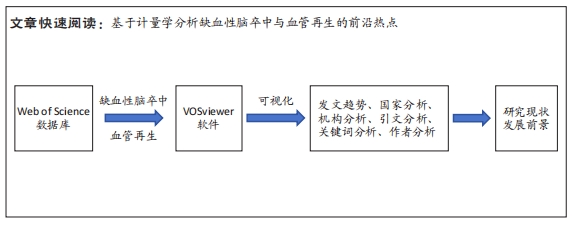
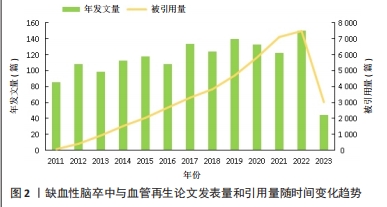
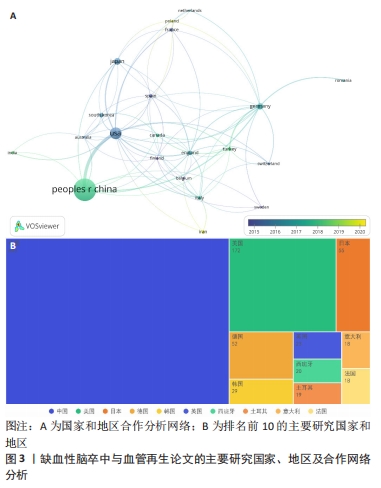
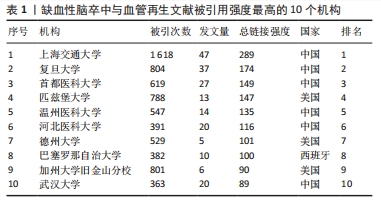
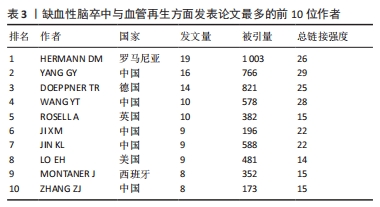
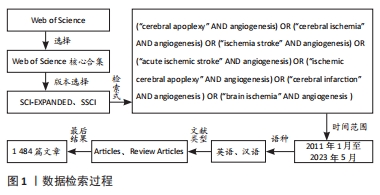
[1] ZHOU M, WANG H, ZHU J, et al. Cause-specific mortality for 240 causes in China during 1990-2013: a systematic subnational analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2013. Lancet. 2016;387(10015):251-272.
[2] 王励,肖雪梅,许志斌,等.出血性与缺血性脑卒中住院患者危险因素比较分析[J].慢性病学杂志,2014,15(7):526-528.
[3] 李云云,屈洪党.脑出血的诊断与治疗[J].中华全科医学,2019,17(2):171-172.
[4] 李卉,汤永红.脑卒中病因研究进展[J].现代诊断与治疗,2020,31(21):3380-3382.
[5] 马腾云,高玉元,马桂贤,等.缺血性脑卒中脑动脉血栓病理研究及应用进展[J].中华老年心脑血管病杂志,2021,23(12):1339-1341.
[6] GBD 2016 DALYs and HALE Collaborators. Global, regional, and national disability-adjusted life-years (DALYs) for 333 diseases and injuries and healthy life expectancy (HALE) for 195 countries and territories, 1990-2016: a systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2016 . Lancet. 2017;390(10100): 1260-1344.
[7] RANDOLPH SA. Ischemic Stroke. Workplace Health Saf. 2016;64(9):444.
[8] 马林,巢宝华,曹雷,等.2007-2017年中国脑卒中流行趋势及特征分析[J].中华脑血管病杂志(电子版),2020,14(5):253-258.
[9] 张艾嘉,王爽,王萍,等.缺血性脑卒中的病理机制研究进展及中医药防治[J].中国实验方剂学杂志,2020,26(5):227-240.
[10] MA R, XIE Q, LI H, et al. l-Borneol Exerted the Neuroprotective Effect by Promoting Angiogenesis Coupled With Neurogenesis via Ang1-VEGF-BDNF Pathway. Front Pharmacol. 2021;12:641894.
[11] LUNARDI BACCETTO S, LEHMANN C. Microcirculatory Changes in Experimental Models of Stroke and CNS-Injury Induced Immunodepression. Int J Mol Sci. 2019; 20(20):5184.
[12] WANG SN, WANG Z, XU TY, et al. Cerebral Organoids Repair Ischemic Stroke Brain Injury. Transl Stroke Res. 2020;11(5):983-1000.
