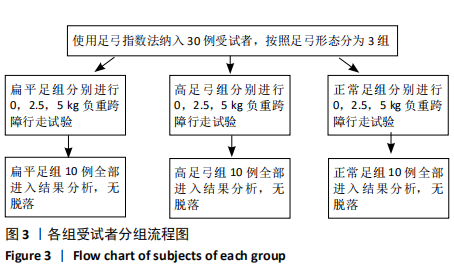
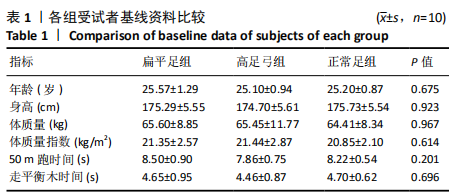
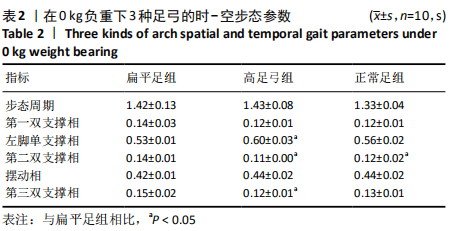
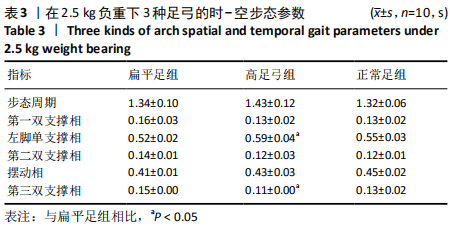
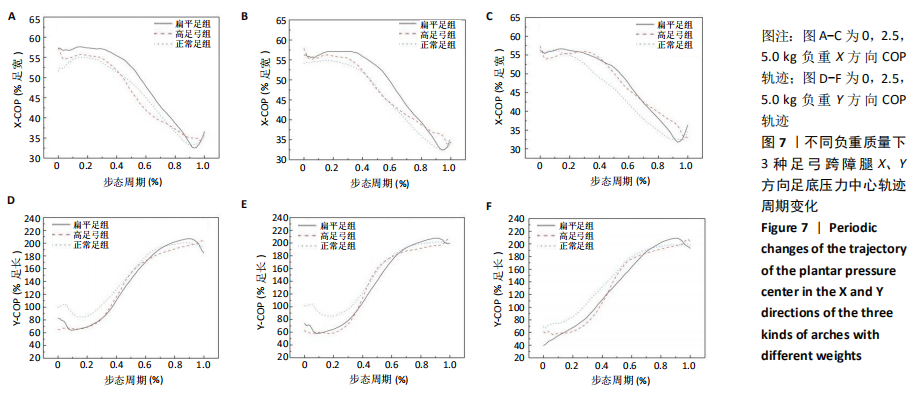
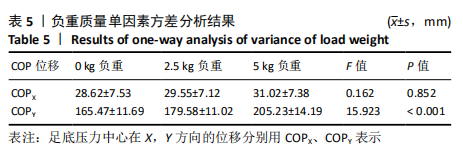
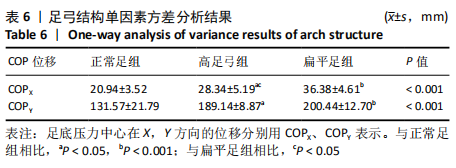
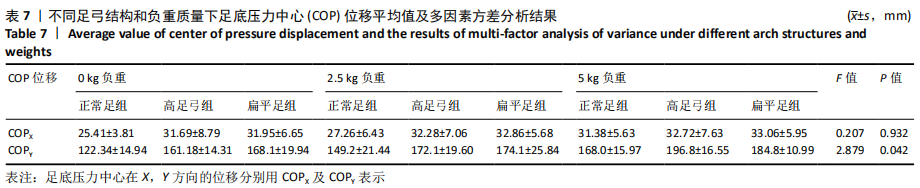
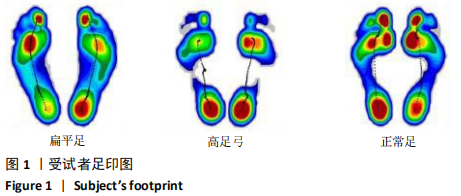
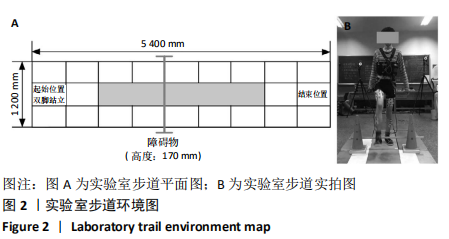
[1] 雷露,朱明海. 足部畸形的特点与类型[J]. 中国中医药现代远程教育,2016,14(3):148-151.
[2] 王新亭, 王鸥, 吴永红. 扁平足楼梯行走的下肢表面肌电特性[J]. 中国康复理论与实践,2020,26(8):941-946.
[3] 毛晓锟. 高弓足不同高度单腿下落着地的生物力学特征[D]. 苏州: 苏州大学,2016.
[4] WIERSON M, LONG PJ, FOREHAND RL. Toward a new understanding of early menarche: the role of environmental stress in pubertal timing. Adolescence. 1993;28(112):913-924.
[5] 高虹,孔德刚. 高弓足与正常足男性大学生足底压力及步态特征研究[J]. 中国学校卫生,2013,34(10):1207-1209+1213.
[6] YAN S, LI R, SHI B, et al. Mixed factors affecting plantar pressures and center of pressure in obese children: Obesity and flatfoot. Gait Posture. 2020;16(80):7-13.
[7] 马沐佳. 不同矫形鞋垫对高足弓者跑步时下肢生物力学特征的影响[D].北京:北京体育大学,2019.
[8] 赵晓光. 不同足弓高度对踝关节肌力和运动能力的影响[J].体育科学,2018,38(4):61-66.
[9] WILLIAMS DS 3RD, MCCLAY IS, HAMILL J. Arch structure and injury patterns in runners. Clin Biomech (Bristol, Avon). 2001;16(4):341-347.
[10] 汤运启,张移帆,王志康,等.性别与足弓类型对慢跑时足底压力中心轨迹的影响[J].陕西科技大学学报,2019,37(6):40-45.
[11] 李洋,张峻霞,司莹.基于足底压力和步态参数分析的水平行走遇滑失稳的自适应平衡反应研究[J].生物医学工程学杂志,2015, 32(6):1217-1222.
[12] CHOI YH, KIM JD, LEE JH, et al. Walking and balance ability gain from two types of gait intervention in adult patients with chronic hemiplegic stroke: A pilot study. Assist Technol. 2019;31(2):112-115.
[13] 耿海燕. 单、双肩书包负重行走儿童的足底压力测量[J]. 中国组织工程研究与临床康复,2011,15(33):6267-6270.
[14] 赵美雅, 倪义坤, 田山, 等. 行走过程中不同背包负重方式对人体生理参数的影响[J].医用生物力学,2015,30(1):8-13.
[15] 廖苏. 矫形鞋垫对扁平足和内翻膝步态矫正效果的研究[D]. 北京: 北京体育大学,2013.
[16] 李波, 赵佳华, 仲映旭. 足弓结构对足部运动特性的影响[J]. 中国皮革,2016,45(7):52-55+60.
[17] 杨凤娇, 王芗斌, 侯美金,等. 三维步态分析比较青年人与老年人双任务下步态特征的差异[J]. 中国组织工程研究,2021,25(3):344-349.
[18] DEMURA T, DEMURA S, UCHIYAMA M, et al. Examination of factors affecting gait properties in healthy older adults: focusing on knee extension strength, visual acuity, and knee joint pain. J Geriatr Phys Ther. 2014;37(2):52-57.
[19] 孔祥伦. 膝内翻者步态的生物力学特征[D]. 苏州: 苏州大学,2015.
[20] CHAM MB, MOHSENI-BANDPEI MA, BAHRAMIZADEH M, et al. The effects of vibro-medical insole on sensation and plantar pressure distribution in diabetic patients with mild-to-moderate peripheral neuropathy. Clin Biomech (Bristol, Avon). 2018;59:34-39.
[21] TANAKA R, ISHII Y, YAMASAKI T, et al. Measurement of the total body center of gravity during sit-to-stand motion using a markerless motion capture system. Med Eng Phys. 2019;66:91-95.
[22] KIM D, GILL SV. Changes in center of pressure velocities during obstacle crossing one year after bariatric surgery. Gait Posture. 2020;76:377-381.
[23] 郑陈帆,刘艳成,闫松华,等.坐骨神经痛患者的步态特征[J].医用生物力学,2016,31(1):73-77.
[24] HSU J, LI Y, DUTTA T, et al. Assessing the performance of winter footwear using a new maximum achievable incline method. Appl Ergon. 2015;50:218-225.
[25] 苏延虎. 脑出血偏瘫患者步态时空参数对其平衡功能的影响[J].中国实用神经疾病杂志,2015,18(5):71-72.
[26] 毋江波,王静,金宗学.足底压力中心轨迹预警人体膝关节慢性损伤研究进展[J].体育研究与教育,2019,34(5):92-96.
[27] 张腾宇, 张静莎, 季润, 等. 不同负重方式对老年人行走影响的比较分析[J]. 中国运动医学杂志,2018,37(12):1005-1010.
[28] LUXIMON Y, CONG Y, LUXIMON A, et al. Effects of heel base size, walking speed, and slope angle on center of pressure trajectory and plantar pressure when wearing high-heeled shoes. Hum Mov Sci. 2015;41: 307-319.
[29] WIKSTROM EA, HASS CJ. Gait termination strategies differ between those with and without ankle instability. Clin Biomech (Bristol, Avon). 2012;27(6):619-624.
[30] 蒋杰. 人体负重行走时终止步态的生物力学研究[D].天津:天津科技大学,2015. |