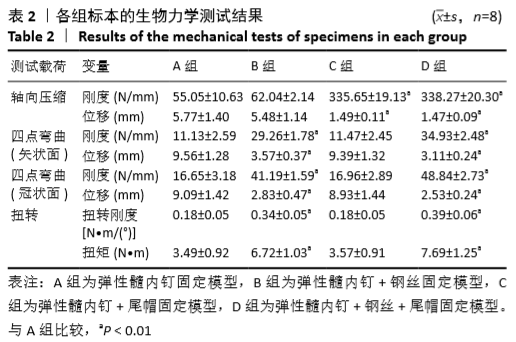
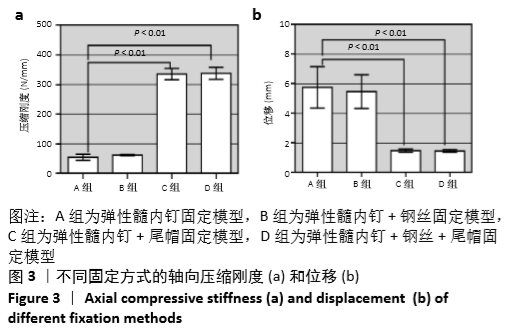
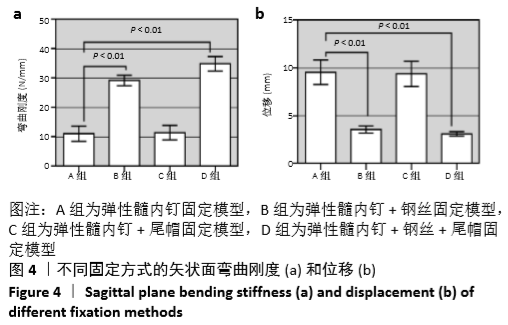
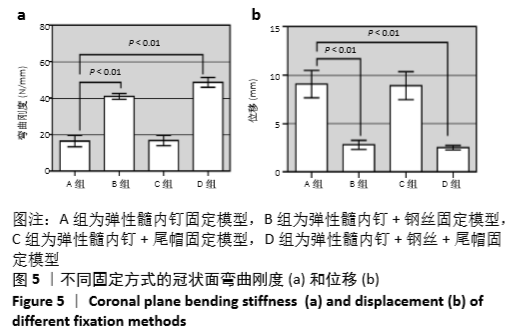
[1] SAHLIN Y. Occurrence of fractures in a defined population: a 1-year study. Injury. 1990; 21(3): 158-160.
[2] MCCARTNEY D, HINTON A, HEINRICH S. Operative stabilization of pediatric femur fractures. Orthop. Clin. North Am. 1994; 25(4): 635-650.
[3] HINTON R, LINCOLN A, CROCKETT M, et al. Fractures of the femoral shaft in children. Incidence, mechanisms, and sociodemographic risk factors. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1999;81(4): 500-509.
[4] SINK EL, GRALLA J, REPINE M. Complications of pediatric femur fractures treated with titanium elastic nails: a comparison of fracture types. J Pediatr Orthop. 2005; 25(5): 577-580.
[5] SALEM KH, KEPPLER P. Limb geometry after elastic stable nailing for pediatric femoral fractures. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2010; 92(6): 1409-1417.
[6] FLINCK M, VON HEIDEKEN J, JANARV PM, et al. Biomechanical comparison of semi-rigid pediatric locking nail versus titanium elastic nails in a femur fracture model. J Child Orthop. 2015; 9(1): 77-84.
[7] VOLPON JB, PERINA MM, OKUBO R, et al. Biomechanical performance of flexible intramedullary nails with end caps tested in distal segmental defects of pediatric femur models. J Pediatr Orthop. 2012;32(5): 461-466.
[8] BERGER L, FISCHERAUER S, WEISS B, et al. Unlocked and locked elastic stable intramedullary nailing in an ovine tibia fracture model: a biomechanical study. Mater Sci Eng C Mater Biol Appl. 2014;40: 267-274.