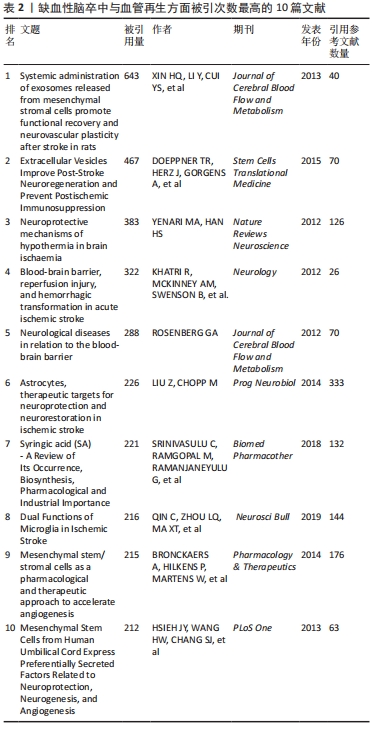
[13] LIU Z, CHOPP M. Astrocytes, therapeutic targets for neuroprotection and neurorestoration in ischemic stroke. Prog Neurobiol. 2016;144:103-120.
[14] HAO L, ZOU Z, TIAN H, et al. Stem cell-based therapies for ischemic stroke. Biomed Res Int. 2014;2014:468748.
[15] Liman TG, Endres M. New vessels after stroke: postischemic neovascularization and regeneration. Cerebrovasc Dis. 2012;33(5):492-499.
[16] 邱均平.文献计量学[M].北京:科学技术文献出版社,1988.
[17] 刁敬东,农晓琳.文献计量学在学术期刊评价中的应用研究[J].医学信息, 2018,31(23):16-18.
[18] 陈莹,常静玲,李新龙,等.基于CNKI的近10年中医药治疗缺血性脑卒中研究的可视化分析[J].时珍国医国药,2021,32(11):2803-2806.
[19] 黄茂茂,胡月,王彬川,等.缺血性脑卒中康复近10年国际文献计量学及可视化分析[J].中国组织工程研究,2021,25(23):3725-3733.
[20] 陈娟.干细胞移植在缺血性脑卒中治疗中的应用[J].中国组织工程研究, 2012,16(19):3576-3583.
[21] KHOSHNAM SE, WINLOW W, FARBOOD Y, et al. Emerging Roles of microRNAs in Ischemic Stroke: As Possible Therapeutic Agents. J Stroke. 2017;19(2):166-187.
[22] DU K, ZHAO C, WANG L, et al. MiR-191 inhibit angiogenesis after acute ischemic stroke targeting VEZF1. Aging (Albany NY). 2019;11(9):2762-2786.
[23] ZHU T, WANG L, WANG LP, et al. Therapeutic targets of neuroprotection and neurorestoration in ischemic stroke: Applications for natural compounds from medicinal herbs. Biomed Pharmacother. 2022;148:112719.
[24] HORIE N, PEREIRA MP, NIIZUMA K, et al. Transplanted stem cell-secreted vascular endothelial growth factor effects poststroke recovery, inflammation, and vascular repair. Stem Cells. 2011;29(2):274-285.
[25] BAO X, WEI J, FENG M, et al. Transplantation of human bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells promotes behavioral recovery and endogenous neurogenesis after cerebral ischemia in rats. Brain Res. 2011;1367:103-113.
[26] LINDVALL O, KOKAIA Z. Stem cell research in stroke: how far from the clinic? Stroke. 2011;42(8):2369-2375.
[27] MACKIE AR, LOSORDO DW. CD34-positive stem cells: in the treatment of heart and vascular disease in human beings. Tex Heart Inst J. 2011;38(5):474-485.
[28] LI L, GAN H, JIN H, et al. Astragaloside IV promotes microglia/macrophages M2 polarization and enhances neurogenesis and angiogenesis through PPARγ pathway after cerebral ischemia/reperfusion injury in rats. Int Immunopharmacol. 2021;92:107335.
[29] SHI YH, ZHANG XL, YING PJ, et al. Neuroprotective Effect of Astragaloside IV on Cerebral Ischemia/Reperfusion Injury Rats Through Sirt1/Mapt Pathway. Front Pharmacol. 2021;12:639898.
[30] CHEN J, ZHANG X, LIU X, et al. Ginsenoside Rg1 promotes cerebral angiogenesis via the PI3K/Akt/mTOR signaling pathway in ischemic mice. Eur J Pharmacol. 2019;856:172418.
