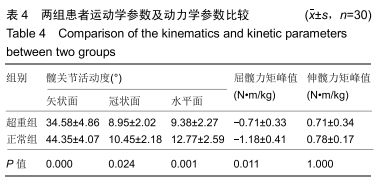
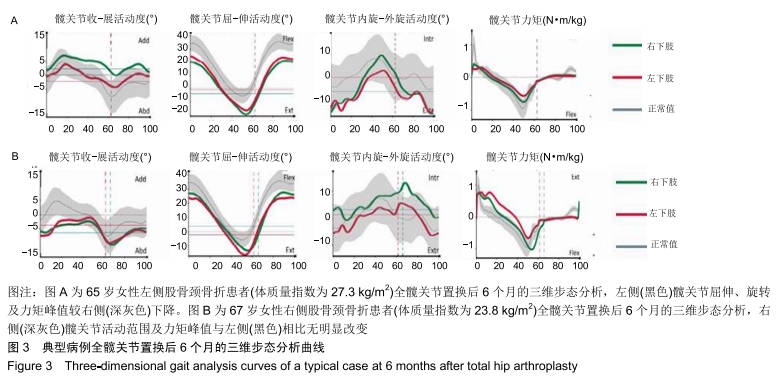
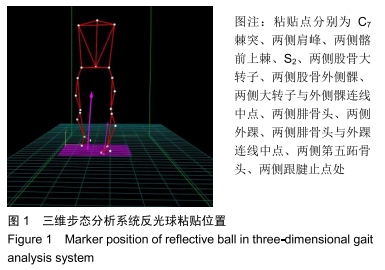
[1] 万修阳,刘永辉,邓念,等.全髋置换术治疗强直髋合并髋臼内陷的临床疗效观察[J].中华关节外科杂志(电子版), 2018,12(5): 614-619.
[2] PELLE AJ, KUPPER N, MOLS F, et al. What is the use? Application of the short form (SF) questionnaires for the evaluation of treatment effects. Qual Life Res. 2013;22(6): 1225-1230.
[3] MEIRA EP, ZENI J. Sports participation following total hip arthroplasty. Int J Sports Phys Ther. 2014;9(6): 839-850.
[4] SCULLY W, PIUZZI NS, SODHI N, et al. The effect of body mass index on 30-day complications after total hip arthroplasty. Hip Int. 2019:1120700019826482.
[5] 杜尧,李悦,刘书茂,等.体质量指数对全膝关节置换术后远期翻修率影响的研究[J].中华保健医学杂志,2017,19(6): 505-508.
[6] 徐闯,刘明廷,尚义美,等.肥胖对初次人工全髋关节置换术临床疗效影响的Meta分析[J].中国矫形外科杂志, 2017,25(13): 1203-1209.
[7] 曹恒,刘明廷,石辉,等. 肥胖对全髋关节置换术后的早期疗效影响分析[J]. 滨州医学院学报, 2017,40(4): 267-270.
[8] BONGERS J, SMULDERS K, NIJHOF MW. Severe obesity increases risk of infection after revision total hip arthroplasty. J Arthroplasty. 2019;34(12):3023-3029.e2.
[9] FOREMAN CW, CALLAGHAN JJ, BROWN TS, et al. Total joint arthroplasty in the morbidly obese: how body mass index≥ 40 influences patient retention, treatment decisions, and treatment outcomes. J Arthroplasty. 2020;35(1):39-44.
[10] DAVIS RB, OUNPUU S, TYBURSKI D, et al. A gait analysis data collection and reduction technique. Human Mov Sci. 1991;10:575-587.
[11] 徐宁,张玉岩,赵怡,等.老年股骨颈骨折患者行全髋关节置换术后体重的变化[J].中华关节外科杂志(电子版), 2018,12(6): 753-756.
[12] PIRRUCCIO K, SLOAN M, SHETH NP. Trends in obesity prevalence among total hip arthroplasty patients and the effect on surgical outcomes, 2008-2016. J Orthop. 2019; 16(4):347-352.
