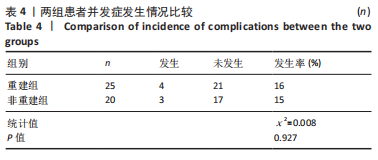
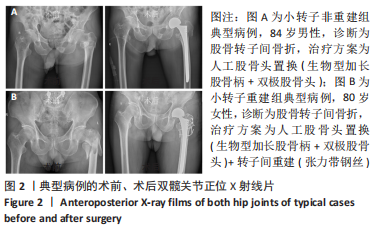
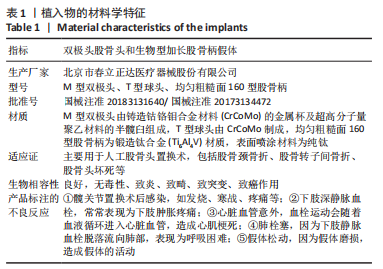
[1] ALEXIOU KI, ROUSHIAS A, VARITIMIDIS SE, et al. Quality of life and psychological consequences in elderly patients after a hip fracture: a review. Clin Interv Aging. 2018;13:143-150.
[2] LEBLANC ES, HILLIER TA, PEDULA KL, et al. Hip fracture and increased short-term but not long-term mortality in healthy older women. Arch Intern Med. 2011;171(20):1831-1837.
[3] VALIZADEH M, MAZLOOMZADEH S, GOLMOHAMMADI S, et al. Mortality after low trauma hip fracture: a prospective cohort study. BMC Musculoskeletal Disorders. 2012;12:143.
[4] 宁瑞, 张卫, 肖蕊. 影响高龄股骨转子间骨折人工股骨头置换术后功能恢复的危险因素[J]. 临床骨科杂志,2015,18(2):32-34.
[5] HAENTJENS P, LAMRASKI G. Endoprosthetic replacement of unstable, comminuted intertrochanteric fracture of the femur in the elderly, osteoporotic patient: a review. Disabil Rehabil. 2005;27(18-19):1167-1180.
[6] 张前法, 庞清江, 黄涛, 等. 双极长柄人工股骨头置换治疗高龄粉碎性股骨转子间骨折的临床应用[J]. 中国修复重建外科杂志,2005,19(3): 198-200.
[7] 王兆杰, 安荣泽, 齐新文, 等. 小转子复位固定在股骨转子间骨折治疗中的临床意义[J]. 中国矫形外科杂志,2009,17(4):312-313.
[8] 刘明轩, 曹成福, 张启宽, 等. 长柄人工髋关节置换治疗高龄股骨转子间骨折的实验及临床研究[J]. 骨与关节损伤杂志,2003,18(7):444-446.
[9] 黄必留, 余楠生. 人工全髋关节置换术后Harris评分[J]. 现代临床医学生物工程学杂志,2004,10(1):44-46.
[10] 孟祥启, 王明绪, 李南, 等. 股骨近端防旋髓内钉与人工股骨头置换术治疗高龄股骨转子间骨折临床效果分析[J]. 中国医药导报,2016, 13(30):83-86.
[11] TONY S, YAU HN, CHIN TL, et al. Clinical outcome following treatment of stable and unstable intertrochanteric fractures with dynamic hip screw. Ann Acad Med Singap. 2011;40:482-487.
[12] 郭晓亮, 卫小春, 王小虎. 股骨转子间骨折髓内固定物治疗的优劣评说[J]. 中国组织工程研究,2013,17(26):4904-4911.
[13] MARCOS CS, RAU´ TC, ALBERT AF, et al. Salvage for nail breakage in femoral intramedullary nailing. Injury. 2015;46(4):729-733.
[14] GAUMETOU E, ZILBER S, HERNIGOU P. Non-simultaneous bilateral hip fracture: epidemiologic study of 241 hip fractures. Orthop Traumatol Surg Res. 2011;97(1):22-27.
[15] 朱奕, 张长青. 内固定治疗骨质疏松性股骨转子间骨折生物力学特性[J]. 国际骨科学杂志,2010,31(2):79-82.
[16] SHI H, XIAO L, WANG Z. Curative effect of artificial femoral head replacement and its effect on hip joint function and complications of senile patients with femoral intertrochanteric fracture. Exp Ther Med. 2018;16(2):623-628.
[17] CHOY WS, AHN JH, KO JH, et al. Cementless bipolar hemiarthroplasty for unstable intertrochanteric fractures in elderly patients. Clin Orthop Surg. 2010;2(4):221-226.
[18] CHANG JD, KIM IS, LEE SS, et al. Unstable intertrochanteric versus displaced femoral neck fractures treated with cementless bipolar hemiarthroplasty in elderly patients; a comparison of 80 matched patients. Orthop Traumatol Surg Res. 2016;102(6):695-699.
[19] EMAMI M, MANAFI A, HASHEMI B, et al. Comparison of intertrochanteric fracture fixation with dynamic hip screw and bipolar hemiarthroplasty techniques. Arch Bone Jt Surg. 2013;1:14-17.
[20] ZHOU S, LIU J, ZHEN P, et al. Proximal femoral nail anti-rotation versus cementless bipolar hemiarthroplasty for unstable femoral intertrochanteric fracture in the elderly: a retrospective study. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2019;20(1):500.
[21] 薄舒心,王倩,陈萍. 生物型人工股骨头置换术和PFNA内固定术治疗老年Evans Ⅲ+Ⅳ型股骨转子间骨折效果对比[J]. 河北医学,2020, 26(2):259-263.
[22] 李国庆, 多力昆·来海提, 马骏. 双极人工股骨头置换术治疗老年不稳定型股骨转子间骨折的疗效观察[J]. 浙江医学,2018,40(16):1870-1872.
[23] CHO SH, CHO HL, CHO H. Primary cementless hip arthroplasty in unstable intertrochanteric femur fracture in elderlys: short-term results. Hip Pelvis. 2014;26(3):157-165.
[24] 梁雨田, 郭义柱, 唐佩福, 等. 股骨转子重建、人工股骨头置换治疗高龄患者非稳定性股骨转子间骨折[J]. 中华创伤杂志,2008,24(7):524-526.
[25] 张永涛, 王春生, 王坤正, 等. 转子间重建并关节置换术治疗老年人不稳定转子间骨折的疗效分析[J]. 西安交通大学学报(医学版), 2013, 34(2):272-274.
[26] 郭新庆, 赵为民, 周海洋, 等. 骨质疏松股骨转子间不稳定型骨折人工股骨头置换的三维有限元应力分析[J]. 中国组织工程研究,2016, 20(9):1261-1267.
[27] 安永刚, 陈浩贤, 昝中学, 等. 钢丝捆绑复位大、小转子重建股骨矩结合全髋关节置换治疗高龄股骨转子间骨折患者的临床疗效[C]. 中华中医药学会骨伤科分会学术年会暨全国中医骨伤科高峰论坛论文集,2016, 1112.
[28] 赵清斌, 王利, 哈巴西•卡肯, 等. 捆绑带重建大转子并半髋关节置换治疗高龄转子间骨折[J]. 中国组织工程研究,2018,22(15):2309-2314.
[29] 毛小成, 赵枫. 人工股骨头置换联合转子重建术治疗老年人股骨转子间骨折[J]. 临床军医杂志,2015,43(11):1184-1185.
[30] 雷林革, 于进祥, 杜东鹏, 等. 股骨转子间骨折人工股骨头置换术中股骨距的重建[J]. 临床军医杂志,2010,38(1):55-56.
|