[31] LI XF, ZHANG XJ, ZHANG C, et al. Ulinastatin protects brain against cerebral ischemia/reperfusion injury through inhibiting MMP-9 and alleviating loss of ZO-1 and occludin proteins in mice. Exp Neurol. 2018;302:68-74.
[32] LI Y, ZHANG X, CUI L, et al. Salvianolic acids enhance cerebral angiogenesis and neurological recovery by activating JAK2/STAT3 signaling pathway after ischemic stroke in mice. J Neurochem. 2017;143(1):87-99.
[33] SONG D, ZHANG X, CHEN J, et al. Wnt canonical pathway activator TWS119 drives microglial anti-inflammatory activation and facilitates neurological recovery following experimental stroke. J Neuroinflammation. 2019;16(1):256.
[34] WANG M, LI Y, ZHANG R, et al. Adiponectin-Transfected Endothelial Progenitor Cells Have Protective Effects After 2-Hour Middle-Cerebral Artery Occlusion in Rats With Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus. Front Neurol. 2021;12:630681.
[35] XIN H, LI Y, CUI Y, et al. Systemic administration of exosomes released from mesenchymal stromal cells promote functional recovery and neurovascular plasticity after stroke in rats. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 2013;33(11):1711-1715.
[36] DOEPPNER TR, HERZ J, GÖRGENS A, et al. Extracellular Vesicles Improve Post-Stroke Neuroregeneration and Prevent Postischemic Immunosuppression. Stem Cells Transl Med. 2015;4(10):1131-1143.
[37] YENARI MA, HAN HS. Neuroprotective mechanisms of hypothermia in brain ischaemia. Nat Rev Neurosci. 2012;13(4):267-278.
[38] SEEVINCK PR, DEDDENS LH, DIJKHUIZEN RM. Magnetic resonance imaging of brain angiogenesis after stroke. Angiogenesis. 2010;13(2):101-111.
[39] NAVARATNA D, GUO S, ARAI K, et al. Mechanisms and targets for angiogenic therapy after stroke. Cell Adh Migr. 2009;3(2):216-223.
[40] ZHU H, ZHANG Y, ZHONG Y, et al. Inflammation-Mediated Angiogenesis in Ischemic Stroke. Front Cell Neurosci. 2021;15:652647.
[41] XIA CF, YIN H, YAO YY, et al. Kallikrein protects against ischemic stroke by inhibiting apoptosis and inflammation and promoting angiogenesis and neurogenesis. Hum Gene Ther. 2006;17(2):206-219.
[42] HUANG YJ, NAN GX. Oxidative stress-induced angiogenesis. J Clin Neurosci. 2019; 63:13-16.
[43] HERMANN DM, ZECHARIAH A. Implications of vascular endothelial growth factor for postischemic neurovascular remodeling. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 2009;29(10):1620-1643.
[44] GAO B, DENG J, ZHANG X, et al. Effects of mesencephalic astrocyte-derived neurotrophic factor on cerebral angiogenesis in a rat model of cerebral ischemia. Neurosci Lett. 2020;715:134657.
[45] LAI DM, LI H, LEE CC, et al. Angiopoietin-like protein 1 decreases blood brain barrier damage and edema following focal cerebral ischemia in mice. Neurochem Int. 2008;52(3):470-477.
[46] ZECHARIAH A, ELALI A, DOEPPNER TR, et al. Vascular endothelial growth factor promotes pericyte coverage of brain capillaries, improves cerebral blood flow during subsequent focal cerebral ischemia, and preserves the metabolic penumbra. Stroke. 2013;44(6):1690-1697.
[47] MA Y, ZECHARIAH A, QU Y, et al. Effects of vascular endothelial growth factor in ischemic stroke. J Neurosci Res. 2012;90(10):1873-1882.
[48] REITMEIR R, KILIC E, REINBOTH BS, et al. Vascular endothelial growth factor induces contralesional corticobulbar plasticity and functional neurological recovery in the ischemic brain [published correction appears in Acta Neuropathol. 2015 Oct;130(4):603]. Acta Neuropathol. 2012;123(2):273-284.
[49] DOEPPNER TR, HERZ J, GÖRGENS A, et al. Extracellular Vesicles Improve Post-Stroke Neuroregeneration and Prevent Postischemic Immunosuppression. Stem Cells Transl Med. 2015;4(10):1131-1143.
[50] HU X, DE SILVA TM, CHEN J, et al. Cerebral Vascular Disease and Neurovascular Injury in Ischemic Stroke. Circ Res. 2017;120(3):449-471.