[13] 郭仰丹,林涌生,陈松亮,等.肥胖患者全髋关节置换术的加速康复策略探讨[J].中华关节外科杂志(电子版),2017,11(4): 352-358.
[14] SERSHON RA, DIAZ A, BOHL DD, et al. Effect of body mass index on digital templating for total hip arthroplasty. J Arthroplasty. 2017;32(3):1024-1026.
[15] 谢齐林,杨辉,孔天天,等.肥胖患者人工全髋关节置换早期临床疗效分析[J].重庆医学,2015,44(23):3255-3257.
[16] 米尔阿里木•木尔提扎,赵巍,王利,等.患者体重指数对全髋关节置换手术时间的影响研究[J].实用骨科杂志, 2014,20(10): 938-941.
[17] ANTONIADIS A, DIMITRIOU D, FLURY A, et al. Is direct anterior approach a credible option for severely obese patients undergoing total hip arthroplasty? A matched-control, retrospective, clinical study. J Arthroplasty. 2018;33(8): 2535-2540.
[18] 赵巍,王利,袁宏. 患者体重指数对全髋关节置换手术时间的影响研究[J]. 实用骨科杂志, 2014, 20(10): 938-941.
[19] DUCHMAN KR, PUGELY AJ, MARTIN CT, et al. Operative time affects short-term complications in total joint arthroplasty. J Arthroplasty. 2017;32(4):1285-1291.
[20] BRODT S, NOWACK D, JACOB B, et al. Patient obesity influences pelvic lift during cup insertion in total hip arthroplasty through a lateral transgluteal approach in supine position. J Arthroplasty. 2017;32(9):2762-2767.
[21] 崔志刚,张德光,刘福全,等. 全髋关节置换术前的肥胖状态对术后远期翻修率的影响[J].中华保健医学杂志, 2017, 19(1): 49-51.
[22] 古丽米热•吐尼牙孜. 肥胖与静脉血栓栓塞症相关性的Meta分析[D].乌鲁木齐:新疆医科大学,2015.
[23] GURUNATHAN U, ANDERSON C, BERRY KE, et al. Body mass index and in-hospital postoperative complications following primary total hip arthroplasty. HIP Int. 2018; 28(6): 613-621.
[24] ROTH A, KHLOPAS A, GEORGE J, et al. The effect of body mass index on 30-day complications after revision total hip and knee arthroplasty. J Arthroplasty. 2019; 34(7): S242-S248.
[25] ADHIKARY SD, LIU WM, MEMTSOUDIS SG, et al. Body mass index more than 45 kg/m2 as a cutoff point is associated with dramatically increased postoperative complications in total knee arthroplasty and total hip arthroplasty. J Arthroplasty. 2016; 31(4): 749-753.
[26] PONNUSAMY KE, MARSH JD, SOMERVILLE LE, et al. Ninety-day costs, reoperations, and readmissions for primary total knee arthroplasty patients with varying body mass index levels. Arthroplasty. 2018;33(7): S157-S161.
[27] 王鹏斌,王立松,祝建勇,等.老年髋关节置换术发生感染独立危险因素分析及预防措施[J].陕西医学杂志, 2018,47(10):1309-1312.
[28] 王方兴,薛华明,马童,等.单髁关节置换术治疗中重度肥胖膝前内侧骨关节炎患者的近期疗效分析[J].中国骨与关节杂志, 2019, 8(4):249-254.
[29] 甘玉云,李伦兰,汪璐璐,等.身体质量指数对全膝关节置换患者膝关节功能的影响[J].中华关节外科杂志(电子版), 2019,13(5): 575-583.
[30] YEUNG E, JACKSON M, SEXTON S, et al. The effect of obesity on the outcome of hip and knee arthroplasty. Int Orthop. 2011;35(6): 929-934.
[31] FOUCHER KC, FREELS S. Preoperative factors associated with postoperative gait kinematics and kinetics after total hip arthroplasty. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2015; 23(10): 1685-1694.
|