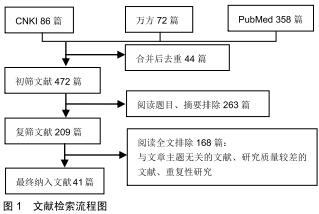
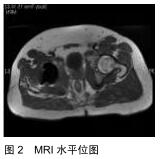
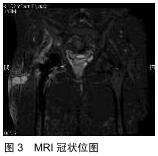
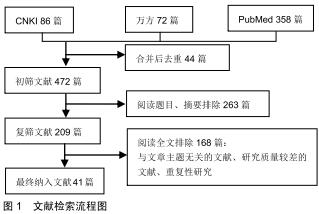
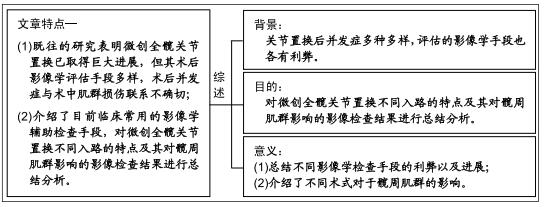
|
[1] WANG T, SHAO L, XU W, et al. Surgical injury and repair of hip external rotators in THA via posterior approach: a three-dimensional MRI-evident quantitative prospective study. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2019; 20(1):22.
[2] WANG T, SHAO L, XU W, et al. Comparison of morphological changes of gluteus medius and abductor strength for total hip arthroplasty via posterior and modified direct lateral approaches. Int Orthop. 2019;43(11):2467-2475.
[3] 黄行健,周一新,杨德金,等.全髋关节置换术后晚期并发症的影像学评估[J].骨科临床与研究杂志,2017,2(1):57-63.
[4] AGTEN CA, SUTTER R, DORA C, et al. MR imaging of soft tissue alterations after total hip arthroplasty: comparison of classic surgical approaches. Eur Radiol. 2017;27(3):1312-1321.
[5] VAN DEN WYNGAERT T, PAYCHA F, STROBEL K, et al. SPECT/CT in Postoperative Painful Hip Arthroplasty. Semin Nucl Med.2018;48(5):425-438.
[6] ALEXANDROV T, AHLMANN ER, MENENDEZ LR. Early clinical and radiographic results of minimally invasive anterior approach hip arthroplasty. Adv Orthop. 2014;2014: 954208.
[7] PENENBERG BL, SAMAGH SP, RAJAEE SS, et al. Digital Radiography in Total Hip Arthroplasty: Technique and Radiographic Results. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2018;100(3):226-235.
[8] DOBRINDT O, AMTHAUER H, KRUEGER A, et al. Hybrid SPECT/CT for the assessment of a painful hip after uncemented total hip arthroplasty. BMC Med Imaging. 2015;15:18.
[9] TOKUNAGA K, OKAMOTO M, WATANABE K. Implant Orientation Measurement After THA Using the EOS X-Ray Image Acquisition System. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2018;1093:335-343.
[10] YUE B, TANG T. The use of nuclear imaging for the diagnosis of periprosthetic infection after knee and hip arthroplasties. Nucl Med Commun. 2015;36(4):305-311.
[11] BREMER AK, KALBERER FC, PFIRRMANN WA, et al. Soft-tissue changes in hip abductor muscles and tendons after total hip replacement: comparison between the direct anterior and the transgluteal approaches. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 2011;93(7): 886-889.
[12] MÜLLER M, TOHTZ S, DEWEY M, et al. Muscle trauma in primary total hip arthroplasty depending on age, BMI, and surgical approach: minimally invasive anterolateral versus modified direct lateral approach. Orthopade. 2011;40(3):217-223.
[13] VASILAKIS I, SOLOMOU E, VITSAS V, et al. Correlative analysis of MRI-evident abductor hip muscle degeneration and power after minimally invasive versus conventional unilateral cementless THA. Orthopedics. 2012;35(12):e1684-1691.
[14] FRITZ J, LURIE B, MILLER TT, et al. MR imaging of hip arthroplasty implants. Radiographics. 2014;34(4):E106-132.
[15] BLUM A, MEYER JB, RAYMOND A, et al. CT of hip prosthesis: New techniques and new paradigms. Diagn Interv Imaging.2016; 97(7-8):725-733.
[16] KHAN RJK, LAM LO, BREIDAHL W, et al. Magnetic resonance imaging features of preserved vs divided and repaired piriformis during total hip arthroplasty: a randomized controlled trial. J Arthroplasty. 2012; 27(4): 551-558.
[17] 艾英风.X线、CT及MRI对髋关节置换术后并发症的诊断价值[J]. 内蒙古医学杂志,2017,49(6):714-716.
[18] 李长军.X线、CT及MRI对髋关节置换术后并发症的诊断价值研究[J]. 中外医疗,2016,35(15):166-167.
[19] 刘红. X线、CT及MRI对髋关节置换术后并发症的诊断价值[J]. 影像研究与医学应用,2017,1(8):225-226.
