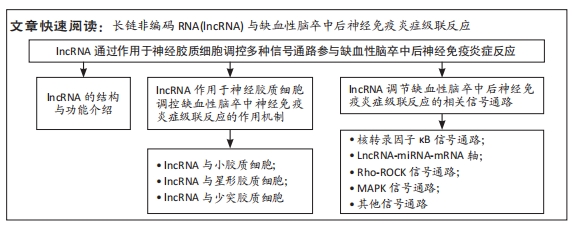
[1] CAPRIO FZ, SOROND FA. Cerebrovascular disease: primary and secondary stroke prevention. Med Clin North Am. 2019;103(2):295-308.
[2] Global, regional, and national burden of stroke and its risk factors, 1990-2019: a systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2019. Lancet Neurol. 2021; 20(10):795-820.
[3] PLUTA R, JANUSZEWSKI S, CZUCZWAR SJ. Neuroinflammation in post-ischemic neurodegeneration of the brain: friend, foe, or both. Int J Mol Sci. 2021;22(9):4405.
[4] JURCAU A, SIMION A. Neuroinflammation in cerebral ischemia and ischemia/reperfusion injuries: from pathophysiology to therapeutic strategies. Int J Mol Sci. 2021; 23(1):14.
[5] CHEN Z, WU H, ZHANG M. Long non-coding RNA: an underlying bridge linking neuroinflammation and central nervous system diseases. Neurochem Int. 2021;148: 105101.
[6] BEGOLLI R, SIDERIS N, GIAKOUNTIS A. LncRNAs as chromatin regulators in cancer: from molecular function to clinical potential. Cancers (Basel). 2019;11(10):1524.
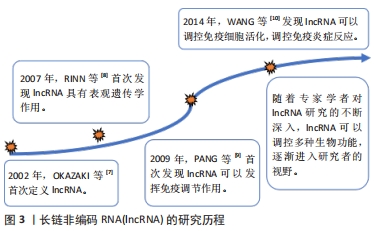
[7] OKAZAKI Y, FURUNO M, KASUKAWA T, et al. Analysis of the mouse transcriptome based on functional annotation of 60,770 full-length cDNAs. Nature. 2002;420(6915):563-573.
[8] RINN JL, KERTESZ M, WANG JK, et al. Functional demarcation of active and silent chromatin domains in human HOX loci by noncoding RNAs. Cell. 2007;129(7):1311-1323.
[9] PANG KC, DINGER ME, MERCER TR, et al. Genome-wide identification of long noncoding RNAs in CD8+ T cells. J Immunol. 2009;182(12):7738-7748.
[10] WANG P, XUE Y, HAN Y, et al. The STAT3-binding long noncoding RNA lnc-DC controls human dendritic cell differentiation. Science. 2014;344(6181):310-313.
[11] ZHU L, LI N, SUN L, et al. Non-coding RNAs: the key detectors and regulators in cardiovascular disease. Genomics. 2021;113(1 Pt 2):1233-1246.
[12] ALVAREZ-DOMINGUEZ JR, LODISH HF. Emerging mechanisms of long noncoding RNA function during normal and malignant hematopoiesis. Blood. 2017;130(18):1965-1975.
[13] QIU Y, XU M, HUANG S. Long noncoding RNAs: emerging regulators of normal and malignant hematopoiesis. Blood. 2021;138(23):2327-2336.
[14] SLABY O, LAGA R, SEDLACEK O. Therapeutic targeting of non-coding RNAs in cancer. Biochem J. 2017;474(24):4219-4251.
[15] LIN C, YANG L. Long noncoding RNA in cancer: wiring signaling circuitry. Trends Cell Biol. 2018;28(4):287-301.
[16] ZHANG X, WANG W, ZHU W, et al. Mechanisms and functions of long non-coding RNAs at multiple regulatory levels. Int J Mol Sci. 2019;20(22):5573.
[17] WANG ZY, WEN ZJ, XU HM, et al. Exosomal noncoding RNAs in central nervous system diseases: biological functions and potential clinical applications. Front Mol Neurosci. 2022;15:1004221.
[18] DAIDONE M, CATALDI M, PINTO A, et al. Non-coding RNAs and other determinants of neuroinflammation and endothelial dysfunction: regulation of gene expression in the acute phase of ischemic stroke and possible therapeutic applications. Neural Regen Res. 2021;16(11):2154-2158.
