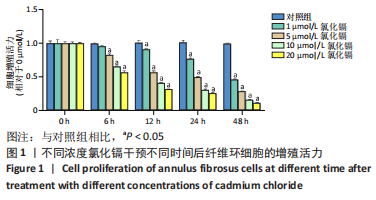
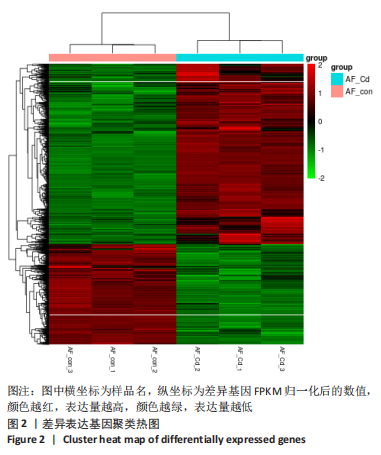
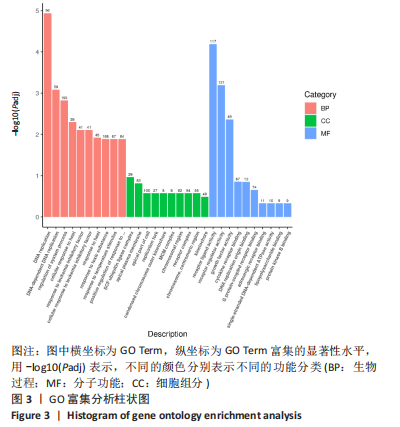
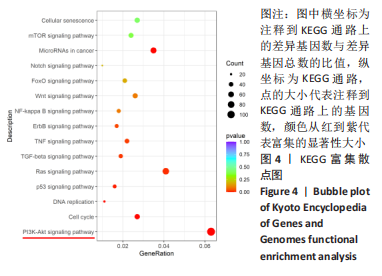
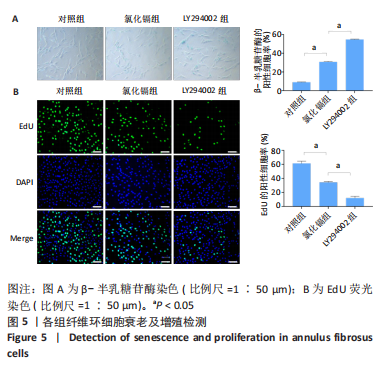
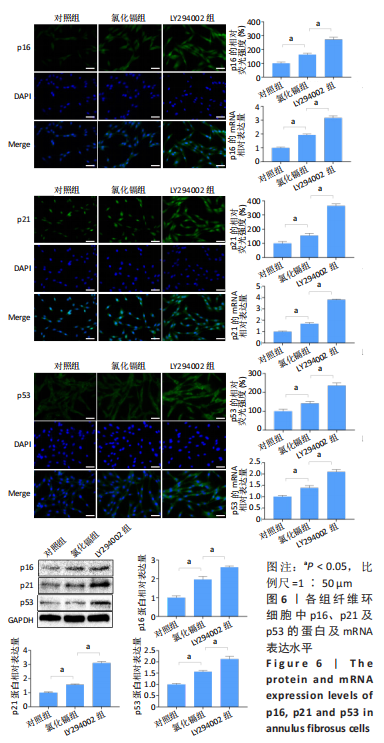
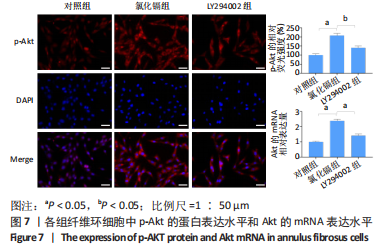
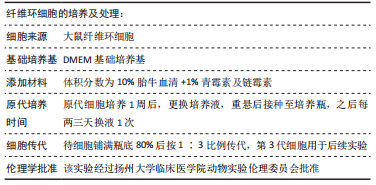
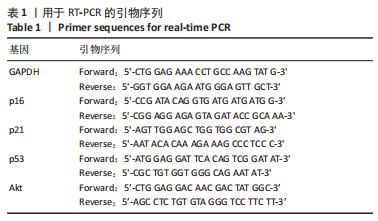
[1] HOY D, MARCH L, BROOKS P, et al. Measuring the global burden of low back pain. Best Pract Res Clin Rheumatol. 2010;24(2):155-165.
[2] FOSTER NE, ANEMA JR, CHERKIN D, et al. Prevention and treatment of low back pain: evidence, challenges, and promising directions. Lancet. 2018;391(10137):2368-2383.
[3] HOY D, MARCH L, BROOKS P, et al. The global burden of low back pain: estimates from the Global Burden of Disease 2010 study. Ann Rheum Dis. 2014;73(6):968-974.
[4] FREBURGER JK, HOLMES GM, AGANS RP, et al. The rising prevalence of chronic low back pain. Arch Intern Med. 2009;169(3):251-258.
[5] SATARUG S, GARRETT SH, SENS MA, et al. Cadmium, environmental exposure, and health outcomes. Environ Health Perspect. 2010;118(2): 182-190.
[6] LE MAITRE CL, FREEMONT AJ, HOYLAND JA. Accelerated cellular senescence in degenerate intervertebral discs: a possible role in the pathogenesis of intervertebral disc degeneration. Arthritis Res Ther. 2007;9(3):R45.
[7] ROBERTS S, EVANS EH, KLETSAS D, et al. Senescence in human intervertebral discs. Eur Spine J. 2006;15 Suppl 3(Suppl 3):S312-316.
[8] DAI X, CHEN Y, YU Z, et al. Advanced oxidation protein products induce annulus fibrosus cell senescence through a NOX4-dependent, MAPK-mediated pathway and accelerate intervertebral disc degeneration. PeerJ. 2022;10:e13826.
[9] NAKAMICHI R, ITO Y, INUI M, et al. Mohawk promotes the maintenance and regeneration of the outer annulus fibrosus of intervertebral discs. Nat Commun. 2016;7:12503.
[10] WANG T, YUAN Y, ZOU H, et al. The ER stress regulator Bip mediates cadmium-induced autophagy and neuronal senescence. Sci Rep. 2016; 6:38091.
[11] LUO H, GU R, OUYANG H, et al. Cadmium exposure induces osteoporosis through cellular senescence, associated with activation of NF-kappaB pathway and mitochondrial dysfunction. Environ Pollut. 2021;290:118043.
[12] ZHANG Y, CAI W, HAN G, et al. Panax notoginseng saponins prevent senescence and inhibit apoptosis by regulating the PI3K‑AKT‑mTOR pathway in osteoarthritic chondrocytes. Int J Mol Med. 2020;45(4): 1225-1236.
[13] WANG Z, WANG L, JIANG R, et al. Ginsenoside Rg1 prevents bone marrow mesenchymal stem cell senescence via NRF2 and PI3K/Akt signaling. Free Radic Biol Med. 2021;174:182-194.
[14] NI BB, LI B, YANG YH, et al. The effect of transforming growth factor β1 on the crosstalk between autophagy and apoptosis in the annulus fibrosus cells under serum deprivation. Cytokine. 2014;70(2):87-96.
[15] JING D, WU W, DENG X, et al. FoxO1a mediated cadmium-induced annulus fibrosus cells apoptosis contributes to intervertebral disc degeneration in smoking. J Cell Physiol. 2021;236(1):677-687.
[16] MELROSE J, SMITH S, LITTLE CB, et al. Spatial and temporal localization of transforming growth factor-beta, fibroblast growth factor-2, and osteonectin, and identification of cells expressing alpha-smooth muscle actin in the injured anulus fibrosus: implications for extracellular matrix repair. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2002;27(16):1756-1764.
[17] 张广智,武作龙,贺学岗,等.细胞衰老与椎间盘退变的相关性研究进展[J].生命科学研究,2021,25(1):58-63,94.
[18] JIN H, WANG Q, WU J, et al. Baicalein Inhibits the IL-1β-Induced Inflammatory Response in Nucleus Pulposus Cells and Attenuates Disc Degeneration In vivo. Inflammation. 2019;42(3):1032-1044.
[19] LIU Y, LIN J, WU X, et al. Aspirin-Mediated Attenuation of Intervertebral Disc Degeneration by Ameliorating Reactive Oxygen Species In Vivo and In Vitro. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2019;2019:7189854.
[20] FENG C, LIU H, YANG M, et al. Disc cell senescence in intervertebral disc degeneration: Causes and molecular pathways. Cell Cycle. 2016; 15(13):1674-1684.
[21] YURUBE T, BUCHSER WJ, MOON HJ, et al. Serum and nutrient deprivation increase autophagic flux in intervertebral disc annulus fibrosus cells: an in vitro experimental study. Eur Spine J. 2019;28(5): 993-1004.
[22] CAVALLI G, HEARD E. Advances in epigenetics link genetics to the environment and disease. Nature. 2019;571(7766):489-499.
[23] BERNHARD D, ROSSMANN A, WICK G. Metals in cigarette smoke. IUBMB Life. 2005;57(12):805-809.
[24] COSSELMAN KE, NAVAS-ACIEN A, KAUFMAN JD. Environmental factors in cardiovascular disease. Nat Rev Cardiol. 2015;12(11):627-642.
[25] NAWROT TS, MARTENS DS, HARA A, et al. Association of total cancer and lung cancer with environmental exposure to cadmium: the meta-analytical evidence. Cancer Causes Control. 2015;26(9):1281-1288.
[26] YANG S, ZHANG F, MA J, et al. Intervertebral disc ageing and degeneration: The antiapoptotic effect of oestrogen. Ageing Res Rev. 2020;57:100978.
[27] 张文捷,张勇,史明,等. 淫羊藿苷调控髓核来源间充质干细胞凋亡修复椎间盘退变[J].中国组织工程研究,2023,27(24):3803-3809.
[28] 王以典. N-乙酰血清素通过激活PI3K/AKT信号通路减轻大鼠髓核细胞的氧化应激损伤[D].兰州:兰州大学,2022.
[29] 牛海名,李建伟,陈妙莲,等.外源性硫化氢通过PI3K/Akt/eNOS通路改善过氧化氢诱导的人脐静脉内皮细胞衰老[J].中山大学学报(医学科学版),2021,42(4):535-542.
[30] 赵丽东,丛淋淋,徐瑶,等.IGF-1通过PI3K/Akt通路对大鼠软骨细胞衰老的影响[J].动物医学进展,2019,40(10):64-68.
[31] 王静欢,刘珂,万东,等.梓醇对大脑皮质神经元的抗衰老保护作用研究[J].中国药理学通报,2017,33(12):1691-1697.
[32] MAIDARTI M, ANDERSON RA, TELFER EE. Crosstalk between PTEN/PI3K/Akt Signalling and DNA Damage in the Oocyte: Implications for Primordial Follicle Activation, Oocyte Quality and Ageing. Cells. 2020; 9(1):200.
[33] WANG F, CAI F, SHI R, et al. Aging and age related stresses: a senescence mechanism of intervertebral disc degeneration. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2016;24(3):398-408.
|