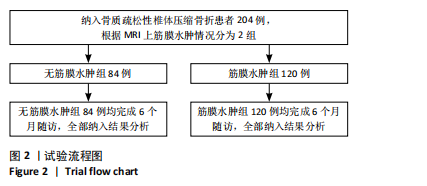
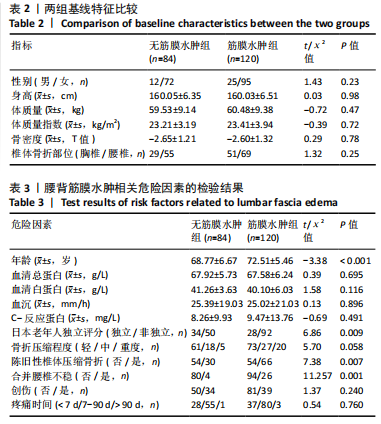
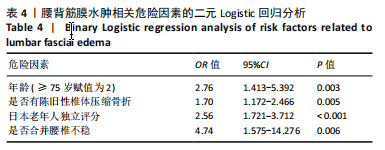
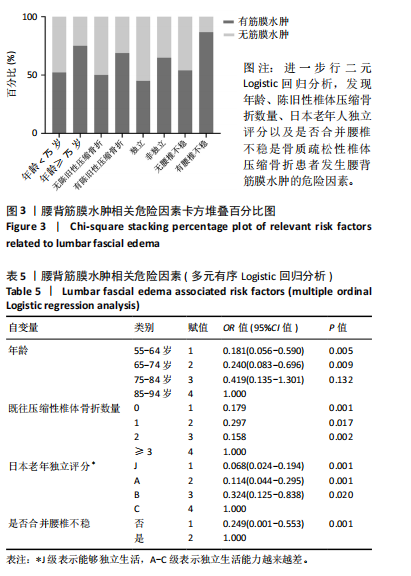
[1] LI J, XU L, LIU Y, et al. Open Surgical Treatments of Osteoporotic Vertebral Compression Fractures. Orthop Surg. 2023;15(11):2743-2748.
[2] 中国骨质疏松症流行病学调查及“健康骨骼”专项行动结果发布[J]. 中华骨质疏松和骨矿盐疾病杂志,2019,12(4):317-318.
[3] 邱晓萍, 刘铠婕, 林宇慧, 等. 骨质疏松症的流行病学、管理与防治研究进展[J]. 山东医药,2023,63(21):107-111.
[4] YU F, XIA W. The epidemiology of osteoporosis, associated fragility fractures, and management gap in China. Arch Osteoporos. 2019;14(1):32.
[5] 耿贵敏, 舒丽, 陈静, 等. 骨质疏松性椎体压缩骨折患者生存质量对心理痛楚的影响[J]. 中国骨质疏松杂志,2023,29(11):1610-1614+1631.
[6] SI L, WINZENBERG TM, JIANG Q. Projection of osteoporosis-related fractures and costs in China: 2010-2050. Osteoporos Int. 2015;26(7):1929-1937.
[7] 庞军, 戴世鹏, 王春杰, 等. MRI诊断腰背部浅筋膜炎的临床应用价值[J]. 中国临床医学影像杂志,2008(11):799-801.
[8] LAKADAMYALI H, TARHAN NC, ERGUN T, et al. STIR Sequence for Depiction of Degenerative Changes in Posterior Stabilizing Elements in Patients with Lower Back Pain. American J Roentgenol. 2008;191(4):973-979.
[9] GENU A, KOCH G, COLIN D, et al. Factors influencing the occurrence of a T2-STIR hypersignal in the lumbosacral adipose tissue. Diagn Interv Imaging. 2014; 95(3):283-288.
[10] WHITING E, MCCREADY ME. Pitting and non-pitting oedema. Med J Aust. 2016; 205(4):157-158.
[11] NOGUCHI T, YAMASHITA K, KAMEI R, et al. Current status and challenges of percutaneous vertebroplasty (PVP). Jpn J Radiol. 2023;41(1):1-13.
[12] CHANG M, ZHANG C, SHI J, et al. Comparison Between 7 Osteoporotic Vertebral Compression Fractures Treatments: Systematic Review and Network Meta-analysis. World Neurosurg. 2021;145:462-470.e1.
[13] 廖邦强, 陈方宽, 张毅, 等. 基于列线图构建骨质疏松压缩性骨折患者PVP术后发生残余痛的预测模型[J]. 医学信息,2023,36(13):19-23.
[14] LI Y, HUANG M, CHEN J, et al. The Impact of Facet Joint Violation on Clinical Outcomes After Percutaneous Kyphoplasty for Osteoporotic Vertebral Compression Fractures. World Neurosurg. 2018;119:e383-e388.
[15] EBELING PR, AKESSON K, BAUER DC, et al. The Efficacy and Safety of Vertebral Augmentation: A Second ASBMR Task Force Report. J Bone Miner Res. 2019;34(1):3-21.
[16] NAKAZAWA F. Subcutaneous edema on back detected by MRI in hospitalized patients with osteoporotic vertebral compression fracture. J Orthop. 2021;28:67-69.
[17] 蒋伟, 俞冬叶, 黄丙仓, 等. STIR序列在腰骶部浅筋膜炎中的诊断价值[J]. 磁共振成像,2016,7(2):126-130.
