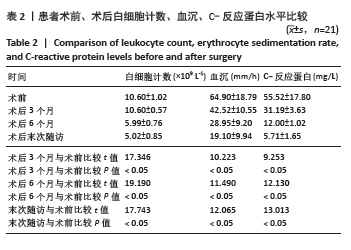
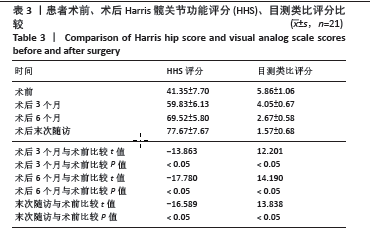
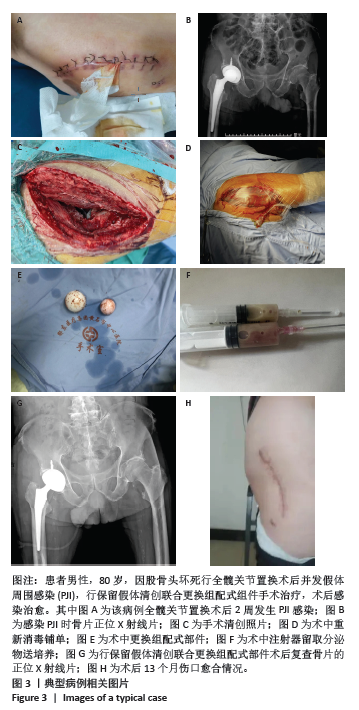
[1] HUMPHREYS H, HOFFMAN P. The conundrum of ultraclean air, deep infections, and artificial joint replacement. J Hosp Infect. 2020;104: 123-124.
[2] MATHEIS C, STÖGGL T. Strength and mobilization training within the first week following total hip arthroplasty. J Bodyw Mov Ther. 2018; 22(2):519-527.
[3] SHI H, XIAO L, WANG Z. Curative effect of artificial femoral head replacement and its effect on hip joint function and complications of senile patients with femoral intertrochanteric fracture. Exp Ther Med. 2018;16(2):623-628.
[4] GUNDTOFT PH, PEDERSEN AB, VARNUM C, et al. Increased Mortality After Prosthetic Joint Infection in Primary THA. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2017;475(11):2623-2631.
[5] MCPHERSON EJ, WOODSON C, HOLTOM P, et al. Periprosthetic total hip infection: outcomes using a staging system. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2002;(403):8-15.
[6] TSUKAYAMA DT, ESTRADA R, GUSTILO RB. Infection after total hip arthroplasty. A study of the treatment of one hundred and six infections. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1996;78(4):512-523.
[7] TRIANTAFYLLOPOULOS GK, SORANOGLOU V, MEMTSOUDIS SG, et al. Implant retention after acute and hematogenous periprosthetic hip and knee infections: Whom, when and how? World J Orthop. 2016;7(9):546-552.
[8] KUIPER JW, WILLINK RT, MOOJEN DJ, et al. Treatment of acute periprosthetic infections with prosthesis retention: Review of current concepts. World J Orthop. 2014;5(5):667-676.
[9] PATEL R, ALIJANIPOUR P, PARVIZI J. Advancements in Diagnosing Periprosthetic Joint Infections after Total Hip and Knee Arthroplasty. Open Orthop J. 2016;10:654-661.
[10] PARVIZI J, TAN TL, GOSWAMI K, et al. The 2018 Definition of Periprosthetic Hip and Knee Infection: An Evidence-Based and Validated Criteria. J Arthroplasty. 2018;33(5):1309-1314.
[11] OTTO-LAMBERTZ C, YAGDIRAN A, WALLSCHEID F, et al. Periprosthetic Infection in Joint Replacement. Dtsch Arztebl Int. 2017;114(20):347-353.
[12] ROMANO CL, MANZI G, LOGOLUSO N, et al. Value of debridement and irrigation for the treatment of peri-prosthetic infections. A systematic review. Hip Int. 2012;22 Suppl 8:S19-S24.
[13] COSTERTON JW, STEWART PS, GREENBERG EP. Bacterial biofilms: a common cause of persistent infections. Science. 1999;284(5418): 1318-1322.
[14] COSTERTON JW. Biofilm theory can guide the treatment of device-related orthopaedic infections. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2005;(437):7-11.
[15] OSMON DR, BERBARI EF, BERENDT AR, et al. Diagnosis and management of prosthetic joint infection: clinical practice guidelines by the Infectious Diseases Society of America. Clin Infect Dis. 2013;56(1): e1-e25.
[16] ACHERMANN Y, STASCH P, PREISS S, et al. Characteristics and treatment outcomes of 69 cases with early prosthetic joint infections of the hip and knee. Infection. 2014;42(3):511-519.
[17] KUIPER JW, VOS SJ, SAOUTI R, et al. Prosthetic joint-associated infections treated with DAIR (debridement, antibiotics, irrigation, and retention): analysis of risk factors and local antibiotic carriers in 91 patients. Acta Orthopaedica. 2013;84(4):380-386.
[18] LAUDERDALE KJ, MALONE CL, BOLES BR, et al. Biofilm dispersal of community-associated methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus on orthopedic implant material. J Orthop Res. 2010;28:55-61.
[19] MA R, HU X, ZHANG X, et al. Strategies to prevent, curb and eliminate biofilm formation based on the characteristics of various periods in one biofilm life cycle. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2022;12:1003033.
[20] NEELIMA M, CHANDRASHEKAR BR, GOEL S, et al. “Is powered toothbrush better than manual toothbrush in removing dental plaque?” - A crossover randomized double-blind study among differently abled, India. J Indian Soc Periodontol. 2017;21(2): 138-143.
[21] CCAHUANA-VASQUEZ RA, ADAM R, CONDE E, et al. A 5-week randomized clinical evaluation of a novel electric toothbrush head with regular and tapered bristles versus a manual toothbrush for reduction of gingivitis and plaque. Int J Dent Hyg. 2019;17(2): 153-160.
[22] SCHMALZ G, KIEHL K, SCHMICKLER J, et al. Correction to: No difference between manual and different power toothbrushes with and without specific instructions in young, oral healthy adults-results of a randomized clinical trial. Clin Oral Investig. 2018;22(3):1609.
[23] GRAMMATOPOULOS G, KENDRICK B, MCNALLY M, et al.Outcome Following Debridement, Antibiotics, and Implant Retention in Hip Periprosthetic Joint Infection-An 18-Year Experience. J Arthroplasty. 2017;32(7):2248-2255.
[24] LORA-TAMAYO J, SENNEVILLE É, RIBERA A, et al. The Not-So-Good Prognosis of Streptococcal Periprosthetic Joint Infection Managed by Implant Retention: The Results of a Large Multicenter Study. Clin Infect Dis. 2017;64(12):1742-1752.
[25] TSANG SJ, TING SIMPSON AHRW, GASTON P. Outcomes following debridement, antibiotics and implant retention in the management of periprosthetic infections of the hip: a review of cohort studies. Bone Joint J. 2017;99-B(11):1458-1466.
[26] QASIM SN, SWANN A, ASHFORD R. The DAIR (debridement, antibiotics and implant retention) procedure for infected total knee replacement - a literature review. SICOT J. 2017;3:2.
[27] HIGUERA C. Another Option in the Armamentarium: Understanding the Role of Irrigation and Debridement to Treat Hip Periprosthetic Joint Infection: Commentary on an article by Andrew J. Bryan, MD, et al.: “Irrigation and Debridement with Component Retention for Acute Infection After Hip Arthroplasty. Improved Results with Contemporary Management”. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2017;99(23):e131.
[28] SOCIÉTÉ DE PATHOLOGIE INFECTIEUSE DE LANGUE FRANÇAISE (SPILF), COLLÈGE DES UNIVERSITAIRES DE MALADIES INFECTIEUSES ET TROPICALES (CMIT), GROUPE DE PATHOLOGIE INFECTIEUSE PÉDIATRIQUE (GPIP), et al. [Recommendations for clinical practice. Osteo-articular infection therapy according to materials used (prosthesis, implants, osteosynthesis)]. Med Mal Infect. 2009;39(10): 745-774.
[29] BENE N, LI X, NANDI S. Factors affecting failure of irrigation and debridement with liner exchange in total knee arthroplasty infection. Knee. 2018; 25(5): 932-938.