[9] CHEN YN, LEE PY, CHANG CW, et al. Biomechanical investigation of titanium elastic nail prebending for treating diaphyseal long bone fractures. Australas Phys Eng Sci Med. 2017; 40(1): 115-126.
[10] 韦盛旺, 石展英, 胡居正, 等. 外固定支架结合有限内固定治疗儿童股骨远端骨折[J]. 中国骨伤, 2016,29(3):275-278.
[11] MARSH JL, SMITH ST, DO TT. External fixation and limited internal fixation for complex fractures of the tibial plateau. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1995; 77(5): 661-673.
[12] LEE SS, MAHAR AT, NEWTON PO. Ender nail fixation of pediatric femur fractures: a biomechanical analysis. J Pediatr Orthop. 2001; 21(4): 442-445.
[13] GWYN DT, OLNEY BW, DART BR, et al. Rotational control of various pediatric femur fractures stabilized with titanium elastic intramedullary nails. J Pediatr Orthop. 2004;24(2):172-177.
[14] GREEN JK, WERNER FW, DHAWAN R, et al. A biomechanical study on flexible intramedullary nails used to treat pediatric femoral fractures. J Orthop Res. 2005; 23(6):1315-1320.
[15] MANI US, SABATINO CT, SABHARWAL S, et al. Biomechanical comparison of flexible stainless steel and titanium nails with external fixation using a femur fracture model. J Pediatr Orthop. 2006; 26(2): 182-187.
[16] KAISER MM, WESSEL LM, ZACHERT G, et al. Biomechanical analysis of a synthetic femur spiral fracture model: Influence of different materials on the stiffness in flexible intramedullary nailing. Clin Biomech. 2011; 26(6): 592-597.
[17] DOSER A, HELWIG P, KONSTANTINIDIS L, et al. Does the extent of prebending affect the stability of femoral shaft fractures stabilized by titanium elastic nails? A biomechanical investigation on an adolescent femur model. J Pediatr Orthop. 2011;31(8): 834-838.
[18] ALLEN JD, MURR K, ALBITAR F, et al. Titanium elastic nailing has superior value to plate fixation of midshaft femur fractures in children 5 to 11 years. J Pediatr Orthop. 2018; 38(3): e111-e117.
[19] KHAN JA, SINGH G, PANDEY A. Outcome of titanium elastic intramedullary nail in the treatment of shaft of femur fracture in children. Kathmandu Univ Med J. 2015;13(51):195-199.
[20] HO CA, SKAGGS DL, TANG CW, et al. Use of flexible intramedullary nails in pediatric femur fractures. J Pediatric Orthop. 2006;26(4): 497-504.
[21] WALL EJ, JAIN V, VORA V, et al. Complications of titanium and stainless steel elastic nail fixation of pediatric femoral fractures. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2008; 90(6):1305-1313.
[22] RAPP M, GROS N, ZACHERT G, et al. Improving stability of elastic stable intramedullary nailing in a transverse midshaft femur fracture model: biomechanical analysis of using end caps or a third nail. J Orthop Surg Res. 2015;10:96.
[23] LI Y, STABILE KJ, SHILT JS. Biomechanical analysis of titanium elastic nail fixation in a pediatric femur fracture model. J Pediatric Orthop. 2008; 28(8):874-878.
[24] LUHMANN S J, SCHOOTMAN M, SCHOENECKER PL, et al. Complications of titanium elastic nails for pediatric femoral shaft fractures. J Pediatr Orthop. 2003;23(4): 443-447.
[25] KAISER MM, ZACHERT G, WENDLANDT R, et al. Biomechanical analysis of a synthetic femoral spiral fracture model: Do end caps improve retrograde flexible intramedullary nail fixation? J Orthop Surg Res. 2011;6:46.
[26] FISHKIN Z, HAN SM, ZIV I. Cerclage wiring technique after proximal femoral fracture in total hip arthroplasty. J Arthroplasty. 1999;14(1): 98-101. |