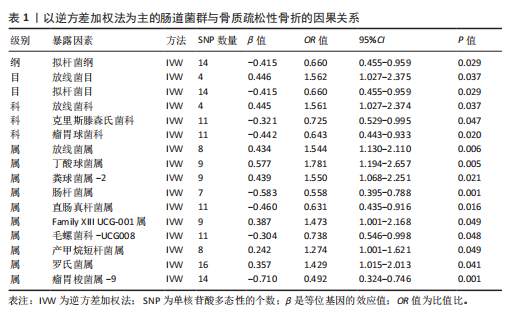
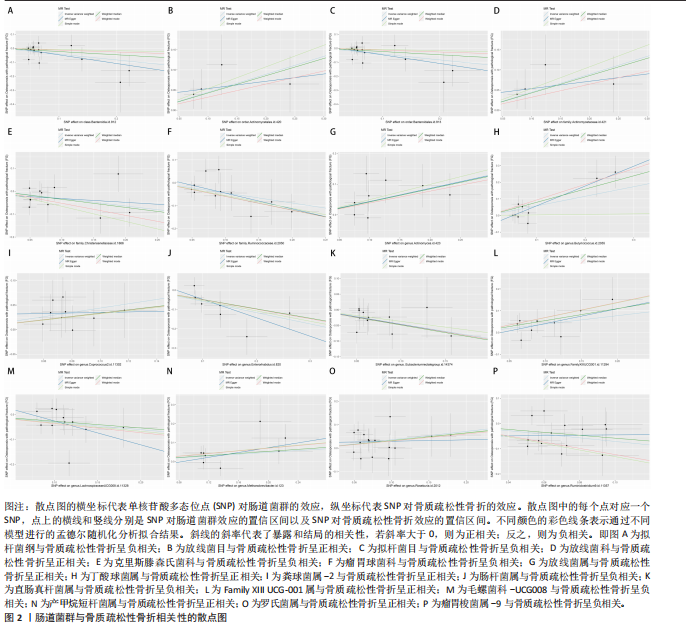
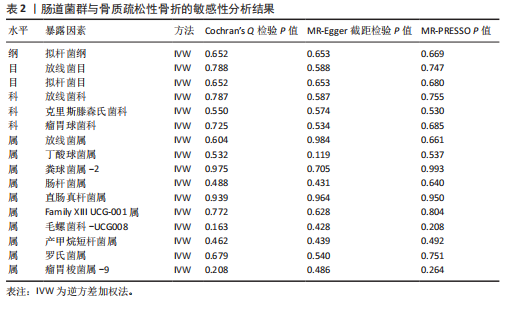
[1] GOLOB AL, LAYA MB. Osteoporosis: screening, prevention, and management. Med Clin North Am. 2015;99(3):587-606.
[2] LEMS WF, DREINHÖFER KE, BISCHOFF-FERRARI H, et al. EULAR/EFORT recommendations for management of patients older than 50 years with a fragility fracture and prevention of subsequent fractures. Ann Rheum Dis. 2017; 76(5):802-810.
[3] SI L, WINZENBERG TM, JIANG Q, et al. Projection of osteoporosis-related fractures and costs in China: 2010-2050. Osteoporos Int. 2015;26(7):1929-1937.
[4] RUBIN CD. Emerging concepts in osteoporosis and bone strength. Curr Med Res Opin. 2005; 21(7):1049-1056.
[5] FAN Y, PEDERSEN O. Gut microbiota in human metabolic health and disease. Nat Rev Microbiol. 2021;19(1):55-71.
[6] YAN J, HERZOG JW, TSANG K, et al. Gut microbiota induce IGF-1 and promote bone formation and growth. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2016;113(47):E7554-E7563.
[7] DING K, HUA F, DING W. Gut microbiome and osteoporosis. Aging Dis. 2020;11(2):438-447.
[8] ORWOLL ES, PARIMI N, WIEDRICK J, et al. Analysis of the associations between the human fecal microbiome and bone density, structure, and strength: the osteoporotic fractures in men (MrOS) Cohort. J Bone Miner Res. 2022;37(4):597-607.
[9] GUSS JD, HORSFIELD MW, FONTENELE FF, et al. Alterations to the gut microbiome impair bone strength and tissue material properties. J Bone Miner Res. 2017;32(6):1343-1353.
[10] ROSELLÓ-AÑÓN A, CHIAPPE C, VALVERDE-VÁZQUEZ MR, et al. Pilot study to determine the association between gut microbiota and fragility hip fracture. Rev Esp Cir Ortop Traumatol. 2023;67(4):279-289.
[11] OZAKI D, KUBOTA R, MAENO T, et al. Association between gut microbiota, bone metabolism, and fracture risk in postmenopausal Japanese women. Osteoporos Int. 2021;32(1):145-156.
[12] BIRNEY E. Mendelian randomization. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Med. 2022;12(4):a041302.
[13] YUAN S, MASON AM, BURGESS S, et al. Genetic liability to insomnia in relation to cardiovascular diseases: a Mendelian Randomisation study. Eur J Epidemiol. 2021;36(4):393-400.
[14] DAVIES NM, HOLMES MV, DAVEY SG. Reading Mendelian randomisation studies: a guide, glossary, and checklist for clinicians. BMJ. 2018;362:k601.
[15] DAVEY SG, HEMANI G. Mendelian randomization: genetic anchors for causal inference in epidemiological studies. Hum Mol Genet. 2014;23(R1):R89-R98.
[16] KURILSHIKOV A, MEDINA-GOMEZ C, BACIGALUPE R, et al. Large-scale association analyses identify host factors influencing human gut microbiome composition. Nat Genet. 2021;53(2):156-165.
[17] SANNA S, VAN ZUYDAM NR, MAHAJAN A, et al. Causal relationships among the gut microbiome, short-chain fatty acids and metabolic diseases. Nat Genet. 2019;51(4):600-605.
[18] LI P, WANG H, GUO L, et al. Association between gut microbiota and preeclampsia-eclampsia: a two-sample Mendelian randomization study. BMC Med. 2022;20(1):443.
[19] XIAO Z, WANG Z, ZHANG T, et al. Bidirectional Mendelian randomization analysis of the genetic association between primary lung cancer and colorectal cancer. J Transl Med. 2023;21(1):722.
[20] KAMAT MA, BLACKSHAW JA, YOUNG R, et al. PhenoScanner V2: an expanded tool for searching human genotype-phenotype associations. Bioinformatics. 2019;35(22): 4851-4853.
[21] PALMER TM, LAWLOR DA, HARBORD RM, et al. Using multiple genetic variants as instrumental variables for modifiable risk factors. Stat Methods Med Res. 2012;21(3):223-242.
[22] SLOB E, BURGESS S. A comparison of robust Mendelian randomization methods using summary data. Genet Epidemiol. 2020;44(4): 313-329.
[23] BOWDEN J, DAVEY SG, HAYCOCK PC, et al. Consistent estimation in mendelian randomization with some invalid instruments using a weighted median estimator. Genet Epidemiol. 2016;40(4):304-314.
[24] LI J, BAI H, QIAO H, et al. Causal effects of COVID-19 on cancer risk: a Mendelian randomization study. J Med Virol. 2023,95(4): e28722.
[25] GRECO MF, MINELLI C, SHEEHAN NA, et al. Detecting pleiotropy in Mendelian randomisation studies with summary data and a continuous outcome. Stat Med. 2015; 34(21):2926-2940.
[26] BOWDEN J, DAVEY SG, BURGESS S. Mendelian randomization with invalid instruments: effect estimation and bias detection through Egger regression. Int J Epidemiol. 2015;44(2):512-525.
[27] VERBANCK M, CHEN CY, NEALE B, et al. Detection of widespread horizontal pleiotropy in causal relationships inferred from Mendelian randomization between complex traits and diseases. Nat Genet. 2018;50(5):693-698.
[28] BURGESS S, BOWDEN J, FALL T, et al. Sensitivity analyses for robust causal inference from mendelian randomization analyses with multiple genetic variants. Epidemiology. 2017; 28(1):30-42.
[29] LAWLOR DA. Commentary: two-sample Mendelian randomization: opportunities and challenges. Int J Epidemiol. 2016;45(3): 908-915.
[30] SHEVROJA E, CAFARELLI FP, GUGLIELMI G, et al. DXA parameters, trabecular bone score (TBS) and bone mineral density (BMD), in fracture risk prediction in endocrine-mediated secondary osteoporosis. Endocrine. 2021;74(1):20-28.
[31] PAN B, CAI J, ZHAO P, et al. Relationship between prevalence and risk of osteoporosis or osteoporotic fracture with non-alcoholic fatty liver disease: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Osteoporos Int. 2022;33(11):2275-2286.
[32] ZHONG X, ZHANG F, YIN X, et al. Bone homeostasis and gut microbial-dependent signaling pathways. J Microbiol Biotechnol. 2021;31(6):765-774.
[33] LU L, CHEN X, LIU Y, et al. Gut microbiota and bone metabolism. FASEB J. 2021;35(7):e21740.
[34] TU Y, YANG R, XU X, et al. The microbiota-gut-bone axis and bone health. J Leukoc Biol. 2021; 110(3):525-537.
[35] WOOTTON RE, JONES HJ, SALLIS HM. Mendelian randomisation for psychiatry: how does it work, and what can it tell us? Mol Psychiatry. 2022;27(1):53-57.
[36] PAGONI P, DIMOU NL, MURPHY N, et al. Using Mendelian randomisation to assess causality in observational studies. Evid Based Ment Health. 2019;22(2):67-71.
[37] HAYCOCK PC, BURGESS S, WADE KH, et al. Best (but oft-forgotten) practices: the design, analysis, and interpretation of Mendelian randomization studies. Am J Clin Nutr. 2016; 103(4):965-978.
