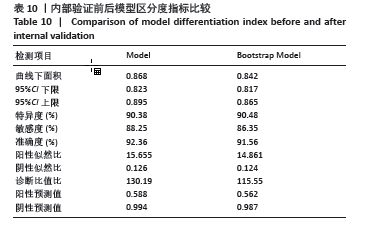
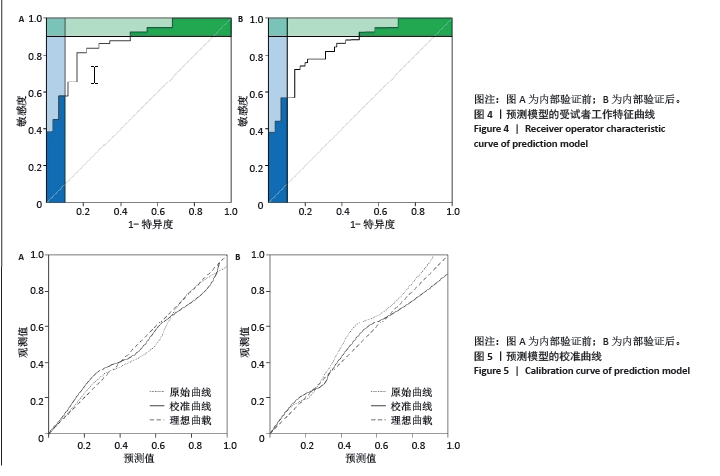
[1] 刘玉波, 张会增, 张同润, 等. 踝关节骨折术后踝穴形态变化与踝关节功能的相关因素分析[J]. 中国组织工程研究,2022,26(3): 440-445.
[2] 薛浩文, 褚虹宇, 左解鹏, 等. 基于CT的中国正常成人踝关节三维形态学分析及应用研究[J]. 中国临床解剖学杂志,2021,39(5): 539-545.
[3] ICHIKAWA K, JIANG Y, SUGI M, et al. Joint angle based motor point tracking stimulation for surface FES: A Study on biceps brachii. Med Eng Phys. 2021;88(2):9-18.
[4] CHUMACERO-POLANCO E, YANG J. Validation of an ankle-hip model of balance on a balance board via kinematic frequency-content. Gait Posture. 2020;82(11):313-321.
[5] LIU Y, WANG C, ZHENG L, et al. Correlation Between Postoperative Morphologic Changes of Ankle Mortise and Ankle Joint Function After Pilon Fracture. Int J Surg. 2020;104(3-4):182-187.
[6] UZUN E, MISIR A, KIZKAPAN TB, et al. Mid-term functional, clinical, and radiological outcomes with factors affecting revision of mobile-bearing medial unicompartmental knee arthroplasty. Knee. 2020;27(2):527-534.
[7] MATSUURA Y, TAKAMURA T, SUGIURA S, et al. Evaluation of anterior oblique ligament tension at the elbow joint angle-a cadaver study. J Shoulder Elbow Surg. 2021;30(2):359-364.
[8] HIRAO M, HASHIMOTO J, EBINA K, et al. Radiographic effects observed in the coronal view after medial malleolar osteotomy at total ankle arthroplasty in rheumatoid arthritis cases. J Orthop Sci. 2020;25(6):1072-1078.
[9] COOKE ME, TORNETTA P, FIROOZABADI R, et al. Open Ankle Fractures: What Predicts Infection? A Multicenter Study. J Orthop Trauma. 2022;36(1):43-48.
[10] 李亚星, 任毅, 唐霞, 等. 特殊命名的踝关节骨折及其诊疗要点[J]. 中华骨科杂志,2019,39(21):1344-1356.
[11] 袁心伟, 张斌, 胡豇, 等. 金属螺钉与可吸收螺钉修复下胫腓韧带复合体近期疗效比较[J]. 中国修复重建外科杂志,2022,36(8): 989-994.
[12] HERNANDEZ-CASTILLEJO LE, ÁLVAREZ-BUENO C, GARRIDO-MIGUEL M, et al. The effect of hallux valgus open and percutaneous surgery on AOFAS scale: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Qual Life Res. 2021;(1):1-10.