[18] QUATTROCCHI CC, GIONA A, DI MARTINO A, et al. Lumbar subcutaneous edema and degenerative spinal disease in patients with low back pain: a retrospective MRI study. Musculoskelet Surg. 2015;99(2):159-163.
[19] WEST W, BRADY-WEST D, WEST KP. A comparison of statistical associations between oedema in the lumbar fat on MRI, BMI and Back Fat Thickness (BFT). Heliyon. 2018;4(1):e00500.
[20] SCHWARZ-NEMEC U, FRIEDRICH KM, ARNOLDNER MA, et al. When an incidental MRI finding becomes a clinical issue. Wiener Klinische Wochenschrift. 2020; 132(1):27-34.
[21] MALBRAIN MLNG, DE KEULENAER BL, ODA J, et al. Intra-abdominal hypertension and abdominal compartment syndrome in burns, obesity, pregnancy, and general medicine. Anaesthesiol Int Ther. 2015;47(3):228-240.
[22] 王聪秀, 管保章. 肥胖相关性肾小球疾病的研究进展[J]. 中国临床新医学, 2022,15(10):995-998.
[23] 郝昆, 张丽, 刘璇, 等. 肥胖对下肢继发性淋巴水肿患者淋巴水肿抽吸术术中指标的影响[J]. 中国医药,2024,19(2):253-256.
[24] HAN GJ, LEE IS, HAN IH, et al. Posterior Lumbar Subcutaneous Edema on Spine Magnetic Resonance Images: What Is the Cause? J Korean Soc Radiol. 2013; 68(4):343-350.
[25] WEST W. Oedema in the Lumbar Subcutaneous Fat, on Routine MRI, of Patients with no History of Cardiac, Renal or Hepatic Disease, is Significantly Associated with Obesity and Age. WIMJ Open. 2015.
[26] 朱炜楷, 隋鸿锦, 付元山, 等. 胸腰筋膜解剖结构的研究进展[J]. 中国临床解剖学杂志,2016,34(3):355-358.
[27] YAN Y, XU R, ZOU T. Is thoracolumbar fascia injury the cause of residual back pain after percutaneous vertebroplasty? A prospective cohort study. Osteoporos Int. 2015;26(3):1119-1124.
[28] WANG F, TONG T, MIAO DC, et al. Clinical correlation between osteoporotic thoracolumbar vertebral compression fractures and lumbar spondylolisthesis.Int Orthop. 2022;46(5):1095-1100.
[29] 张海军, 李仲瑞, 刘经宝, 等. 经皮椎体后凸成形术后残留下腰痛的原因分析及处理[J]. 中国现代医药杂志,2019,21(4):35-37.
[30] 徐人杰, 朱国清, 蔡小强, 等. 椎体成形术后残留腰背痛与腰背筋膜损伤的相关性研究[J]. 中国骨与关节外科,2012,5(5):389-393.
[31] JI C, RONG Y, WANG J, et al. Risk Factors for Refracture following Primary Osteoporotic Vertebral Compression Fractures. Pain Physician. Pain Physician. 2021;24(3):E335-E340.
[32] JEON I, KIM SW, YU D. Paraspinal muscle fatty degeneration as a predictor of progressive vertebral collapse in osteoporotic vertebral compression fractures. Spine J. 2022;22(2):313-320.
[33] ZHANG ZL, YANG JS, HAO DJ, et al. Risk Factors for New Vertebral Fracture After Percutaneous Vertebroplasty for Osteoporotic Vertebral Compression Fractures. Clin Int Aging. 2021;16:1193-1200.
[34] TAO W, BIAO W, XINGMEI C, et al. Predictive Factors for Adjacent Vertebral Fractures After Percutaneous Kyphoplasty in Patients With Osteoporotic Vertebral Compression Fracture. Pain Physician. 2022;25(5):E725-E732.
[35] NING L, ZHU J, TIAN S, et al. Correlation Analysis Between Basic Diseases and Subsequent Vertebral Fractures After Percutaneous Kyphoplasty (PKP) for Osteoporotic Vertebral Compression Fractures. Pain Physician. 2021;24(6): E803-E810.
[36] XIAO Q, ZHAO Y, QU Z, et al. Association Between Bone Cement Augmentation and New Vertebral Fractures in Patients with Osteoporotic Vertebral Compression Fractures: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. World Neurosurg. 2021;153: 98-108.e3.
[37] 袁春, 缪伟, 唐文凯, 等. PVP治疗骨质疏松性椎体压缩骨折术后持续腰背疼痛的影响因素分析[J]. 中国骨与关节损伤杂志,2021,36(9):956-958.
[38] FAN X, LI S, ZENG X, et al. Risk factors for thoracolumbar pain following percutaneous vertebroplasty for osteoporotic vertebral compression fractures. J Int Med Res. 2021;49(1):0300060521989468.
[39] 杨俊松,陈浩,刘鹏,等. 经皮椎体成形术治疗胸腰椎骨质疏松性椎体压缩骨折疗效不佳的多因素分析[J] . 中国脊柱脊髓杂志,2020,30(1):45-52.
[40] YAN Y, XU R, ZOU T. Is thoracolumbar fascia injury the cause of residual back pain after percutaneous vertebroplasty? A prospective cohort study. Osteoporos Int. 2015;26(3):1119-1124.
[41] AL TAHA K, LAUPER N, BAUER DE, et al. Multidisciplinary and Coordinated Management of Osteoporotic Vertebral Compression Fractures: Current State of the Art. J Clin Med. 2024;13(4):930. |