[20] MARATT JD, GAGNIER JJ, BUTLER PD, et al. No Difference in Dislocation Seen in Anterior Vs Posterior Approach Total Hip Arthroplasty. J Arthroplasty. 2016;31(9 Suppl):127-130.
[21] VIDT ME, SANTAGO II AC, TUOHY CJ, et al. Assessments of fatty infiltration and muscle atrophy from a single magnetic resonance image slice are not predictive of 3-Dimensional measurements. Arthroscopy.2016;32(1):128-139.
[22] BABA T, HOMMA Y, TAKAZAWA N, et al. Is urinary incontinence the hidden secret complications after total hip arthroplasty? Eur J Orthop Surg Traumatol. 2014;24(8):1455-1460.
[23] LINDGREN K, ANDERSON MB, PETERS CL, et al. The prevalence of positive findings on metal artifact reduction sequence magnetic resonance imaging in metal-on-metal total hip arthroplasty. J Arthroplasty. 2016;31(7):1519-1523.
[24] JUNGMANN PM, CHRISTOPH A, AGTEN MD, et al. Advances in MRI around metal. J Magn Reson Imaging. 2017;46(4):972-991.
[25] KOVALAK E, ÖZDEMIR H, ERMUTLU C, et al. Assessment of hip abductors by MRI after total hip arthroplasty and effect of fatty atrophy on functional outcome. Acta Orthop Traumatol Turc. 2018; 52(3):196-200.
[26] APAYDIN N, KENDIR S, LOUKAS M, et al. Surgical anatomy of the superior gluteal nerve and landmarks for its localization during minimally invasive approaches to the hip. Clin Anat. 2013;26(5): 614-620.
[27] MÜLLER M, TOHTZ S, DEWEY M, et al. Evidence of reduced muscle trauma through a minimally invasive anterolateral approach by means of MRI. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2010; 468(12): 3192-3200.
[28] PFIRRMANN CWA, NOTZLI HP, DORA C, et al. Abductor tendons and muscles assessed at MR imaging after total hip arthroplasty in asymptomatic and symptomatic patients. Radiology. 2005;235(3):969-976.
[29] URBANEK H, VAN DER SMAGT P. iEMG: Imaging electromyography. J Electromyogr Kinesiol. 2016;27:1-9.
[30] MÜLLER M, TOHTZ S, WINKLER T, et al. MRI findings of gluteus minimus muscle damage in primary total hip arthroplasty and the influence on clinical outcome. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg. 2010; 130(7):927-935.
[31] WANG Z, HOU J, WU C, et al. A systematic review and meta-analysis of direct anterior approach versus posterior approach in total hip arthroplasty. J Orthop Surg Res.2018;13(1): 229.
[32] VADALÀAP, MAZZA D, DESIDERI D, et al. Could the tendon degeneration and the fatty infiltration of the gluteus medius affect clinical outcome in total hip arthroplasty? Int Orthop. 2020;44(2): 275-282.
[33] LAFFOSSE JM, ACCADBLED F, MOLINIER F, et al. Anterolateral mini-invasive versus posterior mini-invasive approach for primary total hip replacement. Comparison of exposure and implant positioning. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg. 2008; 128(4): 363-369.
[34] 邓昶,李盛华,周明旺. SuperPATH入路微创全髋关节置换术的研究进展[J]. 中国微创外科杂志,2018,18(2):169-172.
[35] COHEN RG, KATZ JA, SKREPNIK NV. The relationship between skeletal muscle serum markers and primary THA: a pilot study. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2009;467(7): 747-1752.
[36] BERGIN PF, DOPPELT JD, KEPHART CJ, et al. Comparison of minimally invasive direct anterior versus posterior total hip arthroplasty based on inflammation and muscle damage markers. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2011; 93(15): 1392-1398.
[37] CHEN XX, WANG T, LI J, et al. Relationship between Inflammatory Response and Estimated Complication Rate after Total Hip Arthroplasty. Chin Med J (Engl). 2016;129(21): 2546-2551.
[38] LIN E, CALVANO SE, LOWRY SF. Inflammatory cytokines and cell response in surgery. Surgery. 2000;127(2):117-126.
[39] RUIZ-CABELLO J, CARRERO-GONZÁLEZ B, AVILÉS P, et al. Magnetic resonance imaging in the evaluation of inflammatory lesions in muscular and soft tissues: an experimental infection model induced by Candida albicans. Magn Reson Imaging. 1999; 17(9):1327-1334.
[40] OUYANG L, ZENG S, ZHENG G, et al. Early inflammatory response following traumatic brain injury in rabbits using USPIO- and Gd-Enhanced MRI. Biomed Res Int, 2016;2016: 8431987.
[41] AMIRABADI A, VIDARSSON L, MILLER E, et al. USPIO-related T1 and T2 mapping MRI of cartilage in a rabbit model of blood-induced arthritis: a pilot study. Haemophilia. 2015;21(1): e59-69.
|