[1] SUN D, LIU X, XU L, et al. Advances in the Treatment of Partial-Thickness Cartilage Defect. Int J Nanomedicine. 2022;17:6275-6287.
[2] CHIANG MH, KUO YJ, CHEN YP. Expanded mesenchymal stem cell transplantation following marrow stimulation is more effective than marrow stimulation alone in treatment of knee cartilage defect: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Orthop Traumatol Surg Res. 2020;106(5):977-983.
[3] HACKEN BA, LAPRADE MD, STUART MJ, et al. Small Cartilage Defect Management. J Knee Surg. 2020;33(12):1180-1186.
[4] KATATO H, OZEKI N, KOGA H, et al. Three-dimensional MRI shows cartilage defect extension with no separation from the meniscus in women in their 70 s with knee osteoarthritis. Sci Rep. 2022;12(1):4198.
[5] LU Y, ZHOU L, WANG L, et al. The role of SIRT1 in BMP2-induced chondrogenic differentiation and cartilage maintenance under oxidative stress. Aging (Albany NY). 2020;12(10):9000-9013.
[6] QI H, ZHAO Z, XU L, et al. Antisense Oligonucleotide-Based Therapy on miR-181a-5p Alleviates Cartilage Degradation of Temporomandibular Joint Osteoarthritis via Promoting SIRT1. Front Pharmacol. 2022;13:898334.
[7] LI M, YIN H, YAN Z, et al. The immune microenvironment in cartilage injury and repair. Acta Biomater. 2022;140:23-42.
[8] SALZMANN GM, OSSENDORFF R, GILAT R, et al. Autologous Minced Cartilage Implantation for Treatment of Chondral and Osteochondral Lesions in the Knee Joint: An Overview. Cartilage.2021;13(1_suppl):1124S-1136S.
[9] CHEN C, ZHOU M, GE Y, et al. SIRT1 and aging related signaling pathways. Mech Ageing Dev. 2020;187:111215.
[10] LIANG J, HUANG G, LIU X, et al. The ZIP8/SIRT1 axis regulates alveolar progenitor cell renewal in aging and idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. J Clin Invest. 2022;132(11):e157338.
[11] YAN S, DONG W, LI Z, et al. Metformin regulates chondrocyte senescence and proliferation through microRNA-34a/SIRT1 pathway in osteoarthritis. J Orthop Surg Res. 2023;18(1):198.
[12] YU X, XU X, DONG W, et al. DDIT3/CHOP mediates the inhibitory effect of ER stress on chondrocyte differentiation by AMPKα-SIRT1 pathway. Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Cell Res. 2022;1869(8):119265.
[13] ELAYYAN J, CARMON I, ZECHARYAHU L, et al. Lef1 ablation alleviates cartilage mineralization following posttraumatic osteoarthritis induction. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2022;119(21):e2116855119.
[14] WANG Y, CHEN G, YAN J, et al. Upregulation of SIRT1 by Kartogenin Enhances Antioxidant Functions and Promotes Osteogenesis in Human Mesenchymal Stem Cells. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2018;2018:1368142.
[15] ZHOU ZM, BAO JP, PENG X, et al. Small extracellular vesicles from hypoxic mesenchymal stem cells alleviate intervertebral disc degeneration by delivering miR-17-5p. Acta Biomater. 2022;140:641-658.
[16] YAMAKAWA A, HOJO H, OHBA S. ChIP-Seq Assays from Mammalian Cartilage and Chondrocytes. Methods Mol Biol. 2021;2245:167-178.
[17] AUBOURG G, RICE SJ, BRUCE-WOOTTON P, et al. Genetics of osteoarthritis. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2022;30(5):636-649.
[18] KAWATA M, TERAMURA T, ORDOUKHANIAN P, et al. Krüppel-like factor-4 and Krüppel-like factor-2 are important regulators of joint tissue cells and protect against tissue destruction and inflammation in osteoarthritis. Ann Rheum Dis. 2022;annrheumdis-2021-221867. doi: 10.1136/annrheumdis-2021-221867.
[19] SUN Y, LENG P, GUO P, et al. G protein coupled estrogen receptor attenuates mechanical stress-mediated apoptosis of chondrocyte in osteoarthritis via suppression of Piezo1. Mol Med. 2021;27(1):96.
[20] ZHANG J, SUN X, JIA S, et al. The role of lateral pterygoid muscle in the traumatic temporomandibular joint ankylosis: A gene chip based analysis. Mol Med Rep. 2019;19(5):4297-4305.
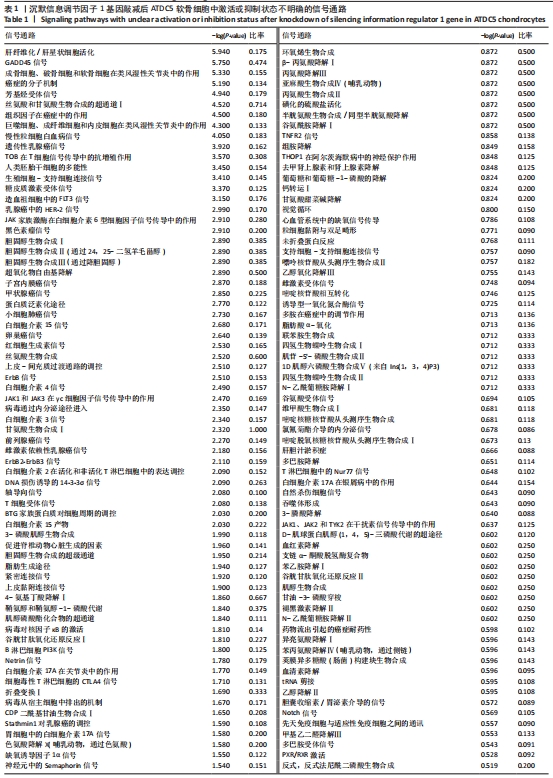
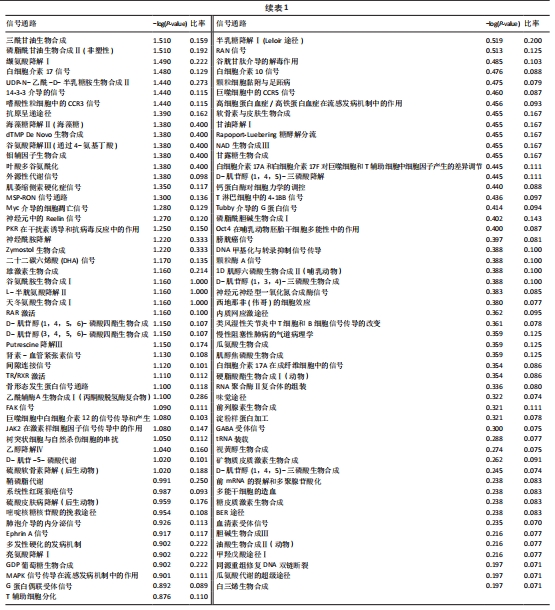
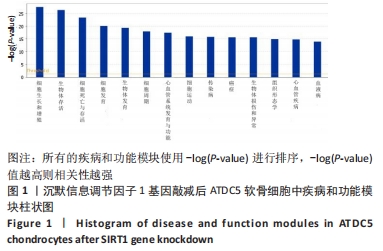
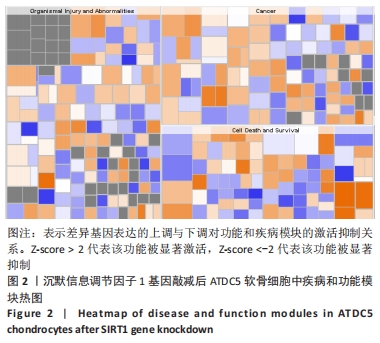
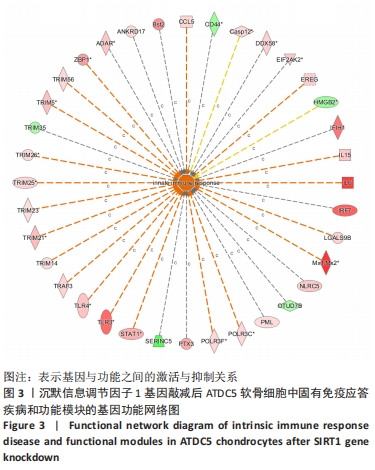
[21] 解笑宸,杨琪,翁鉴,等.沉默信息调节因子1基因敲减后ATDC5小鼠软骨细胞中被激活细胞退变相关信号通路及差异因子的表达[J].中国组织工程研究,2022,26(32):5112-5118.
[22] YU F, YUAN Y, LI D, et al. The Effect of Lentivirus-mediated SIRT1 Gene Knockdown in the ATDC5 Cell Line via inhibition of the Wnt Signaling Pathway. Cell Signal. 2019;53:80-89.
