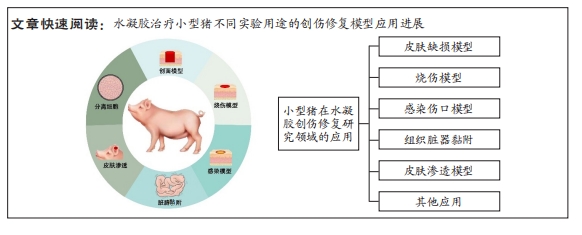
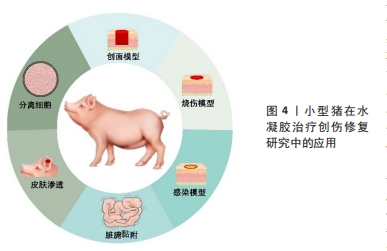
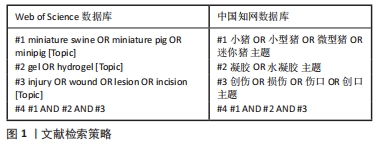
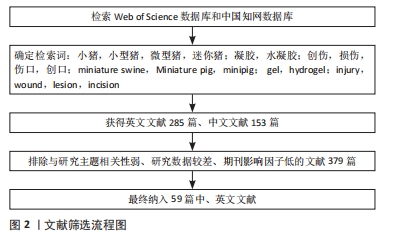
[1] 傅小兵,孙同柱,王亚平,等.表皮细胞生长因子与碱性成纤维细胞生长因子促进创面修复效应的比较性研究[J].中国修复重建外科杂志, 1999,13(5):278-282.
[2] 陈伟,付小兵,孙同柱,等.内皮细胞生长因子表达质粒的构建及其促进烫伤愈合的研究[J].中华实验外科杂志,2002,19(2):144-146.
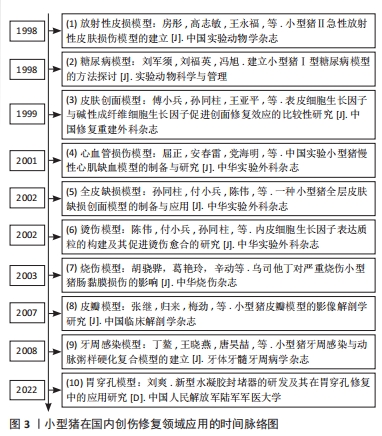
[3] 孙同柱,付小兵,陈伟,等.一种小型猪全层皮肤缺损创面模型的制备与应用[J].中华实验外科杂志,2002,19(5):466-467.
[4] 胡骁骅,葛艳玲,辛动,等.乌司他丁对严重烧伤小型猪肠黏膜损伤的影响[J].中华烧伤杂志,2003,19(S1):18-21.
[5] 张继,归来,梅劲,等.小型猪皮瓣模型的影像解剖学研究[J].中国临床解剖学杂志,2007,25(5):502-506.
[6] 房彤,高志敏,王永福,等.小型猪Ⅱ°急性放射性皮肤损伤模型的建立[J].中国实验动物学杂志,1998(1):29-30.
[7] 丁鳌,王晓燕,唐昊喆,等.小型猪牙周感染与动脉粥样硬化复合模型的建立[J].牙体牙髓牙周病学杂志,2008,18(4):190-194.
[8] 刘爽.新型水凝胶封堵器的研发及其在胃穿孔修复中的应用研究[D].重庆:中国人民解放军陆军军医大学,2023.
[9] 屈正,安春雷,党海明,等.中国实验小型猪慢性心肌缺血模型的制备与研究[J].中华实验外科杂志,2001,18(3):89.
[10] 高富雷,王丹茹,张余光.创伤愈合动物模型的研究进展[J].中国美容医学,2007,16(2):278-281.
[11] 陈雨荣,安星兰,汪正铸,等.猪作为人类疾病模型的研究进展[J].中国比较医学杂志,2020,30(7):110-119.
[12] WEINSTEIN GD. Autoradiographic Studies on Turnover Time and Protein Synthesis in Pig Epidermis. J Invest Dermatol. 1965;44:413-419.
[13] VARDAXIS NJ, BRANS TA, BOON ME, et al. Confocal laser scanning microscopy of porcine skin: implications for human wound healing studies. J Anat. 1997;190(4):601-611.
[14] WINTER GD. Formation of the scab and the rate of epithelization of superficial wounds in the skin of the young domestic pig. Nature. 1962;193: 293-294.
