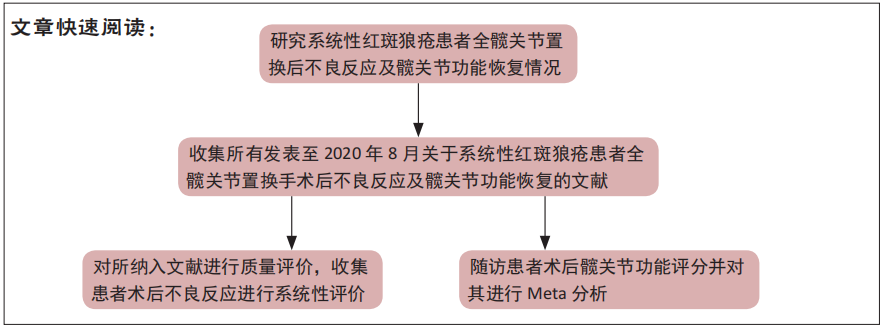
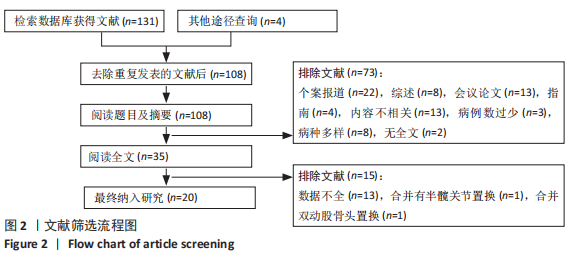
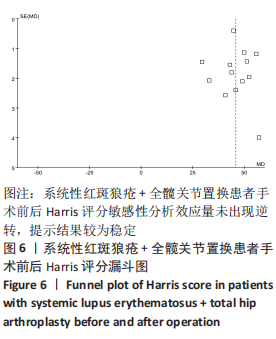
[1] ZUCCHI D, ELEFANTE E, CALABRESI E, et al. One year in review 2019: systemic lupus erythematosus. Clin Exp Rheumatol. 2019;37(5):715-722.
[2] KENNEDY JW, KHAN W. Total hip arthroplasty in systemic lupus erythematosus:a systematic review. Int J Rheumatol. 2015;2015:475-489.
[3] LI Z, DU Y, XIANG S, et al. Risk factors of perioperative complications and transfusion following total hip arthroplasty in systemic lupus erythematosus patients. Lupus. 2019;28(9):1134-1140.
[4] MERTELSMANN-VOSS C, LYMAN S, PAN TJ, et al. Arthroplasty rates are increased among US patients with systemic lupus erythematosus: 1991-2005. J Rheumatol. 2014;41(5):867-874.
[5] AZIZ KT, BEST MJ, SKOLASKY RL, et al. Lupus and perioperative complications in elective primary total hip or knee arthroplasty. Clin Orthop Surg. 2020;12(1):37-42.
[6] 郑晗晗,江学良.粪便菌群移植治疗艰难梭菌感染有效性和安全性的Meta分析[J].中国全科医学,2016,19(2):199-205.
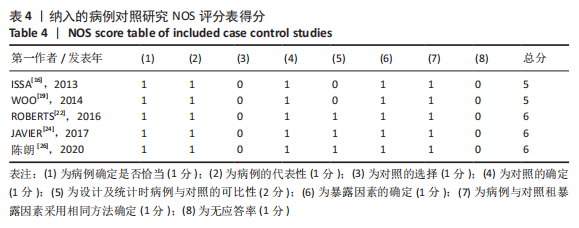
[7] STANG A. Critical evaluation of the Newcastle-Ottawa scale for the assessment of the quality of nonrandomized studies in meta-analyses. Eur J Epidemiol. 2010;25(9):603-605.
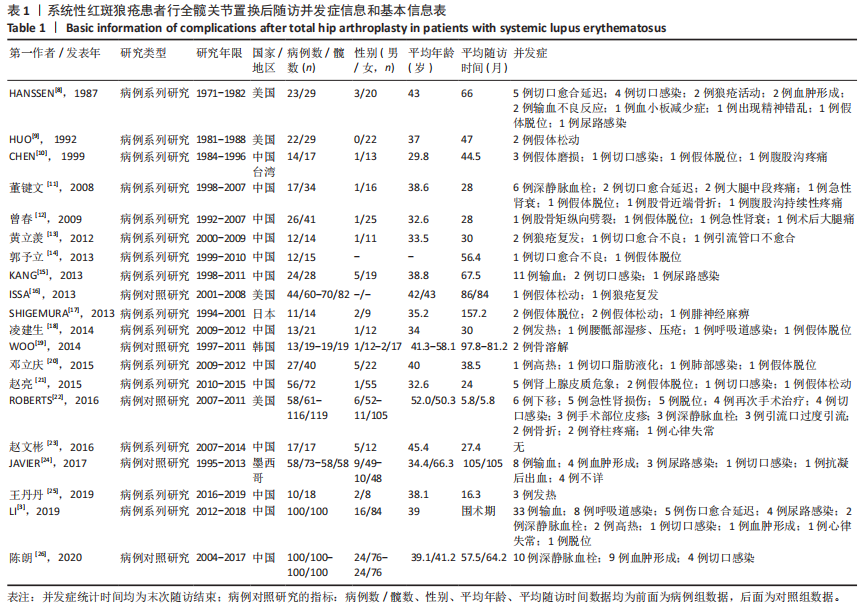
[8] HANSSEN AD, CABANELA ME, MICHET CJ JR. Hip arthroplasty in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1987;69(6): 807-814.