[51] ERGUL A, VALENZUELA JP, FOUDA AY, et al. Cellular connections, microenvironment and brain angiogenesis in diabetes: Lost communication signals in the post-stroke period. Brain Res. 2015;1623:81-96.
[52] GREENBERG DA. Poststroke angiogenesis, pro: making the desert bloom. Stroke. 2015;46(5):e101-e102.
[53] BACIGALUPPI M, PLUCHINO S, PERUZZOTTI-JAMETTI L, et al. Delayed post-ischaemic neuroprotection following systemic neural stem cell transplantation involves multiple mechanisms. Brain. 2009;132(Pt 8):2239-2251.
[54] ZHENG W, HONMOU O, MIYATA K, et al. Therapeutic benefits of human mesenchymal stem cells derived from bone marrow after global cerebral ischemia. Brain Res. 2010;1310:8-16.
[55] HSIEH JY, WANG HW, CHANG SJ, et al. Mesenchymal stem cells from human umbilical cord express preferentially secreted factors related to neuroprotection, neurogenesis, and angiogenesis. PLoS One. 2013;8(8):e72604.
[56] SCHEIBE F, KLEIN O, KLOSE J, et al. Mesenchymal stromal cells rescue cortical neurons from apoptotic cell death in an in vitro model of cerebral ischemia. Cell Mol Neurobiol. 2012;32(4):567-576.
[57] TATE CC, FONCK C, MCGROGAN M, et al. Human mesenchymal stromal cells and their derivative, SB623 cells, rescue neural cells via trophic support following in vitro ischemia. Cell Transplant. 2010;19(8):973-984.
[58] QIU L, CAI Y, GENG Y, et al. Mesenchymal stem cell-derived extracellular vesicles attenuate tPA-induced blood-brain barrier disruption in murine ischemic stroke models. Acta Biomater. 2022;154:424-442.
[59] LIU C, YANG TH, LI HD, et al. Exosomes from bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells are a potential treatment for ischemic stroke. Neural Regen Res. 2023; 18(10):2246-2251.
[60] BHASIN A, SRIVASTAVA MV, KUMARAN SS, et al. Autologous mesenchymal stem cells in chronic stroke. Cerebrovasc Dis Extra. 2011;1(1):93-104.
[61] WU F, YANG Z, LI G. Role of specific microRNAs for endothelial function and angiogenesis. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2009;386(4):549-553.
[62] JEYASEELAN K, LIM KY, ARMUGAM A. MicroRNA expression in the blood and brain of rats subjected to transient focal ischemia by middle cerebral artery occlusion. Stroke. 2008;39(3):959-966.
[63] REDELL JB, LIU Y, DASH PK. Traumatic brain injury alters expression of hippocampal microRNAs: potential regulators of multiple pathophysiological processes. J Neurosci Res. 2009;87(6):1435-1448.
[64] DHARAP A, BOWEN K, PLACE R, et al. Transient focal ischemia induces extensive temporal changes in rat cerebral microRNAome. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 2009;29(4):675-687.
[65] LIU DZ, TIAN Y, ANDER BP, et al. Brain and blood microRNA expression profiling of ischemic stroke, intracerebral hemorrhage, and kainate seizures. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 2010;30(1):92-101.
[66] 钟迪,张舒婷,吴波.《中国急性缺血性脑卒中诊治指南2018》解读[J].中国现代神经疾病杂志,2019,19(11):897-901.
[67] 王珊珊,吴远华.中医药防治缺血性脑卒中的现代分子生物学研究进展[J].中国民间疗法,2022,30(22):113-116.
[68] LI J, LI C, SUBEDI P, et al. Light Alcohol Consumption Promotes Early Neurogenesis Following Ischemic Stroke in Adult C57BL/6J Mice. Biomedicines. 2023;11(4):1074.
[69] LIU Z, LIU M, JIA G, et al. Long-term intermittent fasting improves neurological function by promoting angiogenesis after cerebral ischemia via growth differentiation factor 11 signaling activation. PLoS One. 2023;18(3):e0282338.
[70] ZHANG Y, ZHAO X, GUO C, et al. The Circadian System Is Essential for the Crosstalk of VEGF-Notch-mediated Endothelial Angiogenesis in Ischemic Stroke. Neurosci Bull. 2023. doi: 10.1007/s12264-023-01042-9.
[71] ZHANG W, HAN L, WEN Y, et al. Electroacupuncture reverses endothelial cell death and promotes angiogenesis through the VEGF/Notch signaling pathway after focal cerebral ischemia-reperfusion injury. Brain Behav. 2023;13(3):e2912. |