中国组织工程研究 ›› 2025, Vol. 29 ›› Issue (9): 1810-1819.doi: 10.12307/2025.172
• 骨与关节生物力学Bone and joint biomechanics • 上一篇 下一篇
腰椎“内聚式”对称减压人工诱导突出椎间盘自然回缩的减压机制
张春霖,侯曌华,严 旭,姜 岩,付 苏,宁永明,李东哲,董 超,刘小康,王永魁,曹争明,杨腾跃
- 郑州大学第一附属医院骨科,河南省郑州市 450000
Decompression mechanism of symmetrically adduction of lumbar decompression induced resorption of herniated nucleus pulpous
Zhang Chunlin, Hou Zhaohua, Yan Xu, Jiang Yan, Fu Su, Ning Yongming, Li Dongzhe, Dong Chao, Liu Xiaokang, Wang Yongkui, Cao Zhengming, Yang Tengyue
- Department of Orthopedics, First Affiliated Hospital of Zhengzhou University, Zhengzhou 450000, Henan Province, China
摘要:
文题释义:
腰椎间盘突出:是指腰椎间盘的髓核在退变及外力作用下,从纤维环破裂处突出或脱出于后方或椎管内,侵占椎管空间或挤压椎管内神经出现相应的临床症状。
腰椎“内聚式”对称减压人工诱导突出椎间盘自然回缩术:是指一种于双侧腰椎关节突关节内侧靠近棘突处,对称进行椎板长槽状减压的新术式,即双侧减压槽“内聚”靠近棘突,以免损伤腰椎关节突关节,并向后方移动棘突韧带复合体,达到良好的神经“间接”减压,且术后早期还可诱导突出腰椎间盘出现广泛高效的自然吸收现象,实现神经“直接”减压,“直接”与“间接”双重减压机制有利于该术式获得良好的早期疗效。
人工诱导突出椎间盘自然吸收:是指在没有对突出的椎间盘进行任何直接干预如切除、温度控制、离子体射频消融、臭氧注射等情况下,通过手术的方式间接干预突出椎间盘,令其自然发生萎缩或回缩的现象。
摘要
背景:腰椎间盘突出症传统手术通过“环”神经广泛式切除进行减压及摘除突出腰椎间盘,存在神经损伤造成瘫痪、腰椎失稳、突出复发、椎间隙感染以及邻椎病等多种风险及并发症。
目的:提出腰椎“内聚式”对称减压人工诱导突出椎间盘自然回缩术,观察这种新术式的人工诱导突出椎间盘自然吸收现象及早期临床疗效,并分析其减压机制。
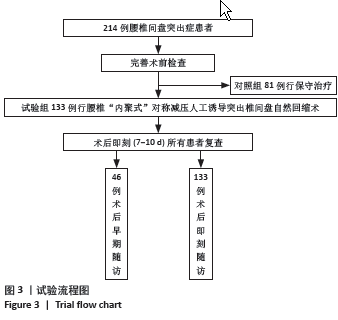
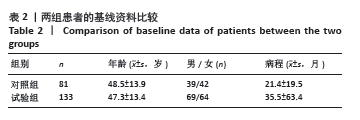
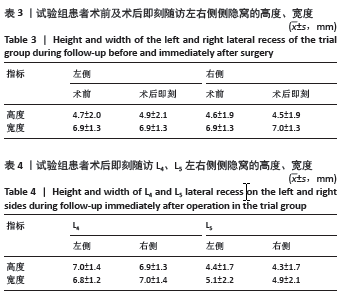
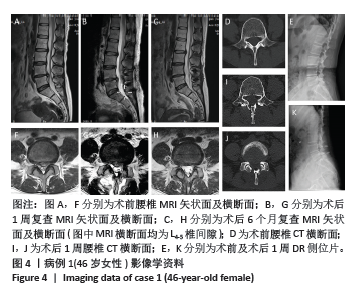
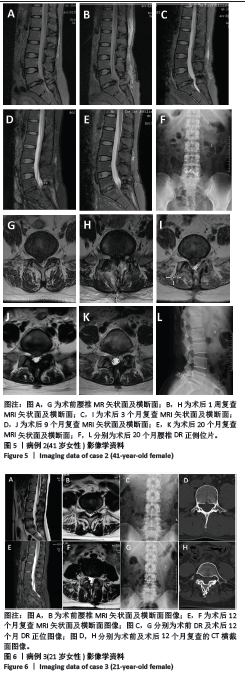
方法:纳入2021年3月至2023年5月郑州大学第一附属医院骨科收治的腰椎间盘突出患者214例,其中对照组81例行保守治疗,试验组133例接受腰椎“内聚式”对称减压人工诱导突出椎间盘自然回缩术治疗。试验组术前、术后即刻(7-14 d)及术后早期(1年以上)分别使用MRI图像测量腰椎间盘突出的体积变化,CT图像测量腰椎棘突韧带复合体后移距离以及侧隐窝宽度和高度,日本骨科学会评分评估患者神经功能恢复情况。
结果与结论:(1)对照组:保守治疗81例腰椎间盘突出患者共171个突出腰椎间盘,平均随访时间(22.7±23.1)个月;171个突出腰椎间盘就诊时及末次随访MRI测量突出腰椎间盘体积分别为(551.6±257.9) mm3和(792.2±330.4) mm3,体积平均增大率为(53.2±44.4)%,差异有显著性意义(P < 0.001);171个突出腰椎间盘中有4个发生了自然回缩现象,吸收比为2.3%(4/171),吸收率为(24.5±9.9)%。(2)试验组:133例腰椎间盘突出患者共285个突出腰椎间盘。①术后即刻:所有患者均完成术后即刻随访,285个突出腰椎间盘中有229个发生回缩,吸收比为80.3%(229/285),平均吸收率为(21.5±20.9)%,显著及完全吸收占6.5%;上腰椎共70个突出腰椎间盘,吸收比为85.7%(60/70),平均吸收率为(23.1±19.5)%,最大吸收率为86.6%;下腰椎共215个突出腰椎间盘,吸收比为78.6%(169/215),平均吸收率为(21.0±21.3)%,最大吸收率为83.2%;上腰椎与下腰椎显著及完全吸收分别占5.7%和6.5%,无统计学差异(P > 0.05);术后即刻棘突韧带复合体后移平均距离为(5.2±2.8) mm;术前和术后即刻相比,左侧、右侧侧隐窝的宽度、高度均无统计学差异(P > 0.05);术后即刻日本骨科学会评分由术前(10.1±3.4)分提升至(17.0±4.8)分,术后即刻有效率达95.6%;②术后早期:其中46例患者完成术后早期随访,共101个突出腰椎间盘,吸收比为94%(95/101),平均吸收率为(36.9±23.7)%,显著及完全吸收占30.6%,最大吸收率为100%;101个突出腰椎间盘中有3个体积未发生变化,体积不变率为2.97%(3/101);101个突出腰椎间盘有3个突出椎间盘体积增大,增大比为2.97%(3/101),增大率为(18.5±18.4)%;日本骨科学会评分由术前(9.3±5.1)分提升至(23.5±4.0)分,优良率达93.4%。(3)对照组和试验组术后早期突出腰椎间盘吸收比分别为2.3%及85.9%,差异有显著性意义(P < 0.001)。(4)并发症:试验组有2例发生切口渗液,延迟愈合,经换药等保守治疗切口愈合,且该组未发生神经损伤或死亡,也未再行二次手术。(5)结果显示,腰椎“内聚式”对称减压人工诱导突出椎间盘自然回缩术是一种可避免“环”神经广泛切除且可获得满意早期临床疗效的治疗腰椎间盘突出的新方法,不破坏腰椎关节突关节,也不改变侧隐窝基本解剖结构,完整保留突出腰椎间盘并可诱导其发生显著甚至完全的人工诱导突出椎间盘自然吸收;腰椎“内聚式”对称减压人工诱导突出椎间盘自然回缩术为腰椎间盘突出症的临床治疗提供了新的依据和方法。
中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:人工关节;骨植入物;脊柱;骨折;内固定;数字化骨科;组织工程
中图分类号: