中国组织工程研究 ›› 2020, Vol. 24 ›› Issue (18): 2811-2816.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2666
• 骨与关节生物力学Bone and joint biomechanics • 上一篇 下一篇
微创治疗拇外翻术后绷带外固定:有限元分析截骨端稳定性
白子兴1,曹旭含1,孙承颐2,陈 思1,胡海威1,温建民1,李晏乐1,林新晓1,孙卫东1
- 1中国中医科学院望京医院骨关节二科,北京市 100102;2北京中医药大学,北京市 100029
Minimally invasive treatment of hallux valgus with bandage for external fixation: finite element analysis of stability of the osteotomy end
Bai
Zixing1, Cao Xuhan1, Sun Chengyi2, Chen Si1,
Hu Haiwei1, Wen Jianmin1, Li Yanle1, Lin
Xinxiao1, Sun Weidong1
- 1Second Department of Orthopedics, Wangjing Hospital of China Academy of Chinese Medical Sciences, Beijing 100102, China; 2Beijing University of Chinese Medicine, Beijing 100029, China
摘要:
文题释义:
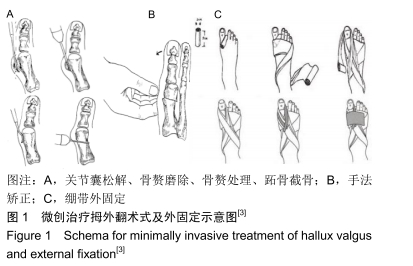
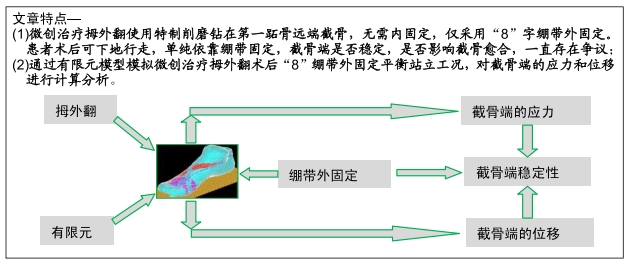
微创治疗拇外翻:根据小夹板纸压垫固定原理,采用1、2趾蹼间夹垫,“8”字绷带和宽胶布作外固定的方法,术后允许患者适当下地活动,进行拇趾关节、踝关节锻炼,避免了患者长期卧床及“石膏病”的发生。经临床应用获得了患者的肯定,总优良率为98.5%。
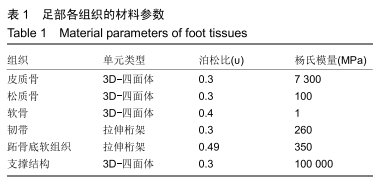
有限元分析法:有即化整为零、集零为整,通过将研究对象的连续求解区域离散为一组有限个单元,且按一定方式相互联结在一起的单元组合体,由于单元能按不同的联结方式进行组合,且单元本身又可有不同形状,因此可以模拟成不同几何形状的求解小区域,然后对单元进行力学分析,最后再整体分析。
背景:微创治疗拇外翻临床效果显著,仅通过绷带外固定维持截骨端稳定,目前缺少有关截骨端稳定性的研究。
目的:研究微创治疗拇外翻术后平衡站立工况“8”绷带外固定对截骨端应力和位移的影响。
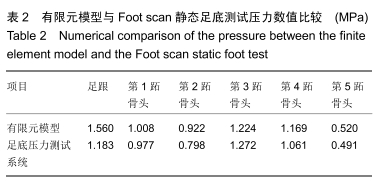
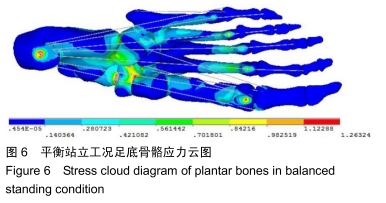
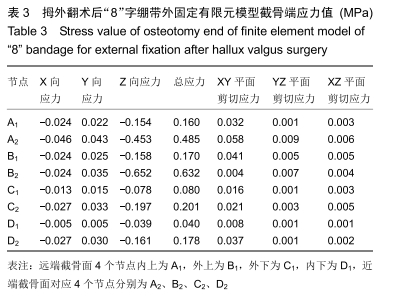
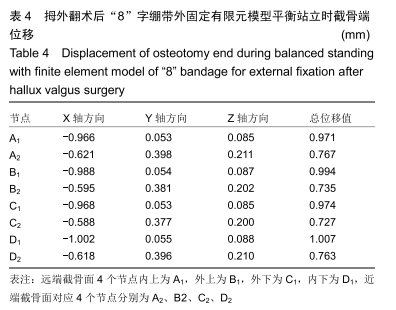
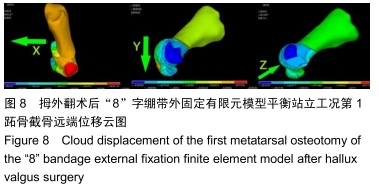
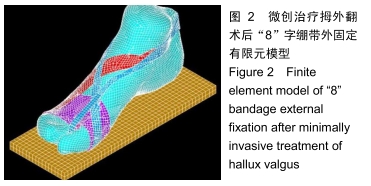
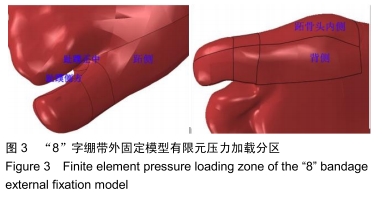
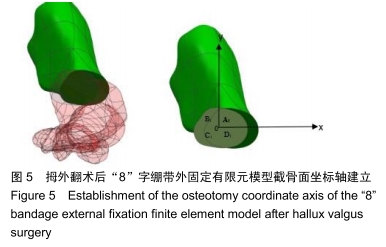
方法:在微创治疗拇外翻术后“8”字绷带外固定有限元模型上,以第一跖骨截骨面为中心,建立3条两两垂直的坐标轴(X轴、Y轴、Z轴)。X、Z轴平行于足水平面,分别指向足内侧、前方;Y轴垂直于足水平面,指向上方;定义远端截骨面4个节点内上为A1,外上为B1,外下为C1,内下为D1,近端截骨面对应4个节点为A2、B2、C2、D2。位移与坐标轴方向一致时为正值,相反时为负值。通过有限元分析得出平衡站立工况截骨面远端及近端各个节点的应力、位移的方向和大小。
结果与结论:①微创治疗拇外翻术后“8”字绷带有限元模型平衡站立工况时,截骨端最大应力在截骨面的背外侧(B2),为0.632 MPa;②截骨面第一主应力在Z轴上,方向与Z轴相反,与总应力相同,属于压应力;剪切力在XY平面最大,最大应力在近端截骨面的背内侧(A2),为0.058 MPa;③第一跖骨截骨远、近端主要位移在X轴上,位移分别在截骨面的跖内侧(D1),为-1.002 mm、跖内侧(A2),为0.621 mm;④结果说明“8”字绷带外固定能够维持微创治疗拇外翻术后截骨端的稳定,有利于截骨端愈合。
ORCID: 0000-0003-3116-7287(白子兴)
中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:人工关节;骨植入物;脊柱;骨折;内固定;数字化骨科;组织工程
中图分类号: