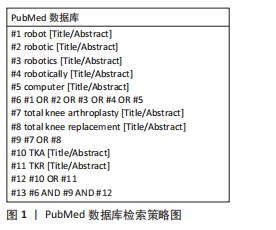
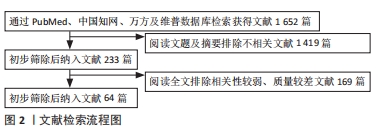
[1] 边焱焱,程开源,常晓,等.2011至2019年中国人工髋膝关节置换手术量的初步统计与分析[J].中华骨科杂志,2020,40(21):1453-1460.
[2] 邵宏翊,吴立东,曹光磊,等.国产机器人辅助全膝关节置换的精准性:一项多中心随机对照临床研究[J].中华骨与关节外科杂志,2023,16(4): 310-316.
[3] ROBERTSSON O, DUNBAR M, PEHRSSON T, et al. Patient satisfaction after knee arthroplasty: a report on 27 372 knees operated on between 1981 and 1995 in Sweden. Acta Orthop Scand. 2000;71(3):262-267.
[4] SCOTT CE, HOWIE CR, MACDONALD D, et al. Predicting dissatisfaction following total knee replacement: a prospective study of 1217 patients. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 2010;92(9):1253-1258.
[5] SIRES JD, WILSON CJ. CT validation of intraoperative implant position and knee alignment as determined by the MAKO total knee arthroplasty system. J Knee Surg. 2021;34(10):1133-1137.
[6] SONG EK, SEON JK, YIM JH, et al. Robotic-assisted TKA reduces postoperative alignment outliers and improves gap balance compared to conventional TKA. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2013;471(1):118-126.
[7] SULTAN AA, SAMUEL LT, KHLOPAS A, et al. Robotic-arm assisted total knee arthroplasty more accurately restored the posterior condylar offset ratio and the insall-salvati index compared to the manual technique: a cohort-matched study. Surg Technol Int. 2019;34:409-413.
[8] 李超,刘宇博,张帅,等.功能对线与限制性运动对线机器人辅助全膝关节置换短期临床研究[J].中华骨与关节外科杂志,2023,16(4):325-332.
[9] BELL C, GRAU L, OROZCO F, et al. The successful implementation of the Navio robotic technology required 29 cases. J Robot Surg. 2022;16(3):495-499.
[10] KAYANI B, KONAN S, HUQ SS, et al. Robotic-arm assisted total knee arthroplasty has a learning curve of seven cases for integration into the surgical workflow but no learning curve effect for accuracy of implant positioning. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2019;27(4):1132-1141.
[11] LIOW MHL, CHIN PL, PANG HN, et al. THINK surgical TSolution-One(®) (Robodoc) total knee arthroplasty. SICOT J. 2017;3:63.
[12] VANLOMMEL L, NEVEN E, ANDERSON M B, et al. The initial learning curve for the ROSA® Knee System can be achieved in 6-11 cases for operative time and has similar 90-day complication rates with improved implant alignment compared to manual instrumentation in total knee arthroplasty. J Exp Orthop. 2021;8(1):119.
[13] WAKELIN EA, SHALHOUB S, LAWRENCE JM, et al. Improved total knee arthroplasty pain outcome when joint gap targets are achieved throughout flexion. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2022;30(3):939-947.
[14] KAYANI B, KONAN S, AYUOB A, et al. Robotic technology in total knee arthroplasty: a systematic review. EFORT Open Rev. 2019;4(10):611-617.
[15] MANCINO F, CACCIOLA G, MALAHIAS M A, et al. What are the benefits of robotic-assisted total knee arthroplasty over conventional manual total knee arthroplasty? A systematic review of comparative studies. Orthop Rev. 2020;12(Suppl 1):8657.
[16] INNOCENTI B, BORI E. Robotics in orthopaedic surgery: why, what and how? Arch Orthop Trauma Surg. 2021;141(12):2035-2042.
[17] SOUSA PL, SCULCO PK, MAYMAN DJ, et al. Robots in the operating room during hip and knee arthroplasty. Curr Rev Musculoskelet Med. 2020;13(3): 309-317.
[18] SIDDIQI A, HARDAKER WM, EACHEMPATI KK, et al. Advances in computer-aided technology for total knee arthroplasty. Orthopedics. 2017;40(6):338-352.
[19] MARCHAND R C, SODHI N, KHLOPAS A, et al. Patient satisfaction outcomes after robotic arm-assisted total knee arthroplasty: a short-term evaluation. J Knee Surg. 2017;30(9):849-853.
[20] 冼达亨,赵晶,王英杰,等.机器人辅助全膝关节置换治疗合并关节外畸形的外翻膝1例报道及文献复习[J].中华骨与关节外科杂志,2023, 16(4):367-371.
[21] SIDDIQI A, MONT MA, KREBS VE, et al. Not all robotic-assisted total knee arthroplasty are the same. J Am Acad Orthop Surg. 2021;29(2):45-59.
[22] JACOFSKY DJ, ALLEN M. Robotics in arthroplasty: a comprehensive review. J Arthroplasty. 2016;31(10):2353-2363.
[23] PARRATTE S, PRICE AJ, JEYS LM, et al. Accuracy of a new robotically assisted technique for total knee arthroplasty: a cadaveric study. J Arthroplasty. 2019;34(11):2799-2803.
[24] SEIDENSTEIN A, BIRMINGHAM M, FORAN J, et al. Better accuracy and reproducibility of a new robotically-assisted system for total knee arthroplasty compared to conventional instrumentation: a cadaveric study. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2021;29(3):859-866.
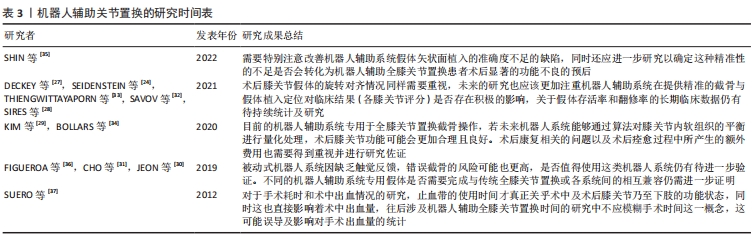
[25] KEGGI JM, WAKELIN EA, KOENIG JA, et al. Impact of intra-operative predictive ligament balance on post-operative balance and patient outcome in TKA: a prospective multicenter study. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg. 2021;141(12):2165-2174.
[26] BLUM CL, LEPKOWSKY E, HUSSEIN A, et al. Patient expectations and satisfaction in robotic-assisted total knee arthroplasty: a prospective two-year outcome study. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg. 2021;141(12):2155-2164.
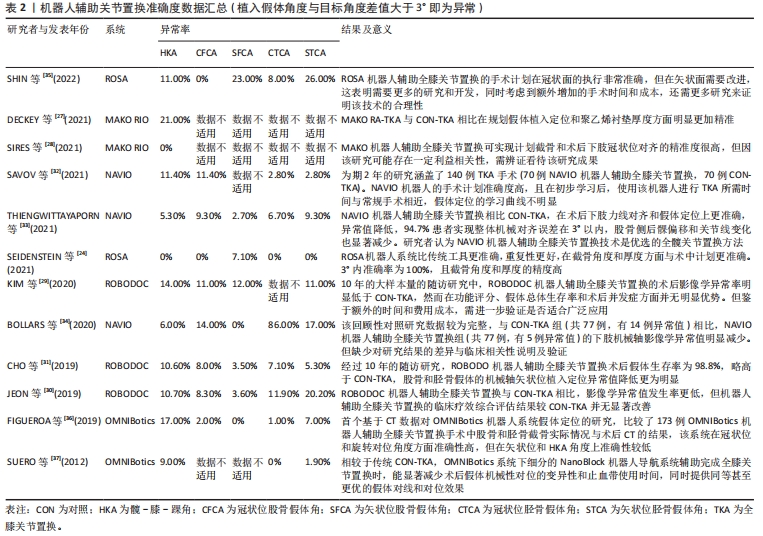
[27] DECKEY DG, ROSENOW CS, VERHEY JT, et al. Robotic-assisted total knee arthroplasty improves accuracy and precision compared to conventional techniques. Bone Joint J. 2021;103-b(6 Supple A):74-80.
