[1] 魏戌, 韩涛, 齐保玉, 等. 中西医结合治疗脊柱退行性疾病的思路与实践[J]. 中国骨伤,2023,36(4):345-347.
[2] YAN J, LIAO Z, YU Y. Finite element analysis of dynamic changes in spinal mechanics of osteoporotic lumbar fracture. Eur J Med Res. 2022;27(1):142.
[3] NISHIDA N, OHGI J, JIANG F, et al. Finite Element Method Analysis of Compression Fractures on Whole-Spine Models Including the Rib Cage. Comput Math Methods Med. 2019;2019:8348631.
[4] KONG M, XU D, GAO C, et al. Risk Factors for Recurrent L4-5 Disc Herniation After Percutaneous Endoscopic Transforaminal Discectomy: A Retrospective Analysis of 654 Cases. Risk Manag Healthc Policy. 2020;13:3051-3065.
[5] BISWAS JK, RANA M, MALAS A, et al. Effect of single and multilevel artificial inter-vertebral disc replacement in lumbar spine: A finite element study. Int J Artif Organs. 2022;45(2):193-199.
[6] SHARABI M, LEVI-SASSON A, WOLFSON R, et al. The Mechanical Role of the Radial Fibers Network Within the Annulus Fibrosus of the Lumbar Intervertebral Disc: A Finite Elements Study. J Biomech Eng . 2019;141(4). doi: 10.1115/1.4042685.
[7] QASIM M, NATARAJAN RN, AN HS, et al. Initiation and progression of mechanical damage in the intervertebral disc under cyclic loading using continuum damage mechanics methodology: A finite element study. J Biomech. 2012;45(11):1934-1940.
[8] KANG S, PARK CH, JUNG H, et al. Analysis of the physiological load on lumbar vertebrae in patients with osteoporosis: a finite-element study. Sci Rep. 2022;12(1):11001.
[9] LIAO JC. Impact of Osteoporosis on Different Type of Short-Segment Posterior Instrumentation for Thoracolumbar Burst Fracture-A Finite Element Analysis. World Neurosurg. 2020;139:e643-e651.
[10] NATARAJAN RN, GARRETSON RB, BIYANI A, et al. Effects of slip severity and loading directions on the stability of isthmic spondylolisthesis: a finite element model study. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2003;28(11):1103-1112.
[11] 刘洋, 赵永飞, 顾晓民, 等. 退变性腰椎滑脱力学模型建立及分析[J]. 脊柱外科杂志,2010,8(1):39-43.
[12] 齐振熙, 马英锋. 退变性腰椎滑脱的三维FEA [J]. 中国骨伤,2004,17(12): 14-16.
[13] JHONG GH, CHUNG YH, LI CT, et al. Numerical Comparison of Restored Vertebral Body Height after Incomplete Burst Fracture of the Lumbar Spine. J Pers Med. 2022;12(2):253.
[14] SCHUIT SCE, VAN DER KLIFT M, WEEL AEAM, et al. Fracture incidence and association with bone mineral density in elderly men and women: the Rotterdam Study. Bone. 2004;34(1):195-202.
[15] COSMAN F, KREGE JH, LOOKER AC, et al. Spine fracture prevalence in a nationally representative sample of US women and men aged ≥40 years: results from the National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (NHANES) 2013-2014. Osteoporos Int. 2017;28(6):1857-1866.
[16] IMAI K. Computed tomography-based finite element analysis to assess fracture risk and osteoporosis treatment. World J Exp Med. 2015;5(3): 182-187.
[17] MARTIN BI, MIRZA SK, SPINA N, et al. Trends in Lumbar Fusion Procedure Rates and Associated Hospital Costs for Degenerative Spinal Diseases in the United States, 2004 to 2015. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2019;44(5):369-376.
[18] CHOI KC, KIM JS, SHIM HK, et al. Changes in the adjacent segment 10 years after anterior lumbar interbody fusion for low-grade isthmic spondylolisthesis. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2014;472(6):1845-1854.
[19] NAKASHIMA H, KAWAKAMI N, TSUJI T, et al. Adjacent Segment Disease After Posterior Lumbar Interbody Fusion: Based on Cases With a Minimum of 10 Years of Follow-up. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2015;40(14):E831-E841.
[20] WANG B, KE W, HUA W, et al. Biomechanical evaluation of anterior and posterior lumbar surgical approaches on the adjacent segment: a finite element analysis. Comput Methods Biomech Biomed Engin. 2020;23(14): 1109-1116.
[21] MANNION AF, LEIVSETH G, BROX JI, et al. ISSLS Prize winner: Long-term follow-up suggests spinal fusion is associated with increased adjacent segment disc degeneration but without influence on clinical outcome: results of a combined follow-up from 4 randomized controlled trials. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2014;39(17):1373-1383.
[22] PARK P, GARTON HJ, GALA VC, et al. Adjacent segment disease after lumbar or lumbosacral fusion: review of the literature. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2004; 29(17):1938-1944.
[23] ZHOU C, CHA T, WANG W, et al. Investigation of Alterations in the Lumbar Disc Biomechanics at the Adjacent Segments After Spinal Fusion Using a Combined In Vivo and In Silico Approach. Ann Biomed Eng. 2021;49(2): 601-616.
[24] LE TV, BAAJ AA, DAKWAR E, et al. Subsidence of polyetheretherketone intervertebral cages in minimally invasive lateral retroperitoneal transpsoas lumbar interbody fusion. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2012;37(14):1268-1273.
[25] LEE N, KIM K N, YI S, et al. Comparison of Outcomes of Anterior, Posterior, and Transforaminal Lumbar Interbody Fusion Surgery at a Single Lumbar Level with Degenerative Spinal Disease. World Neurosurg. 2017;101:216-226.
[26] MALHAM GM, PARKER RM, BLECHER CM, et al. Assessment and classification of subsidence after lateral interbody fusion using serial computed tomography. J Neurosurg Spine. 2015;23(5) 589-597.
[27] YANG ZQ, CAI P, LI JC, et al. Stepwise reduction of bone mineral density increases the risk of cage subsidence in oblique lumbar interbody fusion patients biomechanically: an in-silico study. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2022;23(1):1083.
[28] RASTEGAR S, ARNOUX PJ, WANG X, et al. Biomechanical analysis of segmental lumbar lordosis and risk of cage subsidence with different cage heights and alternative placements in transforaminal lumbar interbody fusion. Comput Methods Biomech Biomed Engin. 2020;23(9):456-466.
[29] GUO Z, LIU G, WANG L, et al. Biomechanical effect of Coflex and X-STOP spacers on the lumbar spine: a finite element analysis. Am J Transl Res. 2022;14(7):5155-5163.
[30] ZHU J, SHEN H, CUI Y, et al. Biomechanical Evaluation of Transforaminal Lumbar Interbody Fusion with Coflex-F and Pedicle Screw Fixation: Finite Element Analysis of Static and Vibration Conditions. Orthop Surg. 2022;14(9):2339-2349.
[31] FAN Y, ZHOU S, XIE T, et al. Topping-off surgery vs posterior lumbar interbody fusion for degenerative lumbar disease: a finite element analysis. J Orthop Surg Res. 2019;14(1):476.
[32] ZHONG J, O’CONNELL B, BALOUCH E, et al. Patient Outcomes After Single-level Coflex Interspinous Implants Versus Single-level Laminectomy. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2021;46(13):893-900.
[33] KAPETANAKIS S, GKASDARIS G, ANGOULES AG, et al. Transforaminal Percutaneous Endoscopic Discectomy using Transforaminal Endoscopic Spine System technique: Pitfalls that a beginner should avoid. World J Orthop. 2017;8(12):874-880.
[34] WEINSTEIN JN, TOSTESON TD, LURIE JD, et al. Surgical versus nonsurgical therapy for lumbar spinal stenosis. N Engl J Med. 2008;358(8):794-810.
[35] JASPER GP, FRANCISCO GM, TELFEIAN AE. Transforaminal endoscopic discectomy with foraminoplasty for the treatment of spondylolisthesis. Pain Physician. 2014;17(6):E703-E708.
[36] JASPER GP, FRANCISCO GM, AGHION D, et al. Technical considerations in transforaminal endoscopic discectomy with foraminoplasty for the treatment of spondylolisthesis: Case report. Clin Neurol Neurosurg. 2014; 119:84-87.
[37] KITAHAMA Y, SAIRYO K, DEZAWA A. Percutaneous endoscopic transforaminal approach to decompress the lateral recess in an elderly patient with spinal canal stenosis, herniated nucleus pulposus and pulmonary comorbidities. Asian J Endosc Surg. 2013;6(2):130-133.
[38] XIE Y, ZHOU Q, WANG X, et al. The biomechanical effects of foraminoplasty of different areas under lumbar percutaneous endoscopy on intervertebral discs: A 3D finite element analysis. Medicine (Baltimore). 2020;99(17): e19847.
[39] YU Y, ZHOU Q, XIE YZ, et al. Effect of Percutaneous Endoscopic Lumbar Foraminoplasty of Different Facet Joint Portions on Lumbar Biomechanics: A Finite Element Analysis. Orthop Surg. 2020;12(4):1277-1284.
[40] LI J, ZHANG X, XU W, et al. Reducing the extent of facetectomy may decrease morbidity in failed back surgery syndrome. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2019;20(1):369.
[41] SHI Y, XIE YZ, ZHOU Q, et al. The biomechanical effect of the relevant segments after facet-disectomy in different diameters under posterior lumbar percutaneous endoscopes: a three-dimensional finite element analysis. J Orthop Surg Res. 2021;16(1):593.
[42] LI J, XU W, JIANG Q, et al. Indications Selection for Surgeons Training in the Translaminar Percutaneous Endoscopic Discectomy Based on Finite Element Analysis. Biomed Res Int. 2020;2020:2960642.
[43] KITAHAMA Y, OHASHI H, NAMBA H, et al. Finite element method for nerve root decompression in minimally invasive endoscopic spinal surgery. Asian J Endosc Surg. 2021;14(3):628-635.
[44] ZHANG X, CHEN T, MENG F, et al. A finite element analysis on different bone cement forms and injection volumes injected into lumbar vertebral body in percutaneous kyphoplasty. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2022;23(1):621.
[45] 吴智华, 李任, 潘慧玲, 等. 骨水泥弥散类型对强化椎体生物力学特性影响的FEA [J]. 中国组织工程研究,2023,27(30):4763-4768.
[46] 赵研, 宋启春, 李东, 等. 骨质疏松性椎体压缩骨折不同骨水泥分布的临床观察及生物力学的FEA [J]. 创伤外科杂志,2022,24(11):818-824+ 836.
[47] KOU YH, ZHANG DY, ZHANG JD, et al. Vertebroplasty with high-viscosity cement versus conventional kyphoplasty for osteoporotic vertebral compression fractures: a meta-analysis. ANZ J Surg. 2022;92(11):2849-2858.
[48] WANG Q, SUN C, ZHANG L, et al. High- versus low-viscosity cement vertebroplasty and kyphoplasty for osteoporotic vertebral compression fracture: a meta-analysis. Eur Spine J. 2022;31(5):1122-1130.
[49] DICKEY BT, TYNDYK MA, DOMAN DA, et al. In silico evaluation of stress distribution after vertebral body augmentation with conventional acrylics, composites and glass polyalkenoate cements. J Mech Behav Biomed Mater. 2012;5(1):283-290.
[50] MEYER C, VAN GAALEN K, LESCHINGER T, et al. Kyphoplasty of Osteoporotic Fractured Vertebrae: A Finite Element Analysis about Two Types of Cement. Biomed Res Int. 2019;2019:9232813.
[51] ZHU J, YANG S, CAI K, et al. Bioactive poly (methyl methacrylate) bone cement for the treatment of osteoporotic vertebral compression fractures. Theranostics. 2020;10(14):6544-6560.
[52] DIAB AA, MOUSTAFA IM. Lumbar lordosis rehabilitation for pain and lumbar segmental motion in chronic mechanical low back pain: a randomized trial. J Manipulative Physiol Ther. 2012;35(4):246-253.
[53] GAGNE AR, HASSON SM. Lumbar extension exercises in conjunction with mechanical traction for the management of a patient with a lumbar herniated disc. Physiother Theory Pract. 2010;26(4):256-266.
[54] ÖTEN E, CIVAN O, UĞUR L. Traction therapy in lumbar disc hernias: A finite element analysis study. Jt Dis Relat Surg. 2022;33(1):86-92.