[19] GHAFOURI-FARD S, SHOOREI H, TAHERI M. Non-coding RNAs participate in the ischemia-reperfusion injury. Biomed Pharmacother. 2020;129:110419.
[20] TRIPATHI S, SHREE B, MOHAPATRA S, et al. The Expanding regulatory mechanisms and cellular functions of long non-coding RNAs (lncRNAs) in neuroinflammation. Mol Neurobiol. 2021;58(6):2916-2939.
[21] XU S, LU J, SHAO A, et al. Glial cells: role of the immune response in ischemic stroke. Front Immunol. 2020;11:294.
[22] LI S, CAO Y, ZHANG H, et al. Construction of lncRNA-mediated ceRNA network for investigating immune pathogenesis of ischemic stroke. Mol Neurobiol. 2021;58(9):4758-4769.
[23] SCHIRMER L, VELMESHEV D, HOLMQVIST S, et al. Neuronal vulnerability and multilineage diversity in multiple sclerosis. Nature. 2019;573(7772):75-82.
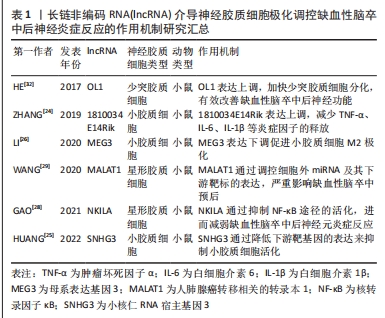
[24] ZHANG X, ZHU XL, JI BY, et al. LncRNA-1810034E14Rik reduces microglia activation in experimental ischemic stroke. J Neuroinflammation. 2019;16(1):75.
[25] HUANG D, CAO Y, ZU T, et al. Interference with long noncoding RNA SNHG3 alleviates cerebral ischemia-reperfusion injury by inhibiting microglial activation. J Leukoc Biol. 2022;111(4):759-769.
[26] LI T, LUO Y, ZHANG P, et al. LncRNA MEG3 regulates microglial polarization through KLF4 to affect cerebral ischemia-reperfusion injury. J Appl Physiol (1985). 2020;129(6):1460-1467.
[27] WILLIAMSON MR, FUERTES CJA, DUNN AK, et al. Reactive astrocytes facilitate vascular repair and remodeling after stroke. Cell Rep. 2021;35(4):109048.
[28] GAO W, NING Y, PENG Y, et al. LncRNA NKILA relieves astrocyte inflammation and neuronal oxidative stress after cerebral ischemia/reperfusion by inhibiting the NF-κB pathway. Mol Immunol. 2021;139:32-41.
[29] WANG H, ZHENG X, JIN J, et al. LncRNA MALAT1 silencing protects against cerebral ischemia-reperfusion injury through miR-145 to regulate AQP4. J Biomed Sci. 2020; 27(1):40.
[30] BARATEIRO A, BRITES D, FERNANDES A. Oligodendrocyte development and myelination in neurodevelopment: molecular mechanisms in health and disease. Curr Pharm Des. 2016;22(6):656-679.
[31] DONG X, CHEN K, CUEVAS-DIAZ DURAN R, et al. Comprehensive identification of long non-coding RNAs in purified cell types from the brain reveals functional lncRNA in OPC fate determination. PLoS Genet. 2015;11(12):e1005669.
[32] HED, WANG J, LU Y, et al. lncRNA functional networks in oligodendrocytes reveal stage-specific myelination control by an lncOL1/Suz12 complex in the CNS. Neuron. 2017;93(2):362-378.
[33] CILDIR G, LOW KC, TERGOANKAR V. Noncanonical NF-κB Signaling in health and disease. Trends Mol Med. 2016;22(5):414-429.
[34] WANG M, JIANG YM, XIA LY, et al. LncRNA NKILA upregulation mediates oxygen glucose deprivation/re-oxygenation-induced neuronal cell death by inhibiting NF-κB signaling. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2018;503(4):2524-2530.
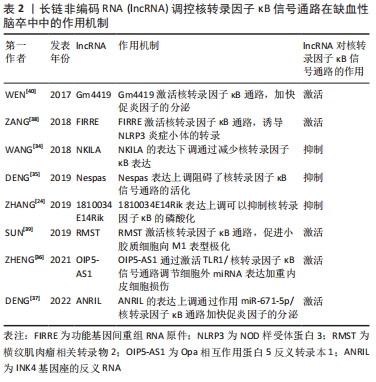
[35] DENG Y, CHEN D, WANG L, et al. Silencing of long noncoding RNA nespas aggravates microglial cell death and neuroinflammation in ischemic stroke. Stroke. 2019;50(7): 1850-1858.
[36] ZHENG Z, ZHANG G, LIANG X, et al. LncRNA OIP5-AS1 facilitates ox-LDL-induced endothelial cell injury through the miR-98-5p/HMGB1 axis. Mol Cell Biochem. 2021; 476(1):443-455.
[37] DENG L, JIANG J, CHEN S, et al. Long non-coding RNA ANRIL downregulation alleviates neuroinflammation in an Ischemia Stroke Model via Modulation of the miR-671-5p/NF-κB pathway. Neurochem Res. 2022;47(7):2002-2015.
[38] ZANG Y, ZHOU X, WANG Q, et al. LncRNA FIRRE/NF-kB feedback loop contributes to OGD/R injury of cerebral microglial cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2018;501(1): 131-138.
[39] SUN XL, WANG ZL, WU Q, et al. LncRNA RMST activates TAK1-mediated NF-κB signaling and promotes activation of microglial cells via competitively binding with hnRNPK. IUBMB Life. 2019;71(11):1785-1793.
[40] WEN Y, YU Y, FU X. LncRNA Gm4419 contributes to OGD/R injury of cerebral microglial cells via IκB phosphorylation and NF-κB activation. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2017;487(4):923-929.
[41] XIONG W, QU Y, CHEN H, et al. Insight into long noncoding RNA-miRNA-mRNA axes in myocardial ischemia-reperfusion injury: the implications for mechanism and therapy. Epigenomics. 2019;11(15):1733-1748.
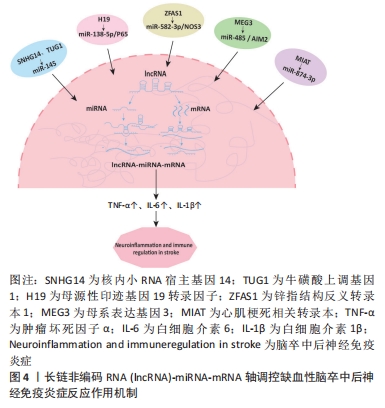
[42] QI X, SHAO M, SUN H, et al. Long non-coding RNA SNHG14 promotes microglia activation by regulating miR-145-5p/PLA2G4A in cerebral infarction. Neuroscience. 2017;348:98-106.
[43] WANG H, LIAO S, LI H, et al. Long non-coding RNA TUG1 sponges mir-145a-5p to regulate microglial polarization after oxygen-glucose deprivation. Front Mol Neurosci. 2019;12:215.
[44] YAO M, LUO Y, LI H, et al. LncRNA Tug1 contributes post-stroke NLRP3 inflammasome-dependent pyroptosis via miR-145a-5p/Tlr4 axis. Mol Neurobiol. 2022;59(11):6701-6712.
[45] LIANG J, WANG Q, LI JQ, et al. Long non-coding RNA MEG3 promotes cerebral ischemia-reperfusion injury through increasing pyroptosis by targeting miR-485/AIM2 axis. Exp Neurol. 2020;325:113139.
[46] LI H, TANG C, WANG D. LncRNA H19 promotes inflammatory response induced by cerebral ischemia-reperfusion injury through regulating the miR-138-5p-p65 axis. Biochem Cell Biol. 2020;98(4):525-536.
[47] ZHANG S, ZHANG Y, WANG N, et al. Long non-coding RNA MIAT impairs neurological function in ischemic stroke via up-regulating microRNA-874-3p-targeted IL1B. Brain Res Bull. 2021;175:81-89.
[48] ZHANG Y, ZHANG Y. lncRNA ZFAS1 improves neuronal injury and inhibits inflammation, oxidative stress, and apoptosis by sponging miR-582 and upregulating NOS3 expression in cerebral ischemia/reperfusion injury. Inflammation. 2020;43(4):1337-1350.
[49] KIMURA T, HORIKOSHI Y, KURIYAGAWA C, et al. Rho/ROCK pathway and noncoding RNAs: implications in ischemic stroke and spinal cord injury. Int J Mol Sci. 2021;22(21):11573.
[50] GU H, YU SP, GUTEKUNST CA, et al. Inhibition of the Rho signaling pathway improves neurite outgrowth and neuronal differentiation of mouse neural stem cells. Int J Physiol Pathophysiol Pharmacol. 2013;5(1):11-20.
[51] WANG QM, LIAO JK. ROCKs as immunomodulators of stroke. Expert Opin Ther Targets. 2012;16(10):1013-1025.
[52] WANG J, FU Z, WANG M, et al. Knockdown of XIST attenuates cerebral ischemia/reperfusion injury through regulation of miR-362/ROCK2 axis. Neurochem Res. 2021; 46(8):2167-2180.
[53] ZHONG Y, YU C, QIN W. LncRNA SNHG14 promotes inflammatory response induced by cerebral ischemia/reperfusion injury through regulating miR-136-5p /ROCK1. Cancer Gene Ther. 2019;26(7-8):234-247.
[54] XU Q, ZHAO B, YE Y, et al. Relevant mediators involved in and therapies targeting the inflammatory response induced by activation of the NLRP3 inflammasome in ischemic stroke. Neuroinflammation. 2021;18(1):123.
[55] ZHANG H, LI M, LIANG J, et al. Long Non-coding RNA PVT1 inhibits miR-30c-5p to upregulate Rock2 to modulate cerebral ischemia/reperfusion injury through MAPK signaling pathway activation. Mol Neurobiol. 2021;58(11):6032-6048.
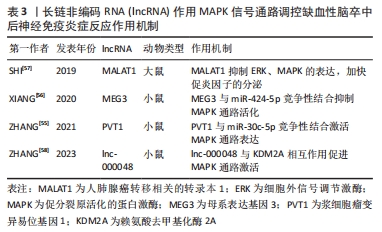
[56] XIANG Y, ZHANG Y, XIA Y, et al. LncRNA MEG3 targeting miR-424-5p via MAPK signaling pathway mediates neuronal apoptosis in ischemic stroke. Aging (Albany NY). 2020;12(4):3156-3174.
[57] SHI YL, WANG Q, WEI JC. Influence of lncRNA-MALAT1 on neuronal apoptosis in rats with cerebral infarction through regulating the ERK/MAPK signaling pathway. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2019;23(18):8039-8048.
[58] ZHANG S, SUN Y, XIAO Q, et al. Lnc_000048 promotes histone H3K4 methylation of MAP2K2 to reduce plaque stability by recruiting KDM1A in carotid atherosclerosis. Mol Neurobiol. 2023;60(5):2572-2586.
[59] GAO M, FU J, WANG Y. The lncRNA FAL1 protects against hypoxia-reoxygenation- induced brain endothelial damages through regulating PAK1. J Bioenerg Biomembr. 2020;52(1):17-25.
[60] ZANG L, YANG H, LI WJ, et al. LncRNA MALAT1 Promotes OGD-Induced apoptosis of brain microvascular endothelial cells by sponging miR-126 to repress PI3K/Akt signaling pathway. Neurochem Res. 2020;45(9):2091-2099.
[61] NI X, SU Q, XIA W, et al. Knockdown lncRNA NEAT1 regulates the activation of microglia and reduces AKT signaling and neuronal apoptosis after cerebral ischemic reperfusion. Sci Rep. 2020;10(1):19658.
[62] FASOLO F, JIN H, WINSKI G, et al. Long Noncoding RNA MIAT controls advanced atherosclerotic lesion formation and plaque destabilization. Circulation. 2021;144(19): 1567-1583.
[63] GUO T, LIU Y, REN X, et al. Errate: promoting role of long non-coding RNA small nucleolar RNA host gene 15 (SNHG15) in neuronal injury following ischemic stroke via the MicroRNA-18a/CXC chemokine ligand 13 (CXCL13)/ERK/MEK axis. Med Sci Monit. 2022;28:e938473. |