[38] WANG Y, ZHANG X, TANG G, et al. The causal relationship between gut microbiota and bone mineral density: a Mendelian randomization study. Front Microbiol. 2023;14:1268935.
[39] ZENG HQ, LI G, ZHOU KX, et al. Causal link between gut microbiota and osteoporosis analyzed via Mendelian randomization. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2024;28(2):542-555.
[40] 李俊杰,贾鹏,徐又佳.骨质疏松性骨折后再骨折现状及管理策略的研究进展[J].中华骨科杂志,2022,42(22):1514-1522.
[41] WANG W, WANG Q, YU L, et al. Bio-orthogonal engineered peptide: a multi-functional strategy for the gene therapy of osteoporotic bone loss. Biomaterials. 2023;302:122352.
[42] LUCAS S, OMATA Y, HOFMANN J, et al. Short-chain fatty acids regulate systemic bone mass and protect from pathological bone loss. Nat Commun. 2018;9(1):55.
[43] ZHAN Z, TANG H, ZHANG Y, et al. Potential of gut-derived short-chain fatty acids to control enteric pathogens. Front Microbiol. 2022;13: 976406.
[44] LIU Y, GUO YL, MENG S, et al. Gut microbiota-dependent Trimethylamine N-Oxide are related with hip fracture in postmenopausal women: a matched case-control study. Aging (Albany NY). 2020;12(11):10633-10641.
[45] 王志凌,郭源源,张浩,等.骨免疫微环境中炎症因子诱导骨丢失的机制及免疫治疗研究进展[J].中国骨与关节杂志,2023, 12(12):943-948.
[46] LYU Z, HU Y, GUO Y, et al. Modulation of bone remodeling by the gut microbiota: a new therapy for osteoporosis. Bone Res. 2023; 11(1):31.
[47] YAN F, CAO H, COVER TL, et al. Colon-specific delivery of a probiotic-derived soluble protein ameliorates intestinal inflammation in mice through an EGFR-dependent mechanism. J Clin Invest. 2011;121(6):2242-2253.
[48] LUTGENDORFF F, AKKERMANS LM, SÖDERHOLM JD. The role of microbiota and probiotics in stress-induced gastro-intestinal damage. Curr Mol Med. 2008;8(4):282-298.
[49] PUJO J, DE PALMA G, LU J, et al. Gut microbiota modulates visceral sensitivity through calcitonin gene-related peptide (CGRP) production. Gut Microbes. 2023;15(1): 2188874.
[50] LIN X, XIAO HM, LIU HM, et al. Gut microbiota impacts bone via Bacteroides vulgatus-valeric acid-related pathways. Nat Commun. 2023; 14(1):6853.
[51] LI S, HAN X, LIU N, et al. Lactobacillus plantarum attenuates glucocorticoid-induced osteoporosis by altering the composition of rat gut microbiota and serum metabolic profile. Front Immunol. 2023;14:1285442.
[52] WANG Z, LIANG Y, YU J, et al. Guchang Zhixie Wan protects mice against dextran sulfate sodium-induced colitis through modulating the gut microbiota in colon. J Ethnopharmacol. 2020;260:112991.
[53] LOW A, LEE J, GOUNOT JS, et al. Mutual exclusion of methanobrevibacter species in the human gut microbiota facilitates directed cultivation of a candidatus methanobrevibacter intestini representative. Microbiol Spectr. 2022;10(4):e84922.
[54] COLLINS KH, PAUL HA, REIMER RA, et al. Relationship between inflammation, the gut microbiota, and metabolic osteoarthritis development: studies in a rat model. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2015;23(11):1989-1998.
[55] LI Y, LIU C, LUO J, et al. Ershiwuwei Lvxue Pill alleviates rheumatoid arthritis by different pathways and produces changes in the gut microbiota. Phytomedicine. 2022;107:154462.
[56] XIE W, HAN Y, LI F, et al. Neuropeptide Y1 receptor antagonist alters gut microbiota and alleviates the ovariectomy-induced osteoporosis in rats. Calcif Tissue Int. 2020; 106(4):444-454.
[57] WANG S, WANG S, WANG X, et al. Effects of icariin on modulating gut microbiota and regulating metabolite alterations to prevent bone loss in ovariectomized rat model. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2022;13:874849.
[58] MA S, QIN J, HAO Y, et al. Structural and functional changes of gut microbiota in ovariectomized rats and their correlations with altered bone mass. Aging (Albany NY). 2020;12(11):10736-10753.
[59] LU H, XU X, FU D, et al. Butyrate-producing Eubacterium rectale suppresses lymphomagenesis by alleviating the TNF-induced TLR4/MyD88/NF-κB axis. Cell Host Microbe. 2022;30(8):1139-1150.
[60] WANG Y, SAKKA M, YAGI H, et al. Ruminiclostridium josui Abf62A-Axe6A: a tri-functional xylanolytic enzyme exhibiting α-l-arabinofuranosidase, endoxylanase, and acetylxylan esterase activities. Enzyme Microb Technol. 2018;117:1-8. |