[28] SIRES JD, CRAIK JD, WILSON J. Accuracy of bone resection in MAKO total knee robotic-assisted surgery. J Knee Surg. 2021;34(7):745-748.
[29] KIM YH, YOON SH, PARK JW. Does Robotic-assisted TKA result in better outcome scores or long-term survivorship than conventional TKA? A randomized, controlled trial. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2020;478(2):266-275.
[30] JEON SW, KIM KI, SONG SJ. Robot-assisted total knee arthroplasty does not improve long-term clinical and radiologic outcomes. J Arthroplasty. 2019;34(8):1656-1661.
[31] CHO KJ, SEON JK, JANG WY, et al. Robotic versus conventional primary total knee arthroplasty: clinical and radiological long-term results with a minimum follow-up of ten years. Int Orthop. 2019;43(6):1345-1354.
[32] SAVOV P, TUECKING LR, WINDHAGEN H, et al. Imageless robotic handpiece-assisted total knee arthroplasty: a learning curve analysis of surgical time and alignment accuracy. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg. 2021;141(12): 2119-2128.
[33] THIENGWITTAYAPORN S, UTHAITAS P, SENWIRUCH C, et al. Imageless robotic-assisted total knee arthroplasty accurately restores the radiological alignment with a short learning curve: a randomized controlled trial. Int Orthop. 2021;45(11):2851-2858.
[34] BOLLARS P, BOECKXSTAENS A, MIEVIS J, et al. Preliminary experience with an image-free handheld robot for total knee arthroplasty: 77 cases compared with a matched control group. Eur J Orthop Surg Traumatol. 2020;30(4):723-729.
[35] SHIN C, CROVETTI C, HUO E, et al. Unsatisfactory accuracy of recent robotic assisting system ROSA for total knee arthroplasty. J Exp Orthop. 2022;9(1):82.
[36] FIGUEROA F, WAKELIN E, TWIGGS J, et al. Comparison between navigated reported position and postoperative computed tomography to evaluate accuracy in a robotic navigation system in total knee arthroplasty. Knee. 2019;26(4):869-875.
[37] SUERO EM, PLASKOS C, DIXON PL, et al. Adjustable cutting blocks improve alignment and surgical time in computer-assisted total knee replacement. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2012;20(9):1736-1741.
[38] RIVIÈRE C, IRANPOUR F, AUVINET E, et al. Alignment options for total knee arthroplasty: a systematic review. Orthop Traumatol Surg Res. 2017; 103(7):1047-1056.
[39] KAZARIAN GS, HADDAD FS, DONALDSON MJ, et al. Implant malalignment may be a risk factor for poor patient-reported outcomes measures (PROMs) following total knee arthroplasty (TKA). J Arthroplasty. 2022;37(6s): S129-S133.
[40] VAN LIESHOUT WAM, VALKERING KP, KOENRAADT KLM, et al. The negative effect of joint line elevation after total knee arthroplasty on outcome. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2019;27(5):1477-1486.
[41] VERMUE H, LUYCKX T, WINNOCK DE GRAVE P, et al. Robot-assisted total knee arthroplasty is associated with a learning curve for surgical time but not for component alignment, limb alignment and gap balancing. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2022;30(2):593-602.
[42] MAHURE SA, TEO GM, KISSIN YD, et al. Learning curve for active robotic total knee arthroplasty. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2022;30(8): 2666-2676.
[43] ALI M, PHILLIPS D, KAMSON A, et al. Learning curve of robotic-assisted total knee arthroplasty for non-fellowship-trained orthopedic surgeons. Arthroplast Today. 2022;13:194-198.
[44] ST MART JP, GOH EL. The current state of robotics in total knee arthroplasty. EFORT Open Rev. 2021;6(4):270-279.
[45] MOSCHETTI WE, KONOPKA JF, RUBASH HE, et al. Can robot-assisted unicompartmental knee arthroplasty be cost-effective? A markov decision analysis. J Arthroplasty. 2016;31(4):759-765.