[15] 侯萍,李铭,马军,等.天然高分子材料水凝胶的制备及其应用进展[J].高分子通报,2022(8):29-36.
[16] 刘羽霄.蛋白水凝胶微载体的制备及其生物医学应用[D].南京:东南大学,2022.
[17] SEVINç-ÖZAKAR R, SEYRET E, ÖZAKAR E, et al. Nanoemulsion-Based Hydrogels and Organogels Containing Propolis and Dexpanthenol: Preparation, Characterization, and Comparative Evaluation of Stability, Antimicrobial, and Cytotoxic Properties. Gels. 2022;8(9):578.
[18] BU YZ, SUN GF, ZHANG LC, et al. POSS-modified PEG adhesives for wound closure. Chin J Polym Sci. 2017;35(10):1231-1242.
[19] 何跃.PCD/PCBR复合植物多糖修复家猪皮肤缺损的疗效观察研究[D].成都:成都中医药大学,2009.
[20] MITHIEUX SM, AGHAEI-GHAREH-BOLAGH B, YAN LP, et al. Tropoelastin Implants That Accelerate Wound Repair. Adv Healthc Mater. 2018;7(10): e1701206.
[21] 谭菊,李巨银,赵天赐,等.自体血小板凝胶对猪皮肤创伤愈合的影响[J].畜牧与兽医,2022,54(10):142-146.
[22] KIRKER KR, LUO Y, MORRIS SE, et al. Glycosaminoglycan hydrogels as supplemental wound dressings for donor sites. J Burn Care Rehabil. 2004; 25(3):276-286.
[23] 肖京.复方中药软膏在猪断层皮创面愈合中作用的实验研究[D].郑州:郑州大学,2013.
[24] JANG MJ, BAE SK, JUNG YS, et al. Enhanced wound healing using a 3D printed VEGF-mimicking peptide incorporated hydrogel patch in a pig model. Biomed Mater. 2021;16(4). doi: 10.1088/1748-605X/abf1a8.
[25] XU ZR, RAN XW. Diabetic foot care in China: challenges and strategy. Lancet Diabetes Endo. 2016;4(4):297-298.
[26] 姚爽.巴马小型猪糖尿病心肌病模型的建立及鉴定[D].桂林:桂林医学院,2019.
[27] ABADIR P, HOSSEINI S, FAGHIH M, et al. Topical Reformulation of Valsartan for Treatment of Chronic Diabetic Wounds. J Invest Dermatol. 2018;138(2): 434-443.
[28] 梁渝捷,李艳,高芸艺,等.芦荟凝胶治疗巴马小型猪糖尿病慢性皮肤溃疡的实验研究[J].四川大学学报(医学版),2022,53(6):953-960.
[29] ZELLNER S, MANABAT R, ROE DF. A dissolved oxygen dressing: A pilot study in an ischemic skin flap model. J Int Med Res. 2015;43(1):93-103.
[30] 王华.局部注射胸腺素β4凝胶预防食管环周内镜黏膜下剥离术后狭窄的有效性及其初步机制[D].上海:第二军医大学,2016.
[31] NISCHWITZ SP, FINK J, SCHELLNEGGER M, et al. The Role of Local Inflammation and Hypoxia in the Formation of Hypertrophic Scars-A New Model in the Duroc Pig. Int J Mol Sci. 2023;24(1):316.
[32] ORTEGA-SáNCHEZ C, PéREZ-DíAZ M, MELGAREJO-RAMíREZ Y, et al. Radiosterilized Pig Skin, Silver Nanoparticles and Skin Cells as an Integral Dressing Treatment for Burns: Development, Pre-Clinical and Clinical Pilot Study. Pharmaceutics. 2023;15(8):2105.
[33] BOUCARD N, VITON C, AGAY D, et al. The use of physical hydrogels of chitosan for skin regeneration following third-degree burns. Biomaterials. 2007;28(24):3478-3488.
[34] BURMEISTER DM, ROY DC, BECERRA SC, et al. In Situ Delivery of Fibrin-Based Hydrogels Prevents Contraction and Reduces Inflammation. J Burn Care Res. 2018;39(1):40-53.
[35] 刘有华.猪脂肪干细胞超表达FTO在皮肤创伤修复中的作用研究[D].杭州:浙江大学,2020.
[36] CUI X, LEE J, NG KR, et al. Food Waste Durian Rind-Derived Cellulose Organohydrogels: Toward Anti-Freezing and Antimicrobial Wound Dressing. Acs Sustain Chem Eng. 2021;9(3):1304-1312.