[23] SUN K, WU Y, ZENG Y, et al. The role of the sirtuin family in cartilage and osteoarthritis: molecular mechanisms and therapeutic targets. Arthritis Res Ther. 2022;24(1):286.
[24] JIANG S, ZHANG C, LU Y, et al. Mechanical stress-caused chondrocyte dysfunction and cartilage injury can be attenuated by dioscin via activating sirtuin1/forkhead box O1. J Biochem Mol Toxicol. 2022;36(12):e23212.
[25] WANG B, SUN W, BI K, et al. Apremilast prevents IL 17 induced cellular senescence in ATDC5 chondrocytes mediated by SIRT1. Int J Mol Med. 2021;47(3):12.
[26] PAPAGEORGIOU AA, LITSAKI M, MOURMOURA E, et al. DNA methylation regulates Sirtuin 1 expression in osteoarthritic chondrocytes. Adv Med Sci. 2023;68(1): 101-110.
[27] MA CH, CHOU WC, WU CH, et al. Ginsenoside Rg3 Attenuates TNF-α-Induced Damage in Chondrocytes through Regulating SIRT1-Mediated Anti-Apoptotic and Anti-Inflammatory Mechanisms. Antioxidants (Basel). 2021;10(12):1972.
[28] CHOI SM, LEE KM, RYU SB, et al. Enhanced articular cartilage regeneration with SIRT1-activated MSCs using gelatin-based hydrogel. Cell Death Dis. 2018;9(9):866.
[29] YU F, LI M, YUAN Z, et al. Mechanism research on a bioactive resveratrol- PLA-gelatin porous nano-scaffold in promoting the repair of cartilage defect. Int J Nanomedicine. 2018;13:7845-7858.
[30] ZHONG J, XIANG D, MA X. Prediction and analysis of osteoarthritis hub genes with bioinformatics. Ann Transl Med. 2023;11(2):66.
[31] HUANG ZY, LUO ZY, CAI YR, et al. Single cell transcriptomics in human osteoarthritis synovium and in silico deconvoluted bulk RNA sequencing. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2022;30(3):475-480.
[32] JI Q, ZHENG Y, ZHANG G, et al. Single-cell RNA-seq analysis reveals the progression of human osteoarthritis. Ann Rheum Dis. 2019;78(1):100-110.
[33] JI ML, JIANG H, LI Z, et al. Sirt6 attenuates chondrocyte senescence and osteoarthritis progression. Nat Commun. 2022;13(1):7658.
[34] YANG L, WANG S, ZHAO G, et al. Comparison of the toxic mechanism of T-2 toxin and deoxynivalenol on human chondrocytes by microarray and bioinformatics analysis. Toxicol Lett. 2020;321:61-68.
[35] SHANG L, MA H, ZHANG X, et al. Docosahexaenoic acid alleviates the excessive degradation of extracellular matrix in the nucleus pulposus by reducing the content of lncRNA NEAT1 to prevent the progression of intervertebral disc degeneration. Clin Exp Pharmacol Physiol. 2023;50(5):403-414.
[36] HUANG M, LIN Y, CHEN X, et al. The value of gene chip detection of bronchoalveolar lavage fluid in the diagnosis of nontuberculous mycobacterial lung disease. Ann Palliat Med. 2021;10(6):6438-6445.
[37] FUNATO N. New Insights Into Cranial Synchondrosis Development: A Mini Review. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2020;8:706.
[38] MEO BURT P, XIAO L, HURLEY MM. FGF23 Regulates Wnt/β-Catenin Signaling-Mediated Osteoarthritis in Mice Overexpressing High-Molecular-Weight FGF2. Endocrinology. 2018;159(6):2386-2396.
[39] DESHMUKH AP, VASAIKAR SV, TOMCZAK K, et al. Identification of EMT signaling cross-talk and gene regulatory networks by single-cell RNA sequencing. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2021;118(19):e2102050118.
[40] WYPYCH D, BARANSKA J. Cross-Talk in Nucleotide Signaling in Glioma C6 Cells. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2020;1202:35-65.
[41] MISHRA AK, SHARMA V, MUTSUDDI M, et al. Signaling cross-talk during development: Context-specific networking of Notch, NF-κB and JNK signaling pathways in Drosophila. Cell Signal. 2021;82:109937. |