[9] HUO MH, SALVATI EA, BROWNE MG, et al. Primary total hip arthroplasty in systemic lupus erythematosus. J Arthroplasty. 1992;7(1):51-56.
[10] CHEN YW, CHANG JK, HUANG KY, et al. Hip arthroplasty for osteonecrosis in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. Kaohsiung J Med Sci. 1999;15(12):697-670.
[11] 董健文,黄冬梅,戎利民,等.Ⅰ期双侧全髋关节置换治疗系统性红斑狼疮合并股骨头坏死的早中期疗效[J].中华损伤与修复杂志,2008, 6(3):705-711.
[12] 曾春,宋炎成,蔡道章,等.系统性红斑狼疮合并股骨头坏死行全髋关节置换术的特点及其并发症的防治[J].中华关节外科杂志,2009,4(3): 454-458.
[13] 黄立羡,练克俭,郭林新,等.系统性红斑狼疮激素治疗后股骨头坏死行人工全髋关节置换术围术期处理[J].临床骨科杂志,2012,6(15):607-609.
[14] 郭予立,胡奕山,林本丹.合并系统性红斑狼疮的股骨头坏死患者行全髋关节置换术的疗效评估[J].广东医学,2013,19(34):2984-2986.
[15] KANG Y, ZHANG ZJ, ZHAO XY, et al. Total hip arthroplasty for vascular necrosis of the femoral head in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus: a midterm follow-up study of 28 hips in 24 patients. Eur J Orthop Surg Traumatol. 2013;23(1):73-79.
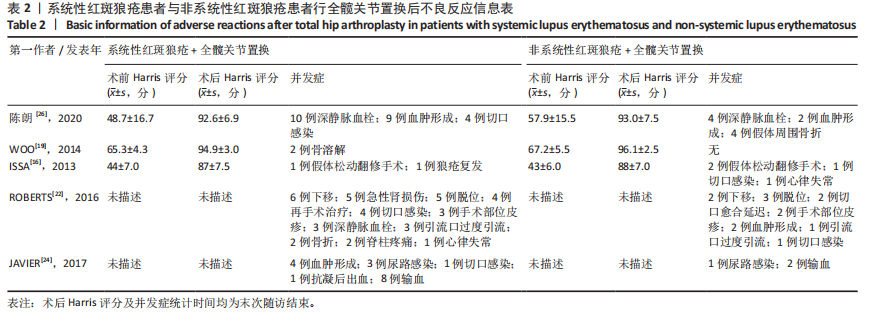
[16] ISSA K, NAZIRI Q, RASQUINHA VJ, et al. Outcomes of primary total hip arthroplasty in systemic lupus erythematosus with a proximally-coated cementless stem. J Arthroplasty. 2013;28(9):1663-1666.
[17] SHIGEMURA T, KISHIDA S, IIDA S. Cementless total hip arthroplasty for osteonecrosis of the femoral head in systemic lupus erythematosus: a study with 10–16 years of follow-up. European Orthopaedics and Traumatology. 2013;1(4):15-20.
[18] 凌建生.人工全髋关节置换治疗系统性红斑狼疮合并股骨头坏死围术期处理及临床疗效分析[D].长春:吉林大学,2014.
[19] WOO MS, KANG JS, MOON KH. Outcome of total hip arthroplasty for avascular necrosis of the femoral head in systemic lupus erythematosus. J Arthroplasty. 2014;29(12):2267-2270.
[20] 邓立庆,康鹏德,裴福兴,等.系统性红斑狼疮合并股骨头坏死行全髋关节置换术围术期处理[J].华西医学,2015,5(30):865-868.
[21] 赵亮,史哲,吴宣平,等.系统性红斑狼疮合并股骨头坏死全髋关节置换术的围术期治疗[J].中华关节外科杂志,2015,9(4):463-467.
[22] ROBERTS JE, MANDL LA, SU EP, et al. Patients with systemic lupus erythematosus have increased risk of short-term adverse events after total hip arthroplasty. J Rheumatol. 2016;43(8):1498-1502.
[23] 赵文彬.合并骨质疏松的系统性红斑狼疮患者行全髋关节置换术的疗效评估[J].中国伤残医学,2016,19(24):28-30.
[24] MERAYO-CHALICO J, GÓNZALEZ-CONTRERAS M, ORTÍZ-HERNÁNDEZ R, et al. Total hip arthroplasty outcomes: an 18-year experience in a single center: is systemic lupus erythematosus a potential risk factor for adverse outcomes? J Arthroplasty. 2017;32(11):3462-3467.
[25] 王丹丹.黄芪寄生汤配合全髋关节置换术治疗系统性红斑狼疮合并股骨头坏死的临床疗效分析[D].济南:山东中医药大学,2019.
[26] 陈朗,冯辉雄,李宏超,等.系统性红斑狼疮患者行全髋关节置换术治疗股骨头坏死的疗效研究[J].中华骨与关节外科杂志,2020,2(13):143-147.
[27] 朱东明,张振,张杰,等.全髋关节置换后假体脱位危险因素的最新进展[J].中国组织工程研究,2020,36(24):5864-5870.
[28] ITO H, MATSUNO T, HIRAYAMA T, et al. Health-related quality of life in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus after medium to long-term follow-up of hip arthroplasty. Lupus. 2007;16(5): 318-323.
[29] ANDRIOLO L, MERLI G, Tobar C, et al. Regenerative therapies increase survivorship of avascular necrosis of the femoral head: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Int Orthop. 2018;42(7):1689-1704.
[30] 黄鑫,孔渝菡,余和平.激素相关性股骨头坏死非手术治疗研究进展[J].现代医药卫生,2020, 8(36):1179-1182.
|