[13] 杨衡, 陈宇, 弋卓君, 等. 小切口联合全修复策略治疗Lauge-Hansen旋前-外旋型Ⅳ度踝关节闭合骨折[J]. 中国修复重建外科杂志,2020,34(6):730-736.
[14] BRAUNSTEIN M, BAUMBACH SF, URRESTI-GUNDLACH M, et al. Arthroscopically Assisted Treatment of Complex Ankle Fractures: Intra-articular Findings and 1-Year Follow-Up - ScienceDirect. J Foot Ankle Surg. 2020;59(1):9-15.
[15] 陈烽, 安忠诚, 周芳, 等. 后踝固定与否对不同Haraguchi分型后踝骨折疗效的影响[J]. 中国修复重建外科杂志,2021,35(6): 722-728.
[16] 罗刚, 倪卫东, 郭世航, 等. 缝合锚修复三角韧带深层治疗混合型内侧损伤踝关节骨折疗效观察[J]. 中国修复重建外科杂志,2020, 34(11):1387-1391.
[17] 韩翔, 李佳伟, 张俊忠. 后外侧联合内侧入路切开复位内固定治疗旋后外旋型三踝骨折[J]. 临床骨科杂志,2022,25(6):885-889.
[18] 黄培镇, 董航, 蔡群斌, 等. 三角韧带修复与下胫腓联合螺钉固定治疗三角韧带损伤的旋后外旋型Ⅳ度踝关节骨折的近期疗效观察[J]. 重庆医学,2019,48(6):1065-1068.
[19] 张绍春, 周彬, 王冶, 等. TightRope带袢钢板与皮质骨螺钉内固定治疗踝关节骨折合并的下胫腓联合损伤疗效比较[J]. 中国骨与关节损伤杂志,2021,36(12):1262-1265.
[20] LARRAINZAR-GARIJO R, MOLANES-LOPEZ EM, MURILLO-VIZUETE D, et al. Mechanical Alignment in Knee Replacement Homogenizes Postoperative Coronal Hip-Knee-Ankle Angle in Varus Knees: A Navigation-Based Study. J Knee Surg. 2022;35(12):1285-1294.
[21] 吴国忠, 王文怀, 陈守勃, 等. 关节镜下改良后踝入路切除治疗成人疼痛性跟距骨桥[J]. 中国修复重建外科杂志,2020,34(1):46-52.
[22] 邱范基, 李金峰. 不同模式本体感觉神经肌肉促进技术干预对功能性踝关节不稳者平衡能力的影响[J]. 中国康复医学杂志,2022, 37(6):773-778.
[23] 袁文杰, 陆大明, 徐雪平, 等. 经腓骨后外侧入路和经腓骨入路内固定术治疗旋后外旋型Ⅳ度踝关节骨折的疗效比较[J]. 中华骨与关节外科杂志,2023,16(2):164-168.
[24] 季磊, 汪玉海, 李卫华, 等. 不同入路内固定术治疗旋后外旋型Ⅳ度踝关节骨折的疗效比较[J]. 中国运动医学杂志,2020,39(4):263-267.
[25] 李朋斌, 陈伟, 邢焕霞, 等. 两种外侧入路接骨板内固定治疗SandersⅢ型跟骨关节内骨折的疗效比较[J]. 中华创伤杂志, 2020, 36(8):698-703.
[26] ZHAO HZ, FAN TS, WANG SL, et al. Closed Reduction for the Treatment of Grade IV Supination-External Rotation Fracture of the Ankle Joint: A Retrospective Analysis. Orthop Surg. 2021; 13(7):2163-2169.
[27] KONRADS C, AHREND MD, BEYER MR, et al. Rotation osteotomy of the distal femur influences coronal femoral alignment and the ischiofemoral space. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg. 2022; 142(5):711-720.
[28] 尹岳桐, 朱光宇, 田向东, 等. 胫骨结节远端单平面截骨对踝关节冠状面角度的影响[J]. 中国组织工程研究,2024,28(21):3349-3354.
[29] NI M, SUN T, ZHANG T, et al. Quantitative initial safety range of early passive rehabilitation after ankle fracture surgery. Injury. 2022;53(6):2281-2286.
|