[55] 林俊山, 李兆文, 林石明, 等. 不同角度和牵引力对腰椎间盘作用的实验研究[J]. 福建中医学院学报,2002,12(1):21-25.
[56] FARAJPOUR H, JAMSHIDI N. Effects of Different Angles of the Traction Table on Lumbar Spine Ligaments: A Finite Element Study. Clin Orthop Surg. 2017;9(4):480-488.
[57] TANG S, REBHOLZ BJ. Does anterior lumbar interbody fusion promote adjacent degeneration in degenerative disc disease? A finite element study. J Orthop Sci. 2011;16(2):221-228.
[58] TANG S, REBHOLZ BJ. Does lumbar microdiscectomy affect adjacent segmental disc degeneration? A finite element study. J Surg Res. 2013; 182(1): 62-67.
[59] ZHANG R, MO Z, LI D, et al. Biomechanical Comparison of Lumbar Fixed-Point Oblique Pulling Manipulation and Traditional Oblique Pulling Manipulation in Treating Lumbar Intervertebral Disk Protrusion. J Manipulative Physiol Ther. 2020;43(5):446-456.
[60] 卢钰, 郑太才, 王琪, 等. 不同体位下斜扳手法治疗腰椎间盘突出的三维FEA [J]. 中国组织工程研究,2021,25(36):5872-5877.
[61] DU HG, LIAO SH, JIANG Z, et al. Biomechanical analysis of press-extension technique on degenerative lumbar with disc herniation and staggered facet joint. Saudi Pharm J. 2016;24(3):305-311.
[62] 陈忻, 于杰, 冯敏山, 等. 坐位旋转手法治疗退行性腰椎滑脱的椎间盘力学分析[J]. 中华中医药杂志,2019,34(4):1395-400.
[63] JIN M, LEI L, LI F, et al. Does Robot Navigation and Intraoperative Computed Tomography Guidance Help with Percutaneous Endoscopic Lumbar Discectomy? A Match-Paired Study. World Neurosurg. 2021;147:e459-e467.
[64] WANG B, CAO J, CHANG J, et al. Effectiveness of Tirobot-assisted vertebroplasty in treating thoracolumbar osteoporotic compression fracture. J Orthop Surg Res. 2021;16(1):65.
[65] GOOD CR, OROSZ L, SCHROERLUCKE SR, et al. Complications and Revision Rates in Minimally Invasive Robotic-Guided Versus Fluoroscopic-Guided Spinal Fusions: The MIS ReFRESH Prospective Comparative Study. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2021;46(23):1661-1668.
[66] LI Y, WANG Y, MA X, et al. Comparison of short-term clinical outcomes between robot-assisted and freehand pedicle screw placement in spine surgery: a meta-analysis and systematic review. J Orthop Surg Res. 2023; 18(1):359.
[67] CHANG M, WANG L, YUAN S, et al. Percutaneous Endoscopic Robot-Assisted Transforaminal Lumbar Interbody Fusion (PE RA-TLIF) for Lumbar Spondylolisthesis: A Technical Note and Two Years Clinical Results. Pain Physician. 2022;25(1): E73-E86.
[68] ZHANG RJ, ZHOU LP, ZHANG L, et al. Safety and risk factors of TINAVI robot-assisted percutaneous pedicle screw placement in spinal surgery. J Orthop Surg Res. 2022;17(1):379.
[69] HAN XG, TANG GQ, HAN X, et al. Comparison of Outcomes between Robot-Assisted Minimally Invasive Transforaminal Lumbar Interbody Fusion and Oblique Lumbar Interbody Fusion in Single-Level Lumbar Spondylolisthesis. Orthop Surg. 2021;13(7):2093-2101.
[70] SHI B, JIANG T, DU H, et al. Application of Spinal Robotic Navigation Technology to Minimally Invasive Percutaneous Treatment of Spinal Fractures: A Clinical, Non-Randomized, Controlled Study. Orthop Surg. 2021;13(4):1236-1243.
[71] HARREN K, DITTRICH F, REINECKE F, et al. [Digitalization and artificial intelligence in orthopedics and traumatology]. Orthopade. 2018;47(12): 1039-1054.
[72] XIE LZ, WANG QL, ZHANG Q, et al. Accuracies of various types of spinal robot in robot-assisted pedicle screw insertion: a Bayesian network meta-analysis. J Orthop Surg Res. 2023;18(1):243.