[46] VERMUE H, TACK P, GRYSON T, et al. Can robot-assisted total knee arthroplasty be a cost-effective procedure? A Markov decision analysis. Knee. 2021;29:345-352.
[47] RAJAN PV, KHLOPAS A, KLIKA A, et al. The Cost-effectiveness of robotic-assisted versus manual total knee arthroplasty: a markov model-based evaluation. J Am Acad Orthop Surg. 2022;30(4):168-176.
[48] STEFFENS D, KARUNARATNE S, MCBRIDE K, et al. Implementation of robotic-assisted total knee arthroplasty in the public health system: a comparative cost analysis. Int Orthop. 2022;46(3):481-488.
[49] BAEK J H, LEE SC, KIM JH, et al. Distal femoral tracker pin placement prevents delayed pin tract-induced fracture in robotic-assisted total knee arthroplasty: results of minimum 1-year follow-up. J Knee Surg. 2022; 36(10):1102-1104.
[50] THOMAS TL, GOH GS, NGUYEN MK, et al. Pin-related complications in computer navigated and robotic-assisted knee arthroplasty: a systematic review. J Arthroplasty. 2022;37(11):2291-2307.
[51] ELLIOTT J, SHATROV J, FRITSCH B, et al. Robotic-assisted knee arthroplasty: an evolution in progress. A concise review of the available systems and the data supporting them. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg. 2021;141(12):2099-2117.
[52] SIDDIQI A, HORAN T, MOLLOY RM, et al. A clinical review of robotic navigation in total knee arthroplasty: historical systems to modern design. EFORT Open Rev. 2021;6(4):252-269.
[53] AGARWAL N, TO K, MCDONNELL S, et al. Clinical and radiological outcomes in robotic-assisted total knee arthroplasty: a systematic review and meta-analysis. J Arthroplasty. 2020;35(11):3393-3409.
[54] KHLOPAS A, SODHI N, SULTAN AA, et al. Robotic arm-assisted total knee arthroplasty. J Arthroplasty. 2018;33(7):2002-2006.
[55] MANCINO F, ROSSI SMP, SANGALETTI R, et al. A new robotically assisted technique can improve outcomes of total knee arthroplasty comparing to an imageless navigation system. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg. 2022;143(5): 2701-2711.
[56] DEFRANCE MJ, YAYAC MF, COURTNEY PM, et al. The impact of author financial conflicts on robotic-assisted joint arthroplasty research. J Arthroplasty. 2021;36(4):1462-1469.
[57] BATAILLER C, PARRATTE S. Assistive technologies in knee arthroplasty: fashion or evolution? Rate of publications and national registries prove the Scott Parabola wrong. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg. 2021;141(12):2027-2034.
[58] ROSSI SMP, MANCINO F, SANGALETTI R, et al. Augmented reality in orthopedic surgery and its application in total joint arthroplasty: a systematic review. Appl Sci. 2022;12(10):5278.
[59] 许中华.机器人辅助技术降低全膝关节置换创伤效应的前瞻性、随机对照研究[D].重庆:中国人民解放军陆军军医大学,2022.
[60] 邵小龙,杜天舒,闫昭,等.机器人辅助全膝关节置换的研究进展[J].中国骨与关节杂志,2022,11(7):521-525.
[61] 张子安,张海宁,李海燕,等.机器人辅助技术在全膝关节置换手术中的应用[J].中国矫形外科杂志,2020,28(11):937-941.
[62] 赵晶,余沐洋,彭慧明,等.机器人辅助全膝关节置换流程优化及学习曲线研究[J].中华骨与关节外科杂志,2023,16(4):333-339.
[63] 智信,平航宇,彭伟,等.鸿鹄机器人辅助全膝关节置换学习曲线初步研究[J].中华骨与关节外科杂志,2023,16(4):340-346.
[64] 荣根祥,张金陵,张弘景,等.机器人辅助全膝关节置换治疗膝骨关节炎的临床研究[J]实用骨科杂志,2022,28(11):976-981.
|