and fibromyalgia: a review of pain and strength outcomes. J Bodyw Mov Ther. 2015;19(2):370-376.
[43] KADETOFF D, KOSEK E. The effects of static muscular contraction on blood pressure, heart rate, pain ratings and pressure pain thresholds in healthy individuals and patients with fibromyalgia. Eur J Pain. 2007;11(1):39-47.
[44] DA SILVA JM, DE BARROS BS, ALMEIDA GJ, et al. Dosage of resistance exercises in fibromyalgia: evidence synthesis for a systematic literature review up-date and meta-analysis. Rheumatol Int. 2022;42(3):413-429.
[45] ANDRADE A, DE AZEVEDO KLUMB STEFFENS R, SIECZKOWSKA SM, et al. A systematic review of the effects of strength training in patients with fibromyalgia: clinical outcomes and design considerations. Adv Rheumatol. 2018;58(1):36.
[46] CHEN J, HAN B, WU C. On the superiority of a combination of aerobic and resistance exercise for fibromyalgia syndrome: a network meta-analysis. Front Psychol. 2022;13:949256.
[47] SOUSA M, OLIVEIRA R, BRITO JP, et al. Effects of combined training programs in individuals with fibromyalgia: a systematic review. Healthcare (Basel). 2023;11(12):1708. |