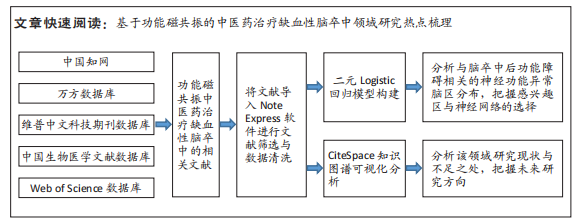
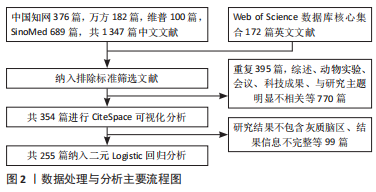
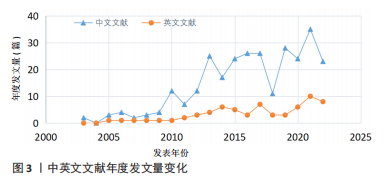
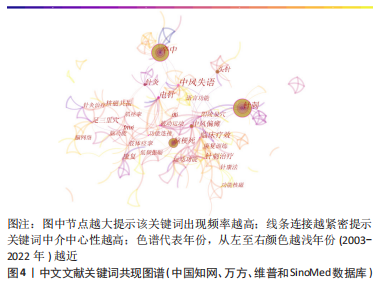
[1] GBD 2019 STROKE COLLABORATORS. Global, regional, and national burden of stroke and its risk factors, 1990-2019: a systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2019. Lancet Neurol. 2021;20(10):795-820.
[2] 周雨帆,徐敏杰,谭逸海,等.基于结构协变网络探索卒中后失语结构损伤特征[J].中国康复理论与实践,2022,28(10):1198-1204.
[3] 林志诚,游咏梅,王君,等.脑卒中后吞咽障碍患者下丘脑功能连接和全脑各向异性的磁共振成像研究[J].中国康复理论与实践,2021,27(5):504-509.
[4] 田婧,范晨雨,李浩正,等.基于功能性近红外光谱技术的脑卒中后运动功能障碍患者脑网络功能连接研究[J].中国康复医学杂志,2022,37(5):600-605.
[5] CAO BQ, TAN F, ZHAN J, et al. Mechanism underlying treatment of ischemic stroke using acupuncture: transmission and regulation. Neural Regen Res. 2021; 16(5):944-954.
[6] SHI P, SUN LL, LEE YS, et al. Electroacupuncture regulates the stress-injury-repair chain of events after cerebral ischemia/reperfusion injury. Neural Regen Res. 2017;12(6):925-930.
[7] SU XT, WANG L, MA SM, et al. Mechanisms of acupuncture in the regulation of oxidative stress in treating ischemic stroke. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2020;2020:7875396.
[8] JIA H, HE J, ZHAO L, et al. Combination of stem cell therapy and acupuncture to treat ischemic stroke: a prospective review. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2022;13(1):87.
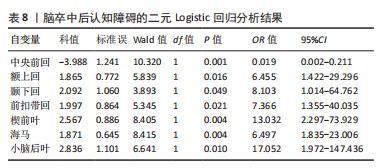
[9] 李沁,肖端,徐亚林.脑卒中后认知障碍的静息态功能磁共振成像研究进展[J].中国康复医学杂志,2022,37(6):850-854.
[10] 俞璐,王踉碕,王丽玮,等.基于功能性磁共振成像评价中医药对缺血性脑卒中脑功能网络连接影响的研究进展[J].世界科学技术-中医药现代化, 2022,24(7):2802-2808.
[11] 陈悦,陈超美,刘则渊,等.CiteSpace知识图谱的方法论功能[J].科学学研究, 2015,33(2):242-253.
[12] CHEN C, HU Z, LIU S, et al. Emerging trends in regenerative medicine: a scientometric analysis in CiteSpace. Expert Opin Biol Ther. 2012;12(5):593-608.
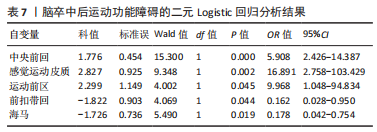
[13] 崔淑兰,李萍,樊一波,等.围绝经期综合征常见证型证候特征的二元Logistic回归分析[J].中华中医药杂志,2022,37(7):4121-4124.
[14] 李杰,陈超美.CiteSpace:科技文本挖掘及可视化[M].北京:首都经济贸易大学出版社, 2016:89.
[15] 涂永梅.通督解痉法配合牵伸康复技术对梗塞后肌痉挛患者的脑功能变化研究[D].成都:成都中医药大学,2015.
[16] 贺洋洋.通督解痉法对中风后肌痉挛患者的脑区激活及其机制的研究[D].成都:成都中医药大学,2014.
[17] 劳祥婷.针刺督脉及被动运动对脑卒中后肢体痉挛的脑功能即时效应的影响[D]. 成都:成都中医药大学,2014.
[18] 阳运秋,唐纯志,崔韶阳,等.靳三针结合镜像疗法对脑卒中上肢功能障碍患者脑功能效应的影响[J].中医杂志,2019,60(8):675-679.
[19] 江征,卓丽萍,廖少钦,等.穴位不同刺激方式改善缺血性脑卒中患者手功能障碍的临床观察[J].康复学报,2017,27(4):7-12.
[20] 张斌龙.基于双流模型网络的失语症“益髓醒神”针刺干预机制研究[D].北京:北京中医药大学,2019.
[21] 李晓琳.“益髓醒神”针刺治疗卒中后失语的脑微观结构与功能网络MRI研究[D].北京:北京中医药大学,2021.
[22] 李晓琳.“形神合一”理论指导下卒中后失语的语言任务fMRI研究[D]. 北京:北京中医药大学,2018.
[23] 李晓琳,张斌龙,樊瑞文,等.词图语言任务在卒中后失语功能磁共振成像实验中的刺激模式及模型研究进展[J].中国康复理论与实践,2020,26(6):668-672.
[24] CHEN Y, PAN Z, MENG F, et al. Magnetic resonance imaging assessment of the therapeutic effect of combined electroacupuncture and stem cells in acute peripheral nerve injury. Front Cell Neurosci. 2022;16:1065557.
[25] CHUNG WY, LIU SY, GAO JC, et al. Modulatory effect of International Standard Scalp Acupuncture on brain activation in the elderly as revealed by resting-state fMRI. Neural Regen Res. 2019;14(12):2126-2131.
[26] CHUNYONG L, YINGKAI L, FUDA L, et al. Longitudinal changes of motor cortex function during motor recovery after stroke. Top Stroke Rehabil. 2022. doi:10.1080/10749357.2022.2051829.
[27] SCHAECHTER JD, CONNELL BD, STASON WB, et al. Correlated change in upper limb function and motor cortex activation after verum and sham acupuncture in patients with chronic stroke. J Altern Complement Med. 2007;13(5):527-532.
[28] ZHANG C, XIA Y, FENG T, et al. Disrupted functional connectivity within and between resting-state networks in the subacute stage of post-stroke aphasia. Front Neurosci. 2021;15:746264.
[29] LI Y, YU Z, ZHOU X, et al. Aberrant interhemispheric functional reciprocities of the default mode network and motor network in subcortical ischemic stroke patients with motor impairment: a longitudinal study. Front Neurol. 2022;13:996621.
[30] 惠小珊,陆诗超,刘咏梅,等.基于多分析方法联合的中医药调控mTOR通路文献计量学及可视化分析[J].中国实验方剂学杂志,2023,29(1):155-162.
[31] CHO SY, JAHNG GH, PARK SU, et al. fMRI study of effect on brain activity according to stimulation method at LI11, ST36: painful pressure and acupuncture stimulation of same acupoints. J Altern Complement Med. 2010;16(4):489-495.
[32] CHEN L, FANG J, MA R, et al. Additional effects of acupuncture on early comprehensive rehabilitation in patients with mild to moderate acute ischemic stroke: a multicenter randomized controlled trial. BMC Complement Altern Med. 2016;16:226.
[33] LI Y, WANG D, ZHANG H, et al. Changes of brain connectivity in the primary motor cortex after subcortical stroke: a multimodal magnetic resonance imaging study. Medicine (Baltimore). 2016;95(6):e2579.
[34] ALMEIDA SR, VICENTINI J, BONILHA L, et al. Brain connectivity and functional recovery in patients with ischemic stroke. J Neuroimaging. 2017;27(1):65-70.
[35] KATAN M, LUFT A. Global Burden of Stroke. Semin Neurol. 2018;38(2):208-211.
[36] HAN X, BAI L, SUN C, et al. Acupuncture enhances communication between cortices with damaged white matters in poststroke motor impairment. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2019;2019:4245753.
[37] NIERHAUS T, CHANG Y, LIU B, et al. Somatosensory stimulation with XNKQ acupuncture modulates functional connectivity of motor areas. Front Neurosci. 2019;13:147.
[38] HAN X, JIN H, LI K, et al. Acupuncture modulates disrupted whole-brain network after ischemic stroke: evidence based on graph theory analysis. Neural Plast. 2020;2020:8838498.
[39] LIU H, CHEN L, ZHANG G, et al. Scalp acupuncture enhances the functional connectivity of visual and cognitive-motor function network of patients with acute ischemic stroke. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2020;2020:8836794.
[40] WANG Y, WANG L, WANG Y, et al. Sensorimotor responses in post-stroke hemiplegic patients modulated by acupuncture at Yanglingquan (GB34): a fMRI study using intersubject functional correlation (ISFC) analysis. Front Neurol. 2022;13:900520.
[41] 刘婷,郭晓鹏,李丽娟,等.卒中后早期认知下降患者默认模式网络和执行控制网络改变的功能磁共振成像研究[J].中华老年心脑血管病杂志,2022, 24(11):1164-1168.
[42] 陈天竹,邹忆怀,杜钟名,等.手足十二针对缺血性脑卒中偏瘫患者大脑初级运动区与小脑功能连接的影响[J].中医杂志,2021,62(17):1514-1521.
[43] 何永强,马铁明,许允发,等.电针头穴治疗脑卒中后肩手综合征Ⅰ期的即刻效应研究和多功能磁共振成像研究[J].中华中医药学刊,2022,40(1):161-164.
[44] 杨福霞,侯冬梅,高进云,等.针刺对脑梗死后运动功能与各部位皮质脊髓束的影响[J].中华中医药杂志,2021,36(11):6888-6892.
[45] 朱丹,刘永康,厉励,等.基于fMRI技术观察中西医结合治疗对急性缺血性脑卒中默认网络的影响[J].南京中医药大学学报,2021,37(6):871-877.
[46] 吕天丽,常静玲,杨财水,等.“形神合一”针刺综合方案治疗卒中后基底节失语验案的脑影像分析[J].环球中医药, 2018,11(6):904-908.
[47] 陆梦馨,杜钟名,江澜,等.基于Granger因果关系探究中风偏瘫患者的针刺脑效应机制[J].中华中医药杂志,2022,37(5):2745-2750.
[48] JIN C, QI S, TENG Y, et al. Altered degree centrality of brain networks in parkinson’s disease with freezing of gait: a resting-state functional MRI study. Front Neurol. 2021;12:743135.
[49] 杜钟名,方继良,陆梦馨,等.针刺中风患者阳陵泉后度中心性及动态度中心性变异系数变化的fMRI研究[J].中国医学物理学杂志,2022,39(1):38-43.
[50] 宋杰,王大明,李永祥,等.脑卒中患者运动网络和默认网络的功能连接变化[J].中华物理医学与康复杂志,2018,40(4):314-317.
[51] 陈美钟,王志敏,邬裕樊,等.基于度中心度和格兰杰因果分析对基底节区早期缺血性脑卒中患者的脑网络有效连接变化研究[J].临床放射学杂志, 2022,41(3):410-414.
[52] LIU L, XIAO Y, ZHANG W, et al. Functional changes of neural circuits in stroke patients with dysphagia: a meta-analysis. J Evid Based Med. 2017;10(3):189-195.
[53] 易小琦,黄俊浩,陈暇女,等.针刺促进缺血性脑卒中功能恢复的静息态功能连接研究[J].中国康复医学杂志,2021,36(4):383-387.
[54] 韩笑,宁艳哲,李匡时,等.基于功能磁共振成像的针刺阳陵泉对脑卒中患者执行控制网络影响研究[J].中华中医药杂志,2017,32(5):2128-2131.
[55] 文巧,兰蕾,刘雅兰,等.基于功能磁共振技术的针刺机制研究现状分析[J].中华中医药杂志,2022,37(9):5463-5466.
[56] 黄亚青,刘斌,杨明,等.慢性缺血性脑卒中患者全脑功能网络小世界属性改变[J].中华医学杂志,2016,96(3):185-188.
[57] CHEN H, SHI M, ZHANG H, et al. Different patterns of functional connectivity alterations within the default-mode network and sensorimotor network in basal ganglia and pontine stroke. Med Sci Monit. 2019;25:9585-9593.
[58] JEUN SS, KIM JS, KIM BS, et al. Acupuncture stimulation for motor cortex activities: a 3T fMRI study. Am J Chin Med. 2005;33(4):573-578.
[59] KIM MS, MOON BS, AHN JY, et al. Elucidating the mechanisms of post-stroke motor recovery mediated by electroacupuncture using diffusion tensor tractography. Front Neurol. 2022;13:888165.
[60] ROLLS ET, CHENG W, DU J, et al. Functional connectivity of the right inferior frontal gyrus and orbitofrontal cortex in depression. Soc Cogn Affect Neurosci. 2020;15(1):75-86.
[61] ROLLS ET. The cingulate cortex and limbic systems for emotion, action, and memory. Brain Struct Funct. 2019;224(9):3001-3018.
[62] 刘琪,陈宇,刘畅,等.小脑卒中患者认知域受损特点及影像学研究进展[J].中国卒中杂志,2021,16(3):298-302.
[63] 邬刚,马鹏程,涂坤,等.吞咽功能相关脑功能区激活机制的血氧水平依赖功能磁共振研究[J].神经损伤与功能重建,2022,17(7):413-415.
[64] BOILLAT Y, BAZIN PL, VAN DER ZWAAG W. Whole-body somatotopic maps in the cerebellum revealed with 7T fMRI. Neuroimage. 2020;211:116624.
[65] LI BJ, FRISTON K, MODY M, et al. A brain network model for depression: from symptom understanding to disease intervention. CNS Neurosci Ther. 2018;24(11): 1004-1019.
[66] CHENG W, ROLLS ET, QIU J, et al. Medial reward and lateral non-reward orbitofrontal cortex circuits change in opposite directions in depression. Brain. 2016;139(Pt 12):3296-3309.
|