[37] YAN W, BANERJEE P, LIU YN, et al. Development of thermosensitive hydrogel wound dressing containing phage against wound infections. Int J Pharm. 2021;602:120508.
[38] LI CC, NYARUABA R, ZHAO XW, et al. Thermosensitive Hydrogel Wound Dressing Loaded with Bacteriophage Lysin LysP53. Viruses. 2022;14(9):1956.
[39] 吴志谷,付小兵,黎君友,等.速愈乐TM敷料促进小型猪感染创面愈合和抑菌作用的实验研究[J]. 感染、炎症、修复,2011,12(4):217-203,封3.
[40] 李静菲.治疗皮肤创伤感染的聚赖氨酸原位水凝胶[D].北京:军事科学院,2023.
[41] PAGANO C, CECCARINI MR, CALARCO P, et al. Bioadhesive polymeric films based on usnic acid for burn wound treatment: Antibacterial and cytotoxicity studies. Colloid Surface B. 2019;178:488-499.
[42] DENG PP, LIANG X, CHEN FX, et al. Novel multifunctional dual-dynamic-bonds crosslinked hydrogels for multi-strategy therapy of MRSA-infected wounds. Appl Mater Today. 2022;26:101362.
[43] SHEN C, LI YJ, MENG Q. Adhesive polyethylene glycol-based hydrogel patch for tissue repair. Colloids Surf B Biointerfaces. 2022;218:112751.
[44] WANG YS, XIONG XR, LIN CH, et al. Natural Dual-Crosslinked Self-Healing Hydrogels for In Situ Wound Healing. Macromol Mater Eng. 2022;307(9).doi:10.1002/mame.202200101
[45] 刘爽.新型水凝胶封堵器的研发及其在胃穿孔修复中的应用研究[D].重庆:中国人民解放军陆军军医大学,2022.
[46] 赵小林.负载MCC950的粘附型双网络水凝胶用于动脉损伤的止血修复[D].重庆:中国人民解放军陆军军医大学,2021.
[47] 周飞飞.光响应型组织黏附性水凝胶用于软组织修复再生的研究[D].杭州:浙江大学,2020.
[48] 汪静.卡泊三醇软膏皮肤渗透性研究[D].长春:吉林大学,2013.
[49] 柳亚锋,刘岱拯,谢珍茗.6种常用防晒剂的透皮吸收和安全评估[J].日用化学工业,2021,51(11):1088-1094.
[50] RÜTHER L, VOSS W. Hydrogel or ointment? Comparison of five different galenics regarding tissue breathability and transepidermal water loss. Heliyon. 2021;7(1):e06071.
[51] BALESTRIN LA, BACK PI, MARQUES MD, et al. Effect of Hydrogel Containing (Asteraceae) Extract-Loaded Nanoemulsions on Wound Healing Activity. Pharmaceutics. 2022;14(12):2726.
[52] TAZRART A, BOLZINGER MA, LAMART S, et al. Actinide-contaminated Skin: Comparing Decontamination Efficacy of Water, Cleansing Gels, and DTPA Gels. Health Phys. 2018;115(1):12-20.
[53] UTTAYARAT P, CHIANGNOON R, THONGNOPKOON T, et al. Electron Beam Irradiation Cross-Linked Hydrogel Patches Loaded with Red Onion Peel Extract for Transdermal Drug Delivery: Formulation, Characterization, Cytocompatibility, and Skin Permeation. Gels. 2023;9(1):52.
[54] 高垚垚.猪胎盘抗衰老药效物质基础及相关作用机制研究[D].扬州:扬州大学,2018.
[55] 刘彤.重组人胶原蛋白水凝胶和人工真皮分别作为微粒皮移植覆盖物修复全层皮肤缺损的实验研究[D].上海:中国人民解放军海军军医大学,2019.
[56] 刘长龙.猪皮促创面愈合活性肽的制备分离及鉴定研究[D].济南:山东中医药大学,2013.
[57] KIM JK, LEE JS, JUNG HJ, et al. Preparation and properties of Collagen/Modified hyaluronic acid hydrogel for biomedical application. J Nanosci Nanotechno. 2007;7(11):3852-3856.
[58] 廖建贵.小肠粘膜下层冷冻凝胶用于细胞移植支架的研究[D].重庆:第三军医大学,2016.
[59] 粟香,葛良鹏,李前勇.猪小肠黏膜下层作为组织修复材料的研究进展[J].中国比较医学杂志,2019,29(8):122-1228. |