[73] MOURAD R, KOLISNYK S, BAIUN Y, et al. Performance of hybrid artificial intelligence in determining candidacy for lumbar stenosis surgery. Eur Spine J. 2022;31(8):2149-2155.
|
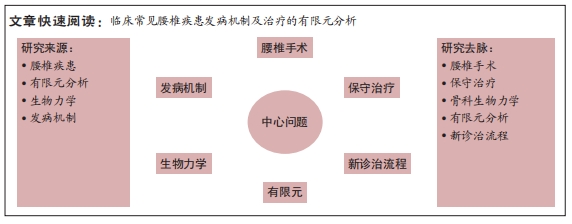

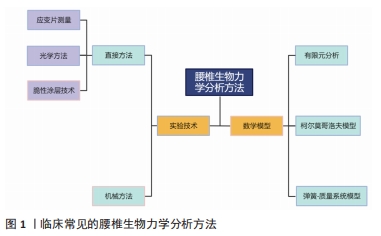
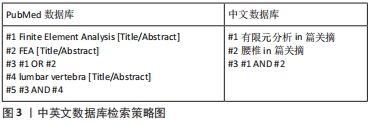
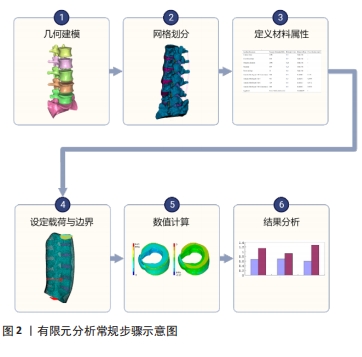 近年来,有限元法在腰椎生物力学方面得到了广泛应用,其主要用于探究腰椎疾患发病的力学机制与治疗方式的力学原理。此外,该分析方法还能够优化手术方式,并制定最佳治疗方案。然而,当前研究仍存在一定弊端,由于临床医师对该分析方法不熟悉,分析操作较为复杂等原因,有限元分析未能在临床得以普及。并且当前关于腰椎疾患的有限元研究纷繁复杂,尚无学者对这方面进行总结归纳,因而,此文就有限元法在临床腰椎疾患的发病机制和常用治疗方式的应用方面进行综述,并提出有限元法与临床相结合的新方式,旨在为进一步探索腰椎疾患的预防与治疗提供依据,并能够进一步推广有限元法与临床相结合。
近年来,有限元法在腰椎生物力学方面得到了广泛应用,其主要用于探究腰椎疾患发病的力学机制与治疗方式的力学原理。此外,该分析方法还能够优化手术方式,并制定最佳治疗方案。然而,当前研究仍存在一定弊端,由于临床医师对该分析方法不熟悉,分析操作较为复杂等原因,有限元分析未能在临床得以普及。并且当前关于腰椎疾患的有限元研究纷繁复杂,尚无学者对这方面进行总结归纳,因而,此文就有限元法在临床腰椎疾患的发病机制和常用治疗方式的应用方面进行综述,并提出有限元法与临床相结合的新方式,旨在为进一步探索腰椎疾患的预防与治疗提供依据,并能够进一步推广有限元法与临床相结合。
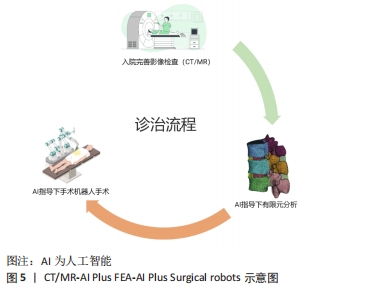 然而,该诊治流程仍存在一定缺陷,如当前手术机器人造价较高,在国内医院尚未得到普及,并且使用手术机器人会增加手术成本,并且能够自行建立有限元模型进行分析的人工智能系统仍在开发阶段。但是随着人工智能与手术机器人技术的发展,这些难题终将会被攻克。
然而,该诊治流程仍存在一定缺陷,如当前手术机器人造价较高,在国内医院尚未得到普及,并且使用手术机器人会增加手术成本,并且能够自行建立有限元模型进行分析的人工智能系统仍在开发阶段。但是随着人工智能与手术机器人技术的发展,这些难题终将会被攻克。