[30] CHAUSSADE H, UCKAY I, VUAGNAT A, et al. Antibiotic therapy duration for prosthetic joint infections treated by Debridement and Implant Retention (DAIR): Similar long-term remission for 6 weeks as compared to 12 weeks. Int J Infect Dis. 2017;63:37-42.
[31] SCHOLTEN R, KLEIN KP, GISOLF J, et al. Empiric antibiotic therapy in early periprosthetic joint infection: a retrospective cohort study. Eur J Orthop Surg Traumatol. 2023;33(1):29-35.
[32] TATARELLI P, ROMANI T, SANTORO V, et al. Debridement, antibiotics and implant retention (DAIR): An effective treatment option for early prosthetic joint infections. J Infect Chemother. 2021;27(8):1162-1168.
[33] ZJMMERLI W, WIDMER AF, BLATTER M, et al. Role of rifampin for treatment of orthopedic implant-related staphylococcal infections: a randomized controlled trial. Foreign-Body Infection (FBI) Study Group. JAMA. 1998;279(19):1537-1541.
[34] RODRiGUEZPARDO D, PlGRAU C, LORAl_AMAYO J, et al. Gram-negative prosthetic joint infection: outcome of a debridement, antibiotics and implant retention approach. A large multicentre study. Clin Microbiol Infect. 2014;20(11):O911-919.
[35] ABOLTINSC, DOWSEY MM, PEEL T, et al. Early prosthetic hip joint infection treated with debridement, prosthesis retention and biofilm-active antibiotics: functional outcomes, quality of life and complications. Intern Med J. 2013;43(7):810-815.
[36] SENDI P, ZJMMERLI W. Antimicrobial treatment concepts for orthopaedic device-related infection. Clin Microbiol Infect. 2012;18(12): 1176-1184.
[37] KARAU MJ, SCHMIDT-MALAN SM, ALBANO M, et al. Novel Use of Rifabutin and Rifapentine to Treat Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus aureus in a Rat Model of Foreign Body Osteomyelitis. J Infect Dis. 2020;222(9):1498-1504.
[38] GOETZ J, KEYSSNER V, HANSES F, et al. Animal experimental investigation on the efficacy of antibiotic therapy with linezolid, vancomycin, cotrimoxazole, and rifampin in treatment of periprosthetic knee joint infections by MRSA. Bone Joint Res. 2022; 11(3):143-151.
[39] RESENDE VAC, NETO AC, NUNES C, et al. Higher age, female gender, osteoarthritis and blood transfusion protect against periprosthetic joint infection in total hip or knee arthroplasties: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2021;29(1):8-43.
[40] LORA-TAMAYO J, MURILLO O, IRIBARREN JA, et al. REIPI Group for the Study of Prosthetic Infection. A large multicenter study of methicillin-susceptible and methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus prosthetic joint infections managed with implant retention. Clin Infect Dis. 2013; 56(2):182-194.
[41] TRIANTAFYLLOPOULOS GK, POUL_TSIDES LA, ZHANG W, et al. Periprosthetic knee infections treated with irrigation and debridement: outcomes and preoperative predictive factors. J Arthroplasty. 2015; 30(4):649-657.
[42] ALY R, MAIBACH HE, MANDEL A. Bacterial flora in psoriasis. Br J Dermatol. 1976;95(6):603-606.
[43] DRANCOURT M, ARGENSON JN, TISSOT DUPONT H, et al. Psoriasis is a risk factor for hip-prosthesis infection. Eur J Epidemiol. 1997;13(2): 205-207.
[44] LOFIN I, LEVINE B, BADLANI N, et al. Psoriatic arthritis and arthroplasty: a review of the literature. Bull NYU Hosp Jt Dis. 2008;66(1):41-48.
[45] BEYER CA, HANSSEN AD, LEWALLEN DG, et al. Primary total knee arthroplasty in patients with psoriasis. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 1991;73(2): 258-259.
[46] KUNUTSOR SK, WHITEHOUSE MR, BLOM AW, et al. Patient-Related Risk Factors for Periprosthetic Joint Infection after Total Joint Arthroplasty: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. PLoS One. 2016;